环境准备
3个节点,以下基于 Centos 7.6 系统, 内核版本:3.10.0-957.12.2.e17.x86_64
| HOST | NODE | CPU | MEM |
| 192.168.1.111 | master | 最低要求2核2C | 最低要求2GB |
| 192.168.1.112 | node1 | 最低要求2核2C | 最低要求2GB |
| 192.168.1.113 | node2 | 最低要求2核2C | 最低要求2GB |
环境初始化-master -node节点都需要操作
host文件信息:
cat >>/etc/hosts<<EOF 192.168.1.111 master 192.168.1.112 node1 192.168.1.113 node2 EOF
集群免密钥设置:
yum -y install expect ssh-keygen -t rsa -P "" -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa for i in 192.168.1.111 192.168.1.112 192.168.1.113;do expect -c " spawn ssh-copy-id -i /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub root@$i expect { "*yes/no*" {send "yes "; exp_continue} "*password*" {send "Flyaway.123 "; exp_continue} "*Password*" {send "Flyaway.123 ";} } " done
配置时间同步/关闭防火墙:
#同步节点时间; yum install ntpdate -y ntpdate pool.ntp.org #临时关闭selinux和防火墙; sed -i '/SELINUX/s/enforcing/disabled/g' /etc/sysconfig/selinux setenforce 0 systemctl stop firewalld.service systemctl disable firewalld.service
hostname:
# 节点的 hostname 必须使用标准的 DNS 命名,另外千万不用什么默认的 localhost 的 hostname,会导致各种错误出现的。在 Kubernetes 项目里,机器的名字以及一切存储在 Etcd 中的 API 对象,都必须使用标准的 DNS 命名(RFC 1123)。可以使用命令 hostnamectl set-hostname ydzs-node1 来修改 hostname。 # 修改对应节点主机名; hostnamectl set-hostname master && ssh node1 "hostnamectl set-hostname node1" && ssh node2 "hostnamectl set-hostname node2" # 拷贝 hosts 文件到 node 节点: for i in node1 node2;do scp -r /etc/hosts $i:/etc/ ;done
由于开启内核 ipv4 转发需要加载 br_netfilter 模块,所以加载下该模块:
modprobe br_netfilter
创建 /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf 文件,添加如下内容:
net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables = 1 net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables = 1 net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 # bridge-nf 解释: # bridge-nf 使得 netfilter 可以对 Linux 网桥上的 IPv4/ARP/IPv6 包过滤。比如,设置net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables=1后,二层的网桥在转发包时也会被 iptables的 FORWARD 规则所过滤。常用的选项包括: # net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-arptables:是否在 arptables 的 FORWARD 中过滤网桥的 ARP 包 # net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-ip6tables:是否在 ip6tables 链中过滤 IPv6 包 # net.bridge.bridge-nf-call-iptables:是否在 iptables 链中过滤 IPv4 包 # net.bridge.bridge-nf-filter-vlan-tagged:是否在 iptables/arptables 中过滤打了 vlan 标签的包。
执行如下命令使文件生效:
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf
安装ipvs:
$ cat > /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules <<EOF #!/bin/bash modprobe -- ip_vs modprobe -- ip_vs_rr modprobe -- ip_vs_wrr modprobe -- ip_vs_sh modprobe -- nf_conntrack_ipv4 EOF $ chmod 755 /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules && bash /etc/sysconfig/modules/ipvs.modules && lsmod | grep -e ip_vs -e nf_conntrack_ipv4 # 安装 ipset ipvsadm 管理工具(便于查看 ipvs 的代理规则) yum install ipset ipvsadm chrony -y # 同步服务器时间 systemctl enable chronyd && systemctl start chronyd && chronyc sources
关闭 swap 分区:
$ swapoff -a #修改/etc/fstab文件,注释掉 SWAP 的自动挂载,使用free -m确认 swap 已经关闭。swappiness 参数调整,修改/etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf添加下面一行: vm.swappiness=0 #执行sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf使修改生效。
# 将 k8s.conf 文件 拷贝到 node 节点 for i in node1 node2;do scp -r /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf $i:/etc/sysctl.d/ ;done ssh node1 "sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf" && ssh node2 "sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.d/k8s.conf"
部署docker:
yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2 # 如果下面命令执行超时,可以使用阿里云的源代替:http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo $ yum-config-manager --add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo $ yum list docker-ce --showduplicates | sort -r # 安装 docker-ce: yum install docker-ce -y && mkdir /etc/docker # 配置 docker 镜像加速器: cat >> /etc/docker/daemon.json<<EOF { "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"], "registry-mirrors" : [ "https://ot2k4d59.mirror.aliyuncs.com/" ] } EOF # 解释 cgroup 驱动 #由于默认情况下 kubelet 使用的 cgroupdriver 是 systemd,所以需要保持 docker 和kubelet 的 cgroupdriver 一致,我们这里修改 docker 的 cgroupdriver=systemd。如果不修改 docker 则需要修改 kubelet 的启动配置,需要保证两者一致。
启动 docker:
for i in start enable status; do systemctl $i docker ;done
配置 Kubeadm 源:
# yum 安装 kubeadm 工具时 默认是从 k8s.io 官网下载,对于不能科学**网的来说 比较头疼,所以提供了如下 阿里源 无需科学**网也可进行下载:
# 可以科学**网 选这个 cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=1 repo_gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg https://packages.cloud.google.com/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF # 不能科学**网选择这个 cat <<EOF > /etc/yum.repos.d/kubernetes.repo [kubernetes] name=Kubernetes baseurl=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/repos/kubernetes-el7-x86_64 enabled=1 gpgcheck=0 repo_gpgcheck=0 gpgkey=http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/yum-key.gpg http://mirrors.aliyun.com/kubernetes/yum/doc/rpm-package-key.gpg EOF
安装 kubeadm、kubelet、kubectl:
# --disableexcludes 禁掉除了kubernetes之外的别的仓库 # 安装 v1.16.2 版本: yum install -y kubelet-1.16.2 kubeadm-1.16.2 kubectl-1.16.2 --disableexcludes=kubernetes kubeadm version # 设置 kubelet 开机启动: systemctl enable --now kubelet
集群初始化
在 master 节点配置 kubeadm 初始化文件, 可以通过如下命令导出默认的初始化配置:
# 为了方便管理 k8s 创建 k8s-install 目录 mkdir k8s-install # 导出初始化配置文件
cd k8s-install/ kubeadm config print init-defaults > kubeadm.yaml
修改 kubeadm.yaml文件:
# 然后根据我们自己的需求修改配置,比如修改 imageRepository 的值,kube-proxy 的模式为 ipvs,另外需要注意的是我们这里是准备安装 flannel 网络插件的,需要将 networking.podSubnet 设置为10.244.0.0/16: apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2 bootstrapTokens: - groups: - system:bootstrappers:kubeadm:default-node-token token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef ttl: 24h0m0s usages: - signing - authentication kind: InitConfiguration localAPIEndpoint: advertiseAddress: 192.168.1.111 # apiserver 节点内网IP bindPort: 6443 nodeRegistration: criSocket: /var/run/dockershim.sock name: master # 默认读取当前master节点的hostname taints: - effect: NoSchedule key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master --- apiServer: timeoutForControlPlane: 4m0s apiVersion: kubeadm.k8s.io/v1beta2 certificatesDir: /etc/kubernetes/pki clusterName: kubernetes controllerManager: {} dns: type: CoreDNS etcd: local: dataDir: /var/lib/etcd imageRepository: registry.aliyuncs.com/google_containers # 修改成阿里云镜像源 kind: ClusterConfiguration kubernetesVersion: v1.16.2 networking: dnsDomain: cluster.local podSubnet: 10.244.0.0/16 # Pod 网段,flannel插件需要使用这个网段 serviceSubnet: 10.96.0.0/12 scheduler: {} --- apiVersion: kubeproxy.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: KubeProxyConfiguration mode: ipvs # kube-proxy 模式
# 配置提示:
对于上面的资源清单的文档比较杂,要想完整了解上面的资源对象对应的属性,可以查看对应的 godoc 文档,地址: https://godoc.org/k8s.io/kubernetes/cmd/kubeadm/app/apis/kubeadm/v1beta2。
修改配置 kubeadm.yaml 文件后, 进行初始化:
$ kubeadm init --config kubeadm.yaml [preflight] If you know what you are doing, you can make a check non-fatal with `--ignore-preflight-errors=...` To see the stack trace of this error execute with --v=5 or higher [init] Using Kubernetes version: v1.16.2 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [preflight] Pulling images required for setting up a Kubernetes cluster [preflight] This might take a minute or two, depending on the speed of your internet connection [preflight] You can also perform this action in beforehand using 'kubeadm config images pull' [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml" [kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service [certs] Using certificateDir folder "/etc/kubernetes/pki" [certs] Generating "ca" certificate and key x[certs] Generating "apiserver" certificate and key [certs] apiserver serving cert is signed for DNS names [ydzs-master kubernetes kubernetes.default kubernetes.default.svc kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local] and IPs [10.96.0.1 10.151.30.11] xxx[certs] Generating "apiserver-kubelet-client" certificate and key x[certs] Generating "front-proxy-ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "front-proxy-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/ca" certificate and key [certs] Generating "etcd/server" certificate and key [certs] etcd/server serving cert is signed for DNS names [ydzs-master localhost] and IPs [10.151.30.11 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/peer" certificate and key [certs] etcd/peer serving cert is signed for DNS names [ydzs-master localhost] and IPs [10.151.30.11 127.0.0.1 ::1] [certs] Generating "etcd/healthcheck-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "apiserver-etcd-client" certificate and key [certs] Generating "sa" key and public key [kubeconfig] Using kubeconfig folder "/etc/kubernetes" [kubeconfig] Writing "admin.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "kubelet.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "controller-manager.conf" kubeconfig file [kubeconfig] Writing "scheduler.conf" kubeconfig file [control-plane] Using manifest folder "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-apiserver" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-controller-manager" [control-plane] Creating static Pod manifest for "kube-scheduler" [etcd] Creating static Pod manifest for local etcd in "/etc/kubernetes/manifests" [wait-control-plane] Waiting for the kubelet to boot up the control plane as static Pods from directory "/etc/kubernetes/manifests". This can take up to 4m0s [apiclient] All control plane components are healthy after 39.504262 seconds [upload-config] Storing the configuration used in ConfigMap "kubeadm-config" in the "kube-system" Namespace [kubelet] Creating a ConfigMap "kubelet-config-1.16" in namespace kube-system with the configuration for the kubelets in the cluster [kubelet-check] Initial timeout of 40s passed. [upload-certs] Skipping phase. Please see --upload-certs [mark-control-plane] Marking the node ydzs-master as control-plane by adding the label "node-role.kubernetes.io/master=''" [mark-control-plane] Marking the node ydzs-master as control-plane by adding the taints [node-role.kubernetes.io/master:NoSchedule] [bootstrap-token] Using token: abcdef.0123456789abcdef [bootstrap-token] Configuring bootstrap tokens, cluster-info ConfigMap, RBAC Roles [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow Node Bootstrap tokens to post CSRs in order for nodes to get long term certificate credentials [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow the csrapprover controller automatically approve CSRs from a Node Bootstrap Token [bootstrap-token] configured RBAC rules to allow certificate rotation for all node client certificates in the cluster [bootstrap-token] Creating the "cluster-info" ConfigMap in the "kube-public" namespace [addons] Applied essential addon: CoreDNS [addons] Applied essential addon: kube-proxy Your Kubernetes control-plane has initialized successfully! To start using your cluster, you need to run the following as a regular user: mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config You should now deploy a pod network to the cluster. Run "kubectl apply -f [podnetwork].yaml" with one of the options listed at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/cluster-administration/addons/ Then you can join any number of worker nodes by running the following on each as root: kubeadm join 192.168.1.111:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:a292e66049e45264f848186d2fa3582dc360f3b5006cc160f137b5d436e078c2
拷贝 kubeconfig 文件:
mkdir -p $HOME/.kube sudo cp -i /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf $HOME/.kube/config sudo chown $(id -u):$(id -g) $HOME/.kube/config
kubeadm init 命令执行流程图:
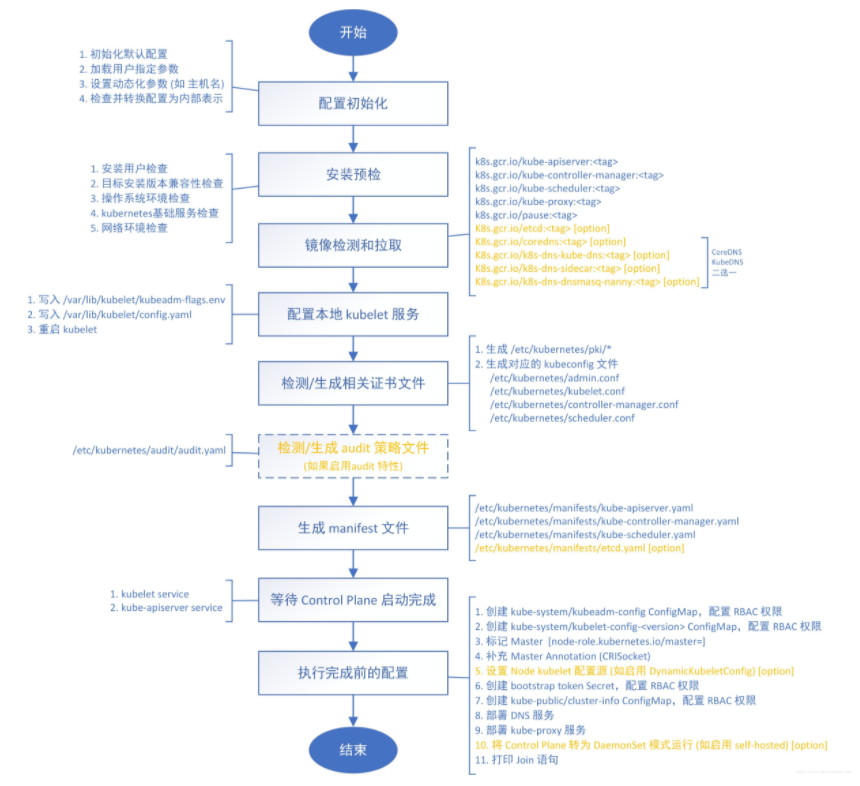
添加 node 节点
记住初始化集群上面的配置和操作要提前做好,将 master 节点上面的 $HOME/.kube/config 文件拷贝到 node 节点对应的文件中,安装 kubeadm、kubelet、kubectl(可选),然后执行上面初始化完成后提示的 join 命令即可:
$ kubeadm join 192.168.1.111:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef > --discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:a292e66049e45264f848186d2fa3582dc360f3b5006cc160f137b5d436e078c2 [preflight] Running pre-flight checks [preflight] Reading configuration from the cluster... [preflight] FYI: You can look at this config file with 'kubectl -n kube-system get cm kubeadm-config -oyaml' [kubelet-start] Downloading configuration for the kubelet from the "kubelet-config-1.16" ConfigMap in the kube-system namespace [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet configuration to file "/var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml" [kubelet-start] Writing kubelet environment file with flags to file "/var/lib/kubelet/kubeadm-flags.env" [kubelet-start] Activating the kubelet service [kubelet-start] Waiting for the kubelet to perform the TLS Bootstrap... This node has joined the cluster: * Certificate signing request was sent to apiserver and a response was received. * The Kubelet was informed of the new secure connection details. Run 'kubectl get nodes' on the control-plane to see this node join the cluster.
join 命令:
如果忘记了上面的 join 命令可以使用 kubeadm token create --print-join-command 重新获取。
kubeadm join 命令执行流程图:
添加 node 节点后 查看:
$ kubectl get nodes NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION master NotReady master 39m v1.16.2 node1 NotReady none1 106s v1.16.2 node1 NotReady none2 106s v1.16.2
网络方案(CNI)两种网络-我们这里选择Flannel 以下作为介绍
1、Calico 推荐方案,支持网络策略
为什么部署CNI网络?
部署CNI是为了不同主机之间的Pod进行通信,因为kubernetes资源调度是需要通信进行计算服务器资源情况进行分配的 Calico是一个纯三层的数据中心网络方案,Calico支持广泛的平台,包括Kubernetes、OpenStack等。 Calico 在每一个计算节点利用 Linux Kernel 实现了一个高效的虚拟路由器( vRouter) 来负责数据转发,<br>而每个 vRouter 通过 BGP 协议负责把自己上运行的 workload 的路由信息向整个 Calico 网络内传播。 此外,Calico 项目还实现了 Kubernetes 网络策略,提供ACL功能
下载官方默认配置文件
https://docs.projectcalico.org/manifests/calico.yaml
下载完后还需要修改里面配置项:
- 定义Pod网络(CALICO_IPV4POOL_CIDR),与前面初始化集群网络pod CIDR配置一样,后面集群所有的pod都会使用这个网络进行分配地址
- 选择工作模式(CALICO_IPV4POOL_IPIP),支持**BGP(Never)**、**IPIP(Always)**、**CrossSubnet**(开启BGP并支持跨子网)
IPIP 隧道模式(overlay网络),基于以太网基础上承载容器数据表
BGP 纯路由方案,要求在二层网络中,比较推荐的模式(对性能要求高的环境)
CrossSubnet 跨网段走IPIP,同网段走BGP
修改完后应用清单和查看状态:
kubectl apply -f calico.yaml
kubectl get pods -n kube-system
2、Flannel 老版本推荐使用
Flannel是CoreOS维护的一个网络组件,Flannel为每个Pod提供全局唯一的IP,Flannel使用ETCD来存储Pod子网与Node IP之间的关系。
flanneld守护进程在每台主机上运行,并负责维护ETCD信息和路由数据包。
yaml下载地址: (国外下载地址比较慢,可以考虑更换为国内的镜像下载地址,推荐 在阿里源下载)
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/master/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
可以看到是 NotReady 状态,这是因为还没有安装网络插件,接下来安装网络插件,可以在文档 https://kubernetes.io/docs/setup/production-environment/tools/kubeadm/create-cluster-kubeadm/ 中选择我们自己的网络插件,这里我们安装 flannel:
$ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/coreos/flannel/2140ac876ef134e0ed5af15c65e414cf26827915/Documentation/kube-flannel.yml
# 因为有节点是多网卡,所以需要在资源清单文件中指定内网网卡
# 搜索到名为 kube-flannel-ds-amd64 的 DaemonSet,在kube-flannel容器下面
$ vi kube-flannel.yml
......
containers:
- name: kube-flannel
image: quay.io/coreos/flannel:v0.11.0-amd64
command:
- /opt/bin/flanneld
args:
- --ip-masq
- --kube-subnet-mgr
- --iface=eth0 # 如果是多网卡的话,指定内网网卡的名称
......
$ kubectl apply -f kube-flannel.yml # 安装 flannel 网络插件
# 稍等一会查看 Pod 运行状态:
$ kubectl get pods -n kube-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
coredns-667f964f9b-wb5fn 1/1 Running 0 20m
coredns-667f964f9b-xmwn2 1/1 Running 0 20m
etcd-ydzs-master 1/1 Running 0 19m
kube-apiserver-ydzs-master 1/1 Running 0 19m
kube-controller-manager-ydzs-master 1/1 Running 0 19m
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-8l2wr 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-flannel-ds-amd64-vwhbh 1/1 Running 0 12m
kube-proxy-8r4d2 1/1 Running 0 17m
kube-proxy-rbjv7 1/1 Running 0 20m
kube-scheduler-ydzs-master 1/1 Running 0 20m
# Flannel 网络插件
当我们部署完网络插件后执行 ifconfig 命令,正常会看到新增的cni0与flannel1这两个虚拟设备,但是如果没有看到cni0这个设备也不用太担心,我们可以观察/var/lib/cni目录是否存在,如果不存在并不是说部署有问题,而是该节点上暂时还没有应用运行,我们只需要在该节点上运行一个 Pod 就可以看到该目录会被创建,并且cni0设备也会被创建出来。
Dashboard
v1.16.2 版本的集群需要安装最新的 2.0+ 版本的 Dashboard:
# 推荐使用下面这种方式 $ wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/v2.0.0-beta5/aio/deploy/recommended.yaml $ vi recommended.yaml # 修改Service为NodePort类型 ...... kind: Service apiVersion: v1 metadata: labels: k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard name: kubernetes-dashboard namespace: kubernetes-dashboard spec: ports: - port: 443 targetPort: 8443 nodePort: 30001 #手工绑定端口 selector: k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard type: NodePort # 加上type=NodePort变成NodePort类型的服务 # 创建及查看: kubectl apply -f recommended.yaml kubectl get pods -n kubernetes-dashboard -l k8s-app=kubernetes- kubectl get svc -n kubernetes-dashboard
登录 Dashboard UI 界面:(注意使用https协议访问,http不可行,master IP+手工绑定的端口,如没有手工绑定端口 会随机生成一个端口)
https://192.168.1.111:30001
创建一个具有全局所有权限的用户来登录Dashboard:(admin.yaml) 可选:
kind: ClusterRoleBinding apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1 metadata: name: admin annotations: rbac.authorization.kubernetes.io/autoupdate: "true" roleRef: kind: ClusterRole name: cluster-admin apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: admin namespace: kubernetes-dashboard --- apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: admin namespace: kubernetes-dashboard
创建:
$ kubectl apply -f admin.yaml $ kubectl get secret -n kubernetes-dashboard|grep admin-token admin-token-lwmmx kubernetes.io/service-account-token 3 1d $ kubectl get secret admin-token-lwmmx -o jsonpath={.data.token} -n kubernetes-dashboard |base64 -d# 会生成一串很长的base64后的字符串
使用上面的 base64 解码后的字符串作为 token 登录 Dashboard 即可,新版本还新增了一个暗黑模式:

清理:
如果 集群安装过程中遇到了其他问题,我们可以使用下面的命令来进行重置:
$ kubeadm reset $ ifconfig cni0 down && ip link delete cni0 $ ifconfig flannel.1 down && ip link delete flannel.1 $ rm -rf /var/lib/cni/