最近算是一段空闲期,不想荒废,记得之前有收藏一个机器学习的链接Andrew Ng的网易公开课,其中的overfiting部分做组会报告时涉及到了,这几天有时间决定把这部课程学完,好歹算是有个粗浅的认识。
本来想去网上查一查机器学习的书籍,发现李航的《统计学习方法》和PRML(Pattern Recognition And Machine Learning)很受人推崇,有空再看吧。
然后在图书馆碰到了天佑,给我推荐了coursera这个网站,上面有Andrew Ng针对网络版的机器学习教程,挺好的。以下笔记基于此课程。
https://www.coursera.org/course/ml
week one:
a:machine learning
Supervised learning:Regression Classification
and Reinforcement learning, recommender systems
b: Linear regression with one variable
Linear regression:
Hypothesis,Cost function(为何最小二乘估计中分母有个系数2),Contour plots(轮廓图中一条线上的值相等)
Gradient descent:
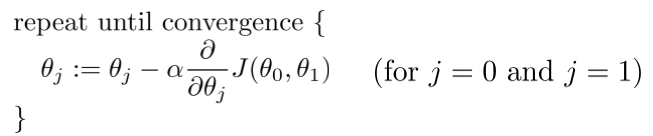
alpha:learning rate
If α is too large, gradient descent can overshoot the minimum. It may fail to converge, or even diverge.
Gradient descent can converge to a local minimum, even with the learning rate α fixed.
Gradient descent for linear regression:
convex Function for it.
“Batch” Gradient Descent:
Batch: Each step of gradient descent uses all the training examples.
c: Linear Algebra Review
If A is an m x m matrix, and if it has an inverse
(如何判断一个矩阵存不存在逆矩阵)
Matrices that don’t have an inverse are “singular” or “degenerate”.
特征缩放为了使梯度下降速度增快(梯度函数图像为何是椭圆形)
week two:
Linear Regression with Multiple Variables:
![]()
->
![]()
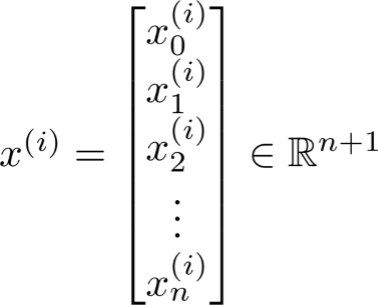
n+1维向量,x0=1
Gradient Descent for Multiple Variables:

Feature Scaling:
Learning rate:
0.01,0.03,0.1...
Features and polynomial regression:
特征选择与多项式回归
Normal equation:
对于线性回归最小二乘函数有如下公式:

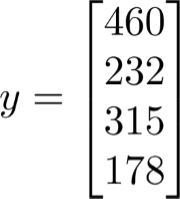
![]()
X是xi的转置集合:
Slow if n is very large.
if it is non-invertible,may be redundant features (linearly dependent) or too many features.