一.概念引入
设A是一个确定性算法,当它的输入实例为x时所需的计算时间记为tA(x)。设Xn是算法A的输入规模为n的实例的全体,则当问题的输入规模为n时,算法A所需的平均时间为![]() 。这显然不能排除存在x∈Xn使得的
。这显然不能排除存在x∈Xn使得的![]() 可能性。希望获得一个随机化算法B,使得对问题的输入规模为n的每一个实例均有
可能性。希望获得一个随机化算法B,使得对问题的输入规模为n的每一个实例均有![]() 。这就是舍伍德算法设计的基本思想。当s(n)与tA(n)相比可忽略时,舍伍德算法可获得很好的平均性能。
。这就是舍伍德算法设计的基本思想。当s(n)与tA(n)相比可忽略时,舍伍德算法可获得很好的平均性能。
概率算法的一个特点是对同一实例多次运用同一概率算法结果可能同。舍伍德算法(O(sqrt(n)),综合了线性表和线性链表的优点)总能求的问题的一个正确解,当一个确定性算法在最坏情况和平均情况下差别较大时可在这个确定性算法中引入随机性将之改造成一个舍伍德算法;引入随机性不是为了消除最坏,而是为了减少最坏和特定实例的关联性。比如线性表a的查找若是找10(独一无二),如果在a[0]则为O(1),若是最后一个则O(n),可见时间与输入实例有关,此时可引入随机性将之改造成一个舍伍德算法。
有时候无法直接把确定性算法改造为舍伍德算法,这时候对输入洗牌。
下面是洗牌算法源代码:

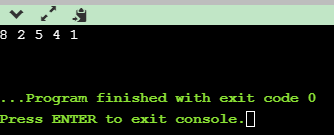
import java.util.Random; public class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) { int a[] = new int[]{1,2,4,5,8}; /* * Collections.shuffle(list)参数只能是list */ myShuffle(a); for(int i:a) { //犯了个低级错误,输出了a[i],结果数组下标越界异常 System.out.print(i+" "); } System.out.println(); } private static void myShuffle(int[] a) { int len = a.length; for(int i=0; i<len; i++) { Random r = new Random(); //直接Random.nextInt(len)提示静态方法里无法引用 int j = r.nextInt(len); //Collections.swap(list,i,j)必须是list类型 if(i!=j) {//原来没加这个条件 int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } } } }
实现如下:
二.舍伍德思想解决迅雷2010年校招--发牌
问题描述:52张扑克牌分发给4人,每人13张,要求保证随机性。已有随机整数生成函数rand(),但开销较大。请编写函数实现void deal(int a[],int b[],int c[],int d[]),扑克牌用序号0-51表示,分别存在大小为13的a,b,c,d四个数组中,要求尽可能高效。
以下是源代码:

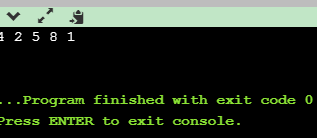
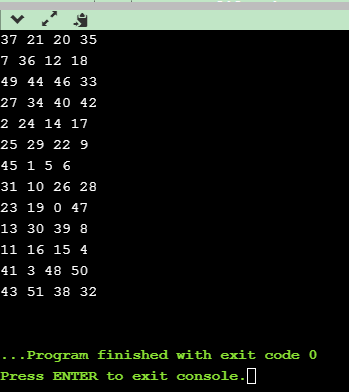
import java.util.Random; public class Poker { /* * 这道题确实不怎么明白,直接初始化后洗牌算法不得了 * 不过解答只是替换nextInt,直接线性同余了,交换次数也减少了 * 交换次数是随机产生的 */ //为方便swap和deal函数使用 static int array[] = new int[52]; public static void main(String[] args) { for(int i=0; i<array.length; i++) { array[i] = i; } int a[] = new int[13]; int b[] = new int[13]; int c[] = new int[13]; int d[] = new int[13]; deal(a,b,c,d); //这样输出方便 for(int i=0; i<13; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]+" "+b[i]+" "+c[i] + " "+d[i]); } } private static void deal(int[] a, int[] b, int[] c, int[] d) { int m = 10; int p = 31;//需要素数 int q = 10; Random r = new Random(); int num = r.nextInt(52);//循环次数 for(int i=0; i<num; i++) { m = m*p + q; m = m%(51-i); int j = 51 - m; if(i!=j) { swap(array,i,j); } } for(int i=0; i<13; i++) { a[i] = array[i]; b[i] = array[i+13]; c[i] = array[i+26]; d[i] = array[i+39]; } } private static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) { //交换是正确的 int temp = a[i]; a[i] = a[j]; a[j] = temp; } }
代码实现结果:
三.线性时间选择算法
1)随机划分选择基准
对于选择问题而言,用拟中位数作为划分基准可以保证在最坏的情况下用线性时间完成选择。如果只简单地用待划分数组的第一个元素作为划分基准,则算法的平均性能较好,而在最坏的情况下需要O(n^2)计算时间。舍伍德选择算法则随机地选择一个数组元素作为划分基准,这样既保证算法的线性时间平均性能,又避免了计算拟中位数的麻烦。非递归的舍伍德型选择算法如下:
参考源代码:

//随机化算法 线性时间选择 随机划分选择基准 //#include "stdafx.h" #include "RandomNumber.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int l,int r,int k); template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int n,int k); template <class Type> inline void Swap(Type &a,Type &b); int main() { int a[] = {5,7,3,4,8,6,9,1,2}; cout<<"原数组为:"<<endl; for(int i=0; i<9; i++) { cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; cout<<"所给数组第7小元素为:"<<select(a,9,7)<<endl; return 0; } //计算a[0:n-1]中第k小元素 //假设a[n]是一个键值无穷大的元素 template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int n,int k) { if(k<1 || k>n) { cout<<"请输入正确的k!"<<endl; return 0; } return select(a,0,n-1,k); } //计算a[l:r]中第k小元素 template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int l,int r,int k) { static RandomNumber rnd; while(true) { if(l>=r) { return a[l]; } int i = l, j = l + rnd.Random(r-l+1);//随机选择划分基准 Swap(a[i],a[j]); j = r+1; Type pivot = a[l]; //以划分基准为轴做元素交换 while(true) { while(a[++i]<pivot); while(a[--j]>pivot); if(i>=j) { break; } Swap(a[i],a[j]); } if(j-l+1 == k)//第k小 { return pivot; } //a[j]必然小于pivot,做最后一次交换,满足左侧比pivot小,右侧比pivot大 a[l] = a[j]; a[j] = pivot; //对子数组重复划分过程 if(j-l+1<k) { k = k-j+l-1;//右侧:k-(j-l+1)=k-j+l-1 l = j + 1; } else { r = j - 1; } } } template <class Type> inline void Swap(Type &a,Type &b) { Type temp = a; a = b; b = temp; }

#include"time.h" //随机数类 const unsigned long maxshort = 65536L; const unsigned long multiplier = 1194211693L; const unsigned long adder = 12345L; class RandomNumber { private: //当前种子 unsigned long randSeed; public: RandomNumber(unsigned long s = 0);//构造函数,默认值0表示由系统自动产生种子 unsigned short Random(unsigned long n);//产生0:n-1之间的随机整数 double fRandom(void);//产生[0,1)之间的随机实数 }; RandomNumber::RandomNumber(unsigned long s)//产生种子 { if(s == 0) { randSeed = time(0);//用系统时间产生种子 } else { randSeed = s;//由用户提供种子 } } unsigned short RandomNumber::Random(unsigned long n)//产生0:n-1之间的随机整数 { randSeed = multiplier * randSeed + adder;//线性同余式 return (unsigned short)((randSeed>>16)%n); } double RandomNumber::fRandom(void)//产生[0,1)之间的随机实数 { return Random(maxshort)/double(maxshort); }
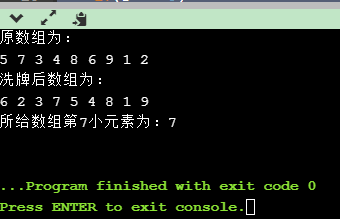
代码实现结果: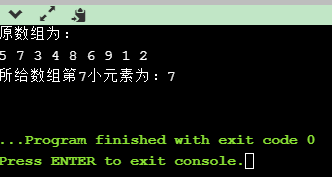
2)随机洗牌预处理
有时也会遇到这样的情况,即所给的确定性算法无法直接改造成舍伍德型算法。此时可借助于随机预处理技术,不改变原有的确定性算法,仅对其输入进行随机洗牌,同样可收到舍伍德算法的效果。例如,对于确定性选择算法,可以用下面的洗牌算法shuffle将数组a中元素随机排列,然后用确定性选择算法求解。这样做所收到的效果与舍伍德型算法的效果是一样的。
参考源代码:

//随机化算法 线性时间选择 输入预处理,洗牌 #include "stdafx.h" #include "RandomNumber.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int l,int r,int k); template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int n,int k); template<class Type> void Shuffle(Type a[],int n); template <class Type> inline void Swap(Type &a,Type &b); int main() { int a[] = {5,7,3,4,8,6,9,1,2}; cout<<"原数组为:"<<endl; for(int i=0; i<9; i++) { cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; Shuffle(a,9);//洗牌 cout<<"洗牌后数组为:"<<endl; for(int i=0; i<9; i++) { cout<<a[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; cout<<"所给数组第7小元素为:"<<select(a,9,7)<<endl; return 0; } //计算a[0:n-1]中第k小元素 //假设a[n]是一个键值无穷大的元素 template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int n,int k) { if(k<1 || k>n) { cout<<"请输入正确的k!"<<endl; return 0; } return select(a,0,n-1,k); } //计算a[l:r]中第k小元素 template<class Type> Type select(Type a[],int l,int r,int k) { while(true) { if(l>=r) { return a[l]; } int i = l; int j = r+1; Type pivot = a[l]; //以划分基准为轴做元素交换 while(true) { while(a[++i]<pivot); while(a[--j]>pivot); if(i>=j) { break; } Swap(a[i],a[j]); } if(j-l+1 == k)//第k小 { return pivot; } //a[j]必然小于pivot,做最后一次交换,满足左侧比pivot小,右侧比pivot大 a[l] = a[j]; a[j] = pivot; //对子数组重复划分过程 if(j-l+1<k) { k = k-j+l-1;//右侧:k-(j-l+1)=k-j+l-1 l = j + 1; } else { r = j - 1; } } } template <class Type> inline void Swap(Type &a,Type &b) { Type temp = a; a = b; b = temp; } //随机洗牌算法 template<class Type> void Shuffle(Type a[],int n) { static RandomNumber rnd; for(int i=0; i<n; i++) { int j = rnd.Random(n-i)+i; Swap(a[i],a[j]); } }

#include"time.h" //随机数类 const unsigned long maxshort = 65536L; const unsigned long multiplier = 1194211693L; const unsigned long adder = 12345L; class RandomNumber { private: //当前种子 unsigned long randSeed; public: RandomNumber(unsigned long s = 0);//构造函数,默认值0表示由系统自动产生种子 unsigned short Random(unsigned long n);//产生0:n-1之间的随机整数 double fRandom(void);//产生[0,1)之间的随机实数 }; RandomNumber::RandomNumber(unsigned long s)//产生种子 { if(s == 0) { randSeed = time(0);//用系统时间产生种子 } else { randSeed = s;//由用户提供种子 } } unsigned short RandomNumber::Random(unsigned long n)//产生0:n-1之间的随机整数 { randSeed = multiplier * randSeed + adder;//线性同余式 return (unsigned short)((randSeed>>16)%n); } double RandomNumber::fRandom(void)//产生[0,1)之间的随机实数 { return Random(maxshort)/double(maxshort); }
代码实现结果:
参考文献:王晓东《算法设计与分析》
https://blog.csdn.net/liufeng_king/article/details/9038771
