Jolly and Emily are two bees studying in Computer Science. Unlike other bees they are fond of playing two-player games. They used to play Tic-tac-toe, Chess etc. But now since they are in CS they invented a new game that definitely requires some knowledge of computer science.
Initially they draw a random rooted tree (a connected graph with no cycles) in a paper which consists of n nodes, where the nodes are numbered from 0 to n-1 and 0 is the root, and the edges are weighted. Initially all the edges are unmarked. And an edge weigh w, has w identical units.
- Jolly has a green marker and Emily has a red marker. Emily starts the game first and they alternate turns.
- In each turn, a player can color one unit of an edge of the tree if that edge has some (at least one) uncolored units and the edge can be traversed from the root using only free edges. An edge is said to be free if the edge is not fully colored (may be uncolored or partially colored).
- If it's Emily's turn, she finds such an edge and colors one unit of it using the red marker.
- If it's Jolly's turn, he finds such an edge and colors one unit of it with the green marker.
- The player, who can't find any edges to color, loses the game.
For example, Fig 1 shows the initial tree they have drawn. The tree contains four nodes and the weights of the edge (0, 1), (1, 2) and (0, 3) are 1, 1 and 2 respectively. Emily starts the game. She can color any edge she wants; she colors one unit of edge (0 1) with her red marker (Fig 2). Since the weight of edge (0 1) is 1 so, this edge is fully colored.
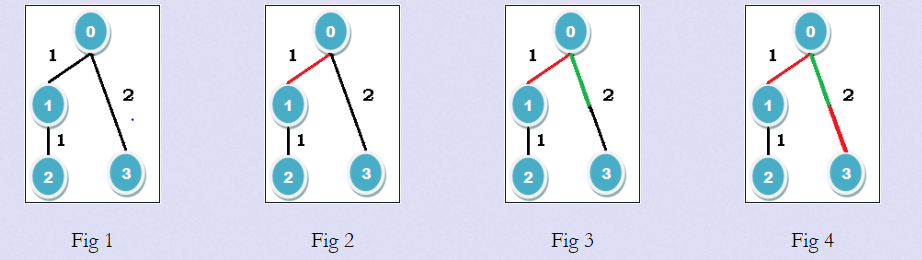
Now it's Jolly's turn. He can only color one unit of edge (0 3). He can't color edge (1 2) since if he wants to traverse it from the root (0), he needs to use (0, 1) which is fully colored already. So, he colors one unit of edge (0 3) with his green marker (Fig 3). And now Emily has only one option and she colors the other unit of (0 3) with the red marker (Fig 4). So, both units of edge (0 3) are colored. Now it's Jolly's turn but he has no move left. Thus Emily wins. But if Emily would have colored edge (1 2) instead of edge (0 1), then Jolly would win. So, for this tree Emily will surely win if both of them play optimally.
Input
Input starts with an integer T (≤ 500), denoting the number of test cases.
Each case starts with a line containing an integer n (2 ≤ n ≤ 1000). Each of the next n-1 lines contains two integers u v w (0 ≤ u, v < n, u ≠ v, 1 ≤ w ≤ 109) denoting that there is an edge between u and v and their weight is w. You can assume that the given tree is valid.
Output
For each case, print the case number and the name of the winner. See the samples for details.
Sample Input
4
4
0 1 1
1 2 1
0 3 2
5
0 1 1
1 2 2
0 3 3
0 4 7
3
0 1 1
0 2 1
4
0 1 1
1 2 1
1 3 1
Sample Output
Case 1: Emily
Case 2: Emily
Case 3: Jolly
Case 4: Emily
Note
Dataset is huge, use faster I/O methods.
题解:green博弈变形,对于都是1的就是green博弈SG[u]^=SG[v]+1;
对于大于1的边,偶数对其没有贡献,奇数有贡献,SG[u]^= SG[v]^(val[v]%2);
参考代码:

1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 #define RI register int 4 #define clr(a,val) memset(a,val,sizeof(a)) 5 typedef long long ll; 6 struct Edge{ 7 int to,val,nxt; 8 } edge[2010]; 9 int x,y,z; 10 int T,n,sum1,sum2,cnt; 11 int head[2010],SG[2010]; 12 inline void addedge(int u,int v,int w) 13 { 14 edge[cnt].to=v; 15 edge[cnt].val=w; 16 edge[cnt].nxt=head[u]; 17 head[u]=cnt++; 18 } 19 inline void dfs(int u,int fa) 20 { 21 SG[u]=0; 22 for(int e=head[u];~e;e=edge[e].nxt) 23 { 24 int v=edge[e].to; 25 if(v==fa) continue; 26 dfs(v,u); 27 if(edge[e].val==1) SG[u]^=(SG[v]+1); 28 else SG[u]^=(SG[v]^(edge[e].val%2)); 29 } 30 } 31 int main() 32 { 33 scanf("%d",&T); 34 for(RI cas=1;cas<=T;++cas) 35 { 36 scanf("%d",&n); 37 clr(head,-1);cnt=0; 38 for(RI i=1;i<n;++i) 39 { 40 scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z); 41 addedge(x,y,z);addedge(y,x,z); 42 } 43 dfs(0,0); 44 if(SG[0]) printf("Case %d: Emily ",cas); 45 else printf("Case %d: Jolly ",cas); 46 } 47 return 0; 48 }
