内部类

1、成员内部类的使用
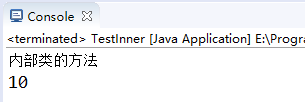
1 public class TestInner { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Outer.Inner inner=new Outer().new Inner(); 4 inner.function(); 5 } 6 } 7 class Outer{ 8 private int num=10; 9 public void method() { 10 System.out.println("我是外部类的方法"); 11 } 12 13 class Inner{ 14 void function() { 15 System.out.println("内部类的方法"); 16 System.out.println(num); 17 } 18 } 19 }
输出:
可以使用权限修饰符修饰成员内部类,但是如果使用私有来修饰,则无法在其他类中访问。如果第13行加上private,第三行会编译出错。
使用static关键字修饰成员内部类,可以不用创建外部对象
1 public class TestInner { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Outer.Inner inner=new Outer.Inner(); 4 inner.function(); 5 Outer.Inner.function();//需要是静态方法 6 } 7 } 8 class Outer{ 9 private static int num=10; 10 public void method() { 11 System.out.println("我是外部类的方法"); 12 } 13 14 static class Inner{ 15 /* static*/ void function() { 16 System.out.println("内部类的方法"); 17 System.out.println(num); 18 } 19 } 20 }
2、局部内部类
1 /** 2 * 局部内部类: 3 * 在方法内,出了方法就无法使用 4 * @author Administrator 5 * 6 */ 7 public class InnerDemo3 { 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 Outer o=new Outer(); 10 o.method(); 11 } 12 } 13 14 class Outer{ 15 public void method() { 16 class Inner{ 17 public void function() { 18 System.out.println("function"); 19 } 20 } 21 Inner i=new Inner(); 22 i.function(); 23 } 24 }
3、匿名内部类
使用场景:作为匿名内部类进行传递
1 public class TestDemo { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 method(new Dog());//输出:狗啃骨头 4 method(new Cat());//输出:猫吃鱼。。 5 } 6 public static void method(Animal a) { 7 a.eat(); 8 } 9 }
1 public interface Animal { 2 void eat(); 3 }
1 public class Dog implements Animal{ 2 @Override 3 public void eat() { 4 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 5 System.out.println("狗啃骨头"); 6 } 7 }
1 public class Cat implements Animal{ 2 @Override 3 public void eat() { 4 System.out.println("猫吃鱼。。"); 5 } 6 7 }
1 public class TestDemo2 { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 method( 4 new Animal() { 5 @Override 6 public void eat() { 7 System.out.println("什么都吃"); 8 } 9 } 10 ); 11 } 12 public static void method(Animal a) { 13 a.eat(); 14 } 15 }