1. 前言
python 中的数组可以说是本人最常用的数据结构了,其中一些方法总是忘记,再次做一下总结。
2. 如何查看某个数据结构的方法
Python 3.9.9 (main, Dec 2 2021, 14:30:08)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> help(list)
执行上面的命令之后,就会显示出所有该数据结构的内置和外置方法
|
| append(self, object, /)
| Append object to the end of the list.
| clear(self, /)
| Remove all items from list.
|
| copy(self, /)
| Return a shallow copy of the list.
|
| count(self, value, /)
| Return number of occurrences of value.
|
| extend(self, iterable, /)
| Extend list by appending elements from the iterable.
|
| index(self, value, start=0, stop=9223372036854775807, /)
| Return first index of value.
|
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| insert(self, index, object, /)
| Insert object before index.
|
| pop(self, index=-1, /)
| Remove and return item at index (default last).
|
| Raises IndexError if list is empty or index is out of range.
|
| remove(self, value, /)
| Remove first occurrence of value.
|
| Raises ValueError if the value is not present.
|
| reverse(self, /)
| Reverse *IN PLACE*.
|
| sort(self, /, *, key=None, reverse=False)
| Sort the list in ascending order and return None.
|
| The sort is in-place (i.e. the list itself is modified) and stable (i.e. the
| order of two equal elements is maintained).
|
| If a key function is given, apply it once to each list item and sort them,
| ascending or descending, according to their function values.
|
| The reverse flag can be set to sort in descending order.
3. 方法解释
3.1 概览
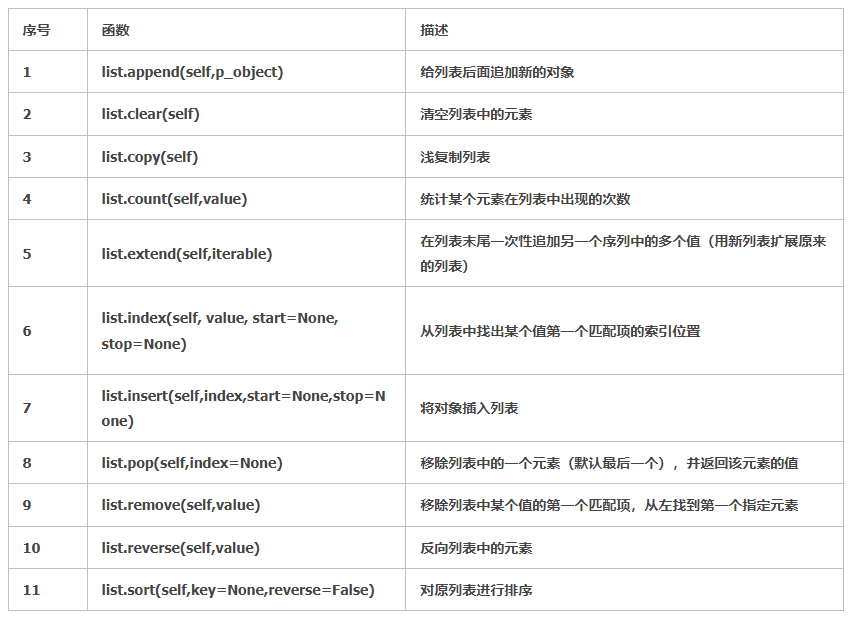
每个函数的基本功能都在表格里有解释了,现在针对几个比较特殊的再做一下详解。另外补充几个适用于list 的方法
3.2 copy
#list.copy(self)
L1 = [1,2,3,4]
L2 = L1.copy()
print(L2)
# [1,2,3,4]
这个函数用于复制列表,做浅拷贝,与之对应的有深拷贝
import copy
l1 = [1,2,3,4]
l2 = copy.deepcopy(l1)
深浅拷贝可以参考下这个文章:
浅拷贝与深拷贝
3.3 insert
在指定位置增加一个元素
L= [1,2,3,3]
print(L.index(3))
# 2
3.4 del
del 是 Python 中的关键字,专门用来执行删除操作,它不仅可以删除整个列表,还可以删除列表中的某些元素。
del 可以删除列表中的单个元素,格式为:
del listname[index]
del 也可以删除中间一段连续的元素,格式为:
del listname[start : end]
其中,start 表示起始索引,end 表示结束索引。del 会删除从索引 start 到 end 之间的元素,不包括 end 位置的元素。
3.5 join
将列表变成字符串
#'str'.join(list)
li = ['my','name','is','bob']
print(' '.join(li))
# 'my name is bob'
print('_'.join(li))
# 'my_name_is_bob'
3.6 split
#split(seq,maxsplit=-1)
b = 'my..name..is..bob'
print(b.split())
# ['my..name..is..bob']
print(b.split(".."))
# ['my', 'name', 'is', 'bob']
原创 https://www.cnblogs.com/gaoshaonian/p/16045599.html
3.7 reverse
此方法是对列表中的元素进行逆序
a = [1,3,6,8,9]
for i in reversed(a):
print(i, end=" ")
除此之外还有其他两种方法,举例如下:
for i in a[::-1]:
print(i, end=" ")
for i in range(len(a)-1,-1,-1):
print(a[i], end=" ")
3.8 filter
filter() 函数用于过滤序列,过滤掉不符合条件的元素,返回由符合条件元素组成的新列表。
该接收两个参数,第一个为函数,第二个为序列,序列的每个元素作为参数传递给函数进行判断,然后返回 True 或 False,最后将返回 True 的元素放到新列表中。
def is_odd(n):
return n % 2 == 1
newlist = filter(is_odd, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
print(newlist)
#[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
本文参考了这个文章:
参考文章