课程目标
多线程之间如何通讯
wait、notify、notifyAll()方法
lock
停止线程
多线程之间如何实现通讯
什么是多线程之间通讯?
多线程之间通讯,其实就是多个线程在操作同一个资源,但是操作的动作不同。
画图演示
多线程之间通讯需求
需求:第一个线程写入(input)用户,另一个线程取读取(out)用户.实现读一个,写一个操作。
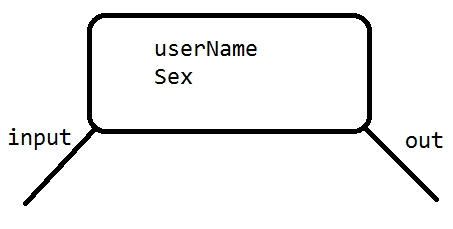
代码实现基本实现
共享资源源实体类
package hongmoshui.com.cnblogs.www.study.day003; /** * 共享资源源实体类 * @author 洪墨水 */ class Res { public String userSex; public String userName; }
输入线程资源
/** * 输入线程资源 * @author 洪墨水 */ class IntThrad extends Thread { private Res res; public IntThrad(Res res) { this.res = res; } @Override public void run() { int count = 0; while (true) { if (count == 0) { res.userName = "余胜军"; res.userSex = "男"; } else { res.userName = "小紅"; res.userSex = "女"; } count = (count + 1) % 2; } } }
输出线程
/** * 输出线程 * @author 洪墨水 */ class OutThread extends Thread { private Res res; public OutThread(Res res) { this.res = res; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { System.out.println(res.userName + "--" + res.userSex); } } }
运行代码
/** * 运行代码 * @author 洪墨水 */ public class Demo1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Res res = new Res(); IntThrad intThrad = new IntThrad(res); OutThread outThread = new OutThread(res); intThrad.start(); outThread.start(); } }
运行结果
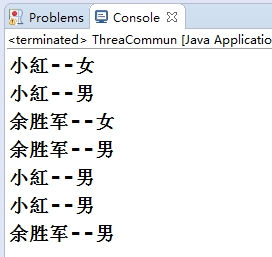
注意:数据发生错乱,造成线程安全问题
解决线程安全问题
IntThrad 加上synchronized
class IntThrad2 extends Thread { private Res res; public IntThrad2(Res res) { this.res = res; } @Override public void run() { int count = 0; while (true) { synchronized (res) { if (count == 0) { res.userName = "余胜军"; res.userSex = "男"; } else { res.userName = "小紅"; res.userSex = "女"; } count = (count + 1) % 2; } } } }
输出线程加上synchronized
package hongmoshui.com.cnblogs.www.study.day003; class Res2 { public String userName; public String sex; } class InputThread extends Thread { private Res2 res2; public InputThread(Res2 res2) { this.res2 = res2; } @Override public void run() { int count = 0; while (true) { synchronized (res2) { if (count == 0) { res2.userName = "余胜军"; res2.sex = "男"; } else { res2.userName = "小红"; res2.sex = "女"; } count = (count + 1) % 2; } } } } class OutThrad extends Thread { private Res2 res2; public OutThrad(Res2 res2) { this.res2 = res2; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (res2) { System.out.println(res2.userName + "," + res2.sex); } } } } /** * 输出线程加上synchronized * @author 洪墨水 */ public class ThreadDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { Res2 res2 = new Res2(); InputThread inputThread = new InputThread(res2); OutThrad outThrad = new OutThrad(res2); inputThread.start(); outThrad.start(); } }
wait()、notify、notifyAll()方法
wait()、notify()、notifyAll()是三个定义在Object类里的方法,可以用来控制线程的状态。
这三个方法最终调用的都是jvm级的native方法。随着jvm运行平台的不同可能有些许差异。
如果对象调用了wait方法就会使持有该对象的线程把该对象的控制权交出去,然后处于等待状态。
如果对象调用了notify方法就会通知某个正在等待这个对象的控制权的线程可以继续运行。
如果对象调用了notifyAll方法就会通知所有等待这个对象控制权的线程继续运行。
注意:一定要在线程同步中使用,并且是同一个锁的资源
package hongmoshui.com.cnblogs.www.study.day003; class Res3 { public String userSex; public String userName; // 线程通讯标识 public boolean flag = false; } class IntThrad3 extends Thread { private Res3 res3; public IntThrad3(Res3 res3) { this.res3 = res3; } @Override public void run() { int count = 0; while (true) { synchronized (res3) { if (res3.flag) { try { // 当前线程变为等待,但是可以释放锁 res3.wait(); } catch (Exception e) { } } if (count == 0) { res3.userName = "余胜军"; res3.userSex = "男"; } else { res3.userName = "小紅"; res3.userSex = "女"; } count = (count + 1) % 2; res3.flag = true; // 唤醒当前线程 res3.notify(); } } } } class OutThread3 extends Thread { private Res3 res3; public OutThread3(Res3 res3) { this.res3 = res3; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { synchronized (res3) { if (!res3.flag) { try { res3.wait(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } System.out.println(res3.userName + "--" + res3.userSex); res3.flag = false; res3.notify(); } } } } public class ThreaCommun { public static void main(String[] args) { Res3 res3 = new Res3(); IntThrad3 intThrad3 = new IntThrad3(res3); OutThread3 outThread3 = new OutThread3(res3); intThrad3.start(); outThread3.start(); } }
wait与sleep区别?
对于sleep()方法,我们首先要知道该方法是属于Thread类中的。而wait()方法,则是属于Object类中的。
sleep()方法导致了程序暂停执行指定的时间,让出cpu该其他线程,但是他的监控状态依然保持者,当指定的时间到了又会自动恢复运行状态。
在调用sleep()方法的过程中,线程不会释放对象锁。
而当调用wait()方法的时候,线程会放弃对象锁,进入等待此对象的等待锁定池,只有针对此对象调用notify()方法后本线程才进入对象锁定池准备
获取对象锁进入运行状态。
JDK1.5-Lock
在 jdk1.5 之后,并发包中新增了 Lock 接口(以及相关实现类)用来实现锁功能,Lock 接口提供了与 synchronized 关键字类似的同步功能,但需要在使用时手动获取锁和释放锁。
Lock写法
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); lock.lock(); try { // 可能会出现线程安全的操作 } finally { // 一定在finally中释放锁 // 也不能把获取锁在try中进行,因为有可能在获取锁的时候抛出异常 lock.unlock(); }
Lock 接口与 synchronized 关键字的区别
Lock 接口可以尝试非阻塞地获取锁 当前线程尝试获取锁。如果这一时刻锁没有被其他线程获取到,则成功获取并持有锁。
Lock 接口能被中断地获取锁 与 synchronized 不同,获取到锁的线程能够响应中断,当获取到的锁的线程被中断时,中断异常将会被抛出,同时锁会被释放。
Lock 接口在指定的截止时间之前获取锁,如果截止时间到了依旧无法获取锁,则返回。
Condition用法
Condition的功能类似于在传统的线程技术中的,Object.wait()和Object.notify()的功能。
代码
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
res. condition.await(); 类似wait
res. Condition. Signal() 类似notify
package hongmoshui.com.cnblogs.www.study.day003; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; class Res4 { public String userName; public String sex; public boolean flag = false; Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); } class InputThread4 extends Thread { private Res4 res4; Condition newCondition; public InputThread4(Res4 res4, Condition newCondition) { this.res4 = res4; this.newCondition = newCondition; } @Override public void run() { int count = 0; while (true) { // synchronized (res4) { try { res4.lock.lock(); if (res4.flag) { try { // res4.wait(); newCondition.await(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } if (count == 0) { res4.userName = "余胜军"; res4.sex = "男"; } else { res4.userName = "小红"; res4.sex = "女"; } count = (count + 1) % 2; res4.flag = true; // res4.notify(); newCondition.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } finally { res4.lock.unlock(); } } // } } } class OutThrad4 extends Thread { private Res4 res4; private Condition newCondition; public OutThrad4(Res4 res4, Condition newCondition) { this.res4 = res4; this.newCondition = newCondition; } @Override public void run() { while (true) { // synchronized (res4) { try { res4.lock.lock(); if (!res4.flag) { try { // res4.wait(); newCondition.await(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } System.out.println(res4.userName + "," + res4.sex); res4.flag = false; // res4.notify(); newCondition.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } finally { res4.lock.unlock(); } // } } } } public class ThreadDemo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { Res4 res4 = new Res4(); Condition newCondition = res4.lock.newCondition(); InputThread4 inputThread4 = new InputThread4(res4, newCondition); OutThrad4 outThrad4 = new OutThrad4(res4, newCondition); inputThread4.start(); outThrad4.start(); } }
如何停止线程?
停止线程思路
1. 使用退出标志,使线程正常退出,也就是当run方法完成后线程终止。
2. 使用stop方法强行终止线程(这个方法不推荐使用,因为stop和suspend、resume一样,也可能发生不可预料的结果)。
3. 使用interrupt方法中断线程。
代码:
package hongmoshui.com.cnblogs.www.study.day003; class StopThread implements Runnable { private boolean flag = true; @Override public synchronized void run() { while (flag) { try { wait(); } catch (Exception e) { // e.printStackTrace(); stopThread(); } System.out.println("thread run.."); } } /** * * 停止线程 * @author: 洪墨水 */ public void stopThread() { flag = false; } } /** * * 停止线程 * @author: 洪墨水 */ public class StopThreadDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { StopThread stopThread1 = new StopThread(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(stopThread1); Thread thread2 = new Thread(stopThread1); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); int i = 0; while (true) { System.out.println("thread main.."); if (i == 300) { // stopThread1.stopThread(); thread1.interrupt(); thread2.interrupt(); break; } i++; } } }
ThreadLocal
什么是ThreadLocal
ThreadLocal提供一个线程的局部变量,访问某个线程拥有自己局部变量。
当使用ThreadLocal维护变量时,ThreadLocal为每个使用该变量的线程提供独立的变量副本,所以每一个线程都可以独立地改变自己的副本,而不会影响其它线程所对应的副本。
ThreadLocal的接口方法
ThreadLocal类接口很简单,只有4个方法,我们先来了解一下:
- void set(Object value)设置当前线程的线程局部变量的值。
- public Object get()该方法返回当前线程所对应的线程局部变量。
- public void remove()将当前线程局部变量的值删除,目的是为了减少内存的占用,该方法是JDK 5.0新增的方法。需要指出的是,当线程结束后,对应该线程的局部变量将自动被垃圾回收,所以显式调用该方法清除线程的局部变量并不是必须的操作,但它可以加快内存回收的速度。
- protected Object initialValue()返回该线程局部变量的初始值,该方法是一个protected的方法,显然是为了让子类覆盖而设计的。这个方法是一个延迟调用方法,在线程第1次调用get()或set(Object)时才执行,并且仅执行1次。ThreadLocal中的缺省实现直接返回一个null。
案例:创建三个线程,每个线程生成自己独立序列号。
代码:
package hongmoshui.com.cnblogs.www.study.day003; class Res5 { // 生成序列号共享变量 public static Integer count = 0; public static ThreadLocal<Integer> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Integer>() { protected Integer initialValue() { return 0; }; }; public Integer getNum() { int count = threadLocal.get() + 1; threadLocal.set(count); return count; } } /** * 创建三个线程,每个线程生成自己独立序列号 * @author 洪墨水 */ public class ThreadLocaDemo3 extends Thread { private Res5 res5; public ThreadLocaDemo3(Res5 res5) { this.res5 = res5; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "---" + "i---" + i + "--num:" + res5.getNum()); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Res5 res5 = new Res5(); ThreadLocaDemo3 threadLocaDemo1 = new ThreadLocaDemo3(res5); ThreadLocaDemo3 threadLocaDemo2 = new ThreadLocaDemo3(res5); ThreadLocaDemo3 threadLocaDemo3 = new ThreadLocaDemo3(res5); threadLocaDemo1.start(); threadLocaDemo2.start(); threadLocaDemo3.start(); } }
ThreadLocal实现原理
ThreadLocal通过map集合
Map.put(“当前线程”,值);