在上文中,介绍了如何安装和使用Suteki,今天我们通过源码来看一下Suteki是如何使用
Controller。
在Suteki中,其使用Abstract的方式来定义一个ControllerBase,以此作为所有Controller
的基类,下面是其Controller的类设计图:
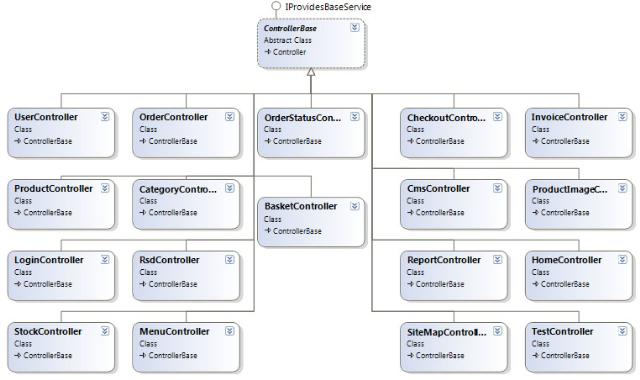
在该基类中定义了一些Controller中常用到的方法,比如为当前视图添加MetaDescription,
Title等:
public abstract class ControllerBase : Controller, IProvidesBaseService
{
private IBaseControllerService baseControllerService;
/// <summary>
/// Supplies services and configuration to all controllers
/// </summary>
public IBaseControllerService BaseControllerService
{
get { return baseControllerService; }
set
{
baseControllerService = value;
ViewData["Title"] = "{0}{1}".With(
baseControllerService.ShopName,
GetControllerName());
ViewData["MetaDescription"] = "\"{0}\"".With(baseControllerService.MetaDescription);
}
}
public ILogger Logger { get; set; }
public virtual string GetControllerName()
{
return " - {0}".With(GetType().Name.Replace("Controller", ""));
}
public virtual void AppendTitle(string text)
{
ViewData["Title"] = "{0} - {1}".With(ViewData["Title"], text);
}
public virtual void AppendMetaDescription(string text)
{
ViewData["MetaDescription"] = text;
}
public string Message
{
get { return TempData["message"] as string; }
set { TempData["message"] = value; }
}
protected override void OnException(ExceptionContext filterContext) {
Response.Clear();
base.OnException(filterContext);
}
}
当然,细心的朋友发现了该抽象类中还包括一个IBaseControllerService接口实例。
该接口的主要定义了一些网店系统信息,如店铺名称,版权信息,Email信息等,如下:
{
IRepository<Category> CategoryRepository { get; }
string GoogleTrackingCode { get; set; }
string ShopName { get; set; }
string EmailAddress { get; set; }
string SiteUrl { get; }
string MetaDescription { get; set; }
string Copyright { get; set; }
string PhoneNumber { get; set; }
string SiteCss { get; set; }
}
而作为唯一一个实现了该接口的子类“BaseControllerService”定义如下:
{
public IRepository<Category> CategoryRepository { get; private set; }
public string GoogleTrackingCode { get; set; }
public string MetaDescription { get; set; }
private string shopName;
private string emailAddress;
private string copyright;
private string phoneNumber;
private string siteCss;
 ..
..}
而初始化BaseControllerService实例并将配置文件中的信息绑定到该类实例中的操作交给了Windsor,
该组件在Castle中用于实现IOC操作,其配置文件位于项目Suteki.Shop\Configuration\Windsor.config.
下面是其配置结点内容:
id="IBaseControllerService:test.jumpthegun.co.uk"
service="Suteki.Shop.Services.IBaseControllerService, Suteki.Shop"
type="Suteki.Shop.Services.BaseControllerService, Suteki.Shop"
lifestyle="transient">
<parameters>
<ShopName>Suteki Shop</ShopName>
<EmailAddress>info@sutekishop.co.uk</EmailAddress>
<GoogleTrackingCode>UA-1643677-4</GoogleTrackingCode>
<MetaDescription>Suteki Shop is a new self service eCommerce solution. Search engine optimised and fully customisable</MetaDescription>
<SiteCss>Site.css</SiteCss>
</parameters>
</component>
这类就完成了把网店的系统信息绑定到Controller中的操作,而Controller就会在其基类中将相关的
信息绑定到ViewData中,如下:
ViewData["MetaDescription"] = "\"{0}\"".With(baseControllerService.MetaDescription);
到这里,其实大家应该发现这种对Controller的处理与我们以前所使用的PageBase方式相似,就是将
项目中所有的Page都继承自PageBase,然后在相应的Page中引用PageBase中定义的属性和方法。
有了ControllerBase,我们看一下在相应的子Controller中是如何使用的,这里有一个例子,
ProductController(位于Suteki.Shop\Controllers\ProductController.cs):
{


public ActionResult Item(string urlName)
{
return RenderItemView(urlName);
}
 ..
..ActionResult RenderItemView(string urlName)
{
var product = productRepository.GetAll().WithUrlName(urlName);
AppendTitle(product.Name);
AppendMetaDescription(product.Description);
return View("Item", ShopView.Data.WithProduct(product));
}


}
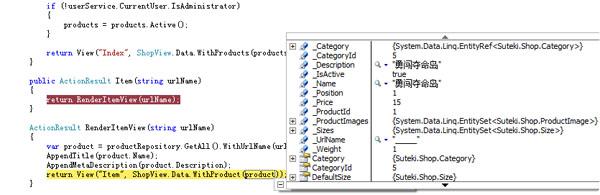
该Controller中的Action:"Item"调用了RenderItemView()就是使用了基类中的AppendTitle,
AppendMetaDescription。下面是其运行时的截图:

除了上面所说的这种ControllerBase方式,Suteki.Shop还使用了Controller<T>方式来实现对
一些公用Action的操作,比如列表,编辑,添加记录,调整记录上下位置等。而这块实现代码被放
置在了Suteki.Common\ScaffoldController.cs和OrderableScaffoldController.cs文件中,其中
ScaffoldController为父类,其中包括列表,编辑,添加Action等。
大家请注意ScaffoldController类中的几个公共属性:
public IRepositoryResolver repositoryResolver { get; set; }
public IValidatingBinder ValidatingBinder { get; set; }
public IHttpContextService httpContextService { get; set; }
其中Repository是一些对数据CRUD的操作对象,下面是Repository中的一些接口成员方法:
{
T GetById(int id);
IQueryable<T> GetAll();
void InsertOnSubmit(T entity);
void DeleteOnSubmit(T entity);
[Obsolete("Units of Work should be managed externally to the Repository.")]
void SubmitChanges();
}
这样就可以在ScaffoldController使用统一的接口函数调用相应子类中的实现方法了。
而ScaffoldController的子类OrderableScaffoldController则实现了对数据集合中的某行元素
上下移动的操作:
{
public IOrderableService<T> OrderableService { get; set; }
protected override ActionResult RenderIndexView(int? page)
{
var items = Repository.GetAll().InOrder().AsPagination(page ?? 1);
return View("Index", ScaffoldView.Data<T>().With(items));
}
public override ActionResult New()
{
T item = new T
{
Position = OrderableService.NextPosition
};
return View("Edit", (object)BuildEditViewData().With(item));
}
[UnitOfWork]
public virtual ActionResult MoveUp(int id, int? page)
{
OrderableService.MoveItemAtPosition(id).UpOne();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
[UnitOfWork]
public virtual ActionResult MoveDown(int id, int? page)
{
OrderableService.MoveItemAtPosition(id).DownOne();
return RedirectToAction("Index");
}
}
注:IOrderableService的实现相对复杂一些,具体内容详见Suteki.Common\Services\OrderableService.cs.
按说有了这些功能之后,只要在相应的子类中直接继承使用就可以了,但在Suteki.Shop项目中
作者又对OrderableScaffoldController进行了一个“继承式”扩展,提供了与前面所说的那个“
ControllerBase"相似的方法定义,如下:
public abstract class ShopScaffoldController<T> : OrderableScaffoldController<T>, IProvidesBaseService where T : class, IOrderable, new()
{
private IBaseControllerService baseControllerService;
/// <summary>
/// Supplies services and configuration to all controllers
/// </summary>
public IBaseControllerService BaseControllerService
{
get { return baseControllerService; }
set
{
baseControllerService = value;
ViewData["Title"] = "{0}{1}".With(
baseControllerService.ShopName,
GetControllerName());
}
}
public virtual string GetControllerName()
{
return " - {0}".With(GetType().Name.Replace("Controller", ""));
}
}
而ShopScaffoldController这个抽象类有三个子类,如下图:

因为这三个Controller的功能需求相似,而相应的Action实现也在基类“ScaffoldController”
中实现,所以相应的类代码基本上就没有什么了。只不过在这几个子类中都被绑定了UnitOfWork过滤
器(UnitOfWorkFilter),其代码如下Suteki.Common\Filters\UnitOfWorkAttribute.cs:
{
public UnitOfWorkAttribute() : base(typeof (UnitOfWorkFilter))
{ }
}
public class UnitOfWorkFilter : IActionFilter
{
private readonly IDataContextProvider provider;
public UnitOfWorkFilter(IDataContextProvider provider)
{
this.provider = provider;
}
public void OnActionExecuting(ActionExecutingContext filterContext)
{}
public void OnActionExecuted(ActionExecutedContext filterContext)
{
var context = provider.DataContext;
if (filterContext.Controller.ViewData.ModelState.IsValid)
{
context.SubmitChanges();
}
}
}
其核心功能就是在对用户提交的数据进行有效验证后调用DataContext的SubmitChanges()方法
(注:该逻辑被放在了OnActionExecuted方法中实现)来保存修改,这种做法在以往的MVC示例子没有
看到过,呵呵,不过这种做法还有待研究。
好了,今天的内容就先到这里了,在下一篇中,将来讨论一下该项目中对MVC框架中Filter的用
法。
原文链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/daizhj/archive/2009/05/12/1451955.html
作者: daizhj,代震军,LaoD
Tags: mvc
网址: http://daizhj.cnblogs.com/