摘自:《机器学习实战》,用python编写的(需要matplotlib和numpy库)
海伦一直使用在线约会网站寻找合适自己的约会对象。尽管约会网站会推荐不同的人选,但她没有从中找到喜欢的人。经过一番总结,她发现曾交往过三种类型的人:
1.不喜欢的人( 以下简称1 );
2.魅力一般的人( 以下简称2 );
3.极具魅力的人(以下简称3 )
尽管发现了上述规律,但海伦依然无法将约会网站推荐的匹配对象归入恰当的分类。她觉得可以在周一到周五约会哪些魅力一般的人,而周末则更喜欢与那些极具魅力的人为伴。海伦希望我们的分类软件可以更好的帮助她将匹配对象划分到确切的分类中。此外海伦还收集了一些约会网站未曾记录的数据信息,她认为这些数据更有助于匹配对象的归类。
我们先提取一下这个案例的目标:根据一些数据信息,对指定人选进行分类(1或2或3)。为了使用kNN算法达到这个目标,我们需要哪些信息?前面提到过,就是需要样本数据,仔细阅读我们发现,这些样本数据就是“ 海伦还收集了一些约会网站未曾记录的数据信息 ”。好的,下面我们就开始吧!
----1.收集数据
海伦收集的数据是记录一个人的三个特征:每年获得的飞行常客里程数;玩视频游戏所消耗的时间百分比;每周消费的冰淇淋公升数。数据是txt格式文件,如下图,前三列依次是三个特征,第四列是分类(1:不喜欢的人,2:魅力一般的人,3:极具魅力的人),每一行代表一个人。
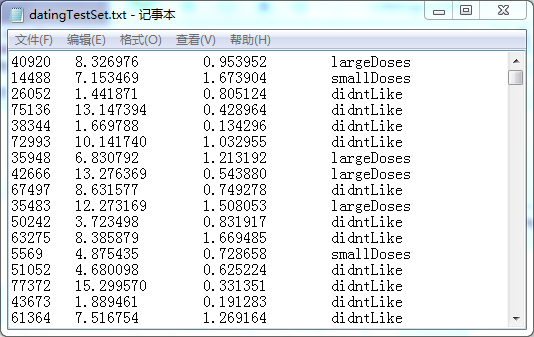
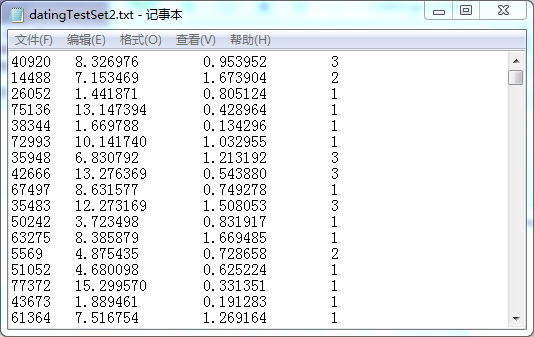
---- 2.准备数据:从文本文件中解析数据
何为准备数据?之前收集到了数据,放到了txt格式的文档中了,看起来也比较规整,但是计算机并不认识啊。计算机需要从txt文档中读取数据,并把数据进行格式化,也就是说存到矩阵中,用矩阵来承装这些数据,这样才能使用计算机处理。
需要两个矩阵:一个承装三个特征数据,一个承装对应的分类。于是,我们定义一个函数,函数的输入时数据文档(txt格式),输出为两个矩阵。
代码如下:
1 #!/usr/bin/python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 from numpy import * #引入科学计算包numpy 4 import operator #经典python函数库,运算符模块 5 6 def file2matrix(filename): 7 fr=open(filename) 8 arrayOLines=fr.readlines() 9 numberOfLines=len(arrayOLines) 10 returnMat=zeros((numberOfLines,3)) 11 classLabelVector=[] 12 index=0 13 for line in arrayOLines: 14 line=line.strip() 15 listFromLine=line.split(' ') 16 returnMat[index,:]=listFromLine[0:3] 17 classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1])) 18 index+=1 19 return returnMat,classLabelVector
简要解读代码:首先打开文件,读取文件的行数,然后初始化之后要返回的两个矩阵(returnMat、classLabelsVector),然后进入循环,将每行的数据各就各位分配给returnMat和classLabelsVector。
在python命令提示符下面输入以下命令:
>>> import kNN >>> reload(kNN) >>> datingDataMat,datingLabels=kNN.file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') >>> datingDataMat array([[ 4.09200000e+04, 8.32697600e+00, 9.53952000e-01], [ 1.44880000e+04, 7.15346900e+00, 1.67390400e+00], [ 2.60520000e+04, 1.44187100e+00, 8.05124000e-01], ..., [ 2.65750000e+04, 1.06501020e+01, 8.66627000e-01], [ 4.81110000e+04, 9.13452800e+00, 7.28045000e-01], [ 4.37570000e+04, 7.88260100e+00, 1.33244600e+00]]) >>> datingLabels[0:20] [3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 3, 3, 1, 3, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 3]
----3.分析数据:使用Matplotlib创建散点图
Matplotlib库提供的scatter函数支持个性化标记散点图上的点。散点图使用了datingDataMat矩阵的第二、三列数据,分别表示特征值“玩视频游戏所耗时间百分比”和“每周所消耗的冰淇淋公升数”。
>>> import matplotlib >>> import kNN >>> datingDataMat,datingLabels=kNN.file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') >>> import matplotlib >>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt >>> fig=plt.figure() >>> ax=fig.add_subplot(111) >>>ax.scatter(datingDataMat[:,1],datingDataMat[:,2],15.0*array(datingLabels),15.0*array(datingLabels)) <matplotlib.collections.PathCollection object at 0x03C85C70> >>> plt.show()
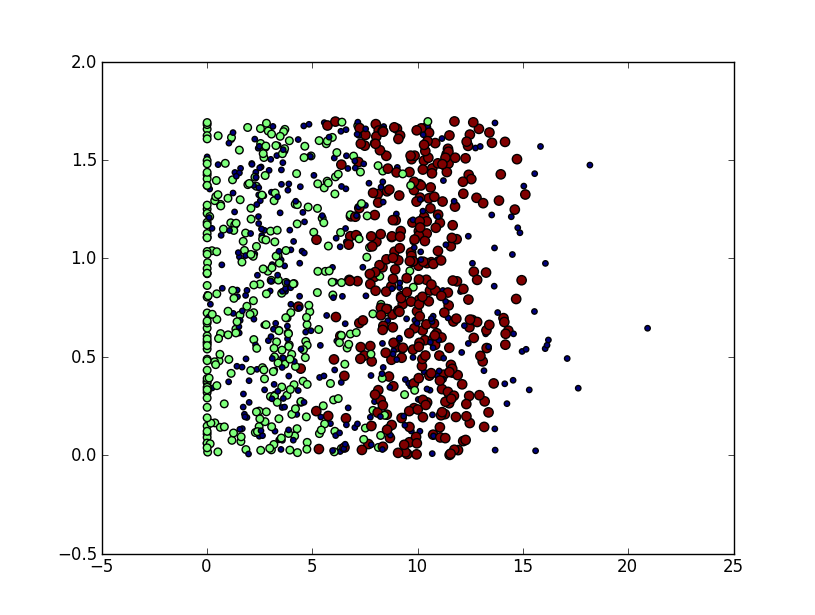
----4.设计算法:用kNN算法
k-近邻算法的目的就是找到新数据的前k个邻居,然后根据邻居的分类来确定该数据的分类。
首先要解决的问题,就是什么是邻居?当然就是“距离”近的了,不同人的距离怎么确定?这个有点抽象,不过我们有每个人的3个特征数据。每个人可以使用这三个特征数据来代替这个人——三维点。比如样本的第一个人就可以用(40920, 8.326976, 0.953952)来代替,并且他的分类是3。那么此时的距离就是点的距离:
A点(x1, x2, x3),B点(y1, y2, y3),这两个点的距离就是:(x1-y1)^2+(x2-y2)^2+(x3-y3)^2的平方根。求出新数据与样本中每个点的距离,然后进行从小到大排序,前k位的就是k-近邻,然后看看这k位近邻中占得最多的分类是什么,也就获得了最终的答案。
这个处理过程也是放到一个函数里的,代码如下:
1 #inX:用户分类的输入向量,即将对其进行分类 2 #dataSet:训练样本集 3 #labels:标签向量 4 5 def classifyO(inX,dataSet,labels,k): 6 #距离计算 7 dataSetSize=dataSet.shape[0] #得到数组的行数,即知道有几个训练数据 8 diffMat=tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-dataSet #tile是numpy中的函数,tile将原来的一个数组,扩充成了4个一样的数组;diffMat得到目标与训练数值之间的差值 9 sqDiffMat=diffMat**2 #各个元素分别平方 10 sqDistances=sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) 11 distances=sqDistances**0.5 #开方,得到距离 12 sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort() #升序排列 13 #选择距离最小的k个点 14 classCount={} 15 for i in range(k): 16 voteIlabel=labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]] 17 classCount[voteIlabel]=classCount.get(voteIlabel,0)+1 18 #排序 19 sortedClassCount=sorted(classCount.iteritems(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True) 20 return sortedClassCount[0][0]
简要解读代码:该函数的4个参数分别为新数据的三个特征inX、样本数据特征集(上一个函数的返回值)、样本数据分类(上一个函数的返回值)、k,函数返回位新数据的分类。第二行dataSetSize获取特征集矩阵的行数,第三行为新数据与样本各个数据的差值,第四行取差值去平方,之后就是再取和,然后平方根。代码中使用的排序函数都是python自带的。

好了,现在我们可以分析数据了,不过,有一点不知道大家有没有注意,我们回到那个数据集,第一列代表的特征数值远远大于其他两项特征,这样在求距离的公式中就会占很大的比重,致使两点的距离很大程度上取决于这个特征,这当然是不公平的,我们需要的三个特征都均平地决定距离,所以我们要对数据进行处理, 希望处理之后既不影响相对大小又可以不失公平 :
这种方法叫做,归一化数值,通过这种方法可以把每一列的取值范围划到0~1或-1~1:,处理的公式为:
newValue = (oldValue - min)/(max - min)
归一化数值的函数代码为:
1 def autoNorm(dataSet): 2 minVals=dataSet.min(0) 3 maxVals=dataSet.max(0) 4 ranges=maxVals-minVals 5 normDataSet=zeros(shape(dataSet)) 6 m=dataSet.shape[0] 7 normDataSet=dataSet-tile(minVals,(m,1)) 8 normDataSet=normDataSet/tile(ranges,(m,1)) 9 return normDataSet,ranges,minVals
在python命令提示符下,重新加载kNN.py模块,执行autoNorm函数,检测函数的执行结果:
>>>import kNN >>>reload(kNN) >>> normMat,ranges,minVals=kNN.autoNorm(datingDataMat) >>> normMat array([[ 0.44832535, 0.39805139, 0.56233353], [ 0.15873259, 0.34195467, 0.98724416], [ 0.28542943, 0.06892523, 0.47449629], ..., [ 0.29115949, 0.50910294, 0.51079493], [ 0.52711097, 0.43665451, 0.4290048 ], [ 0.47940793, 0.3768091 , 0.78571804]]) >>> ranges array([ 9.12730000e+04, 2.09193490e+01, 1.69436100e+00]) >>> minVals array([ 0. , 0. , 0.001156])
---5.测试算法:作为完整程序验证分类器
经过了格式化数据、归一化数值,同时我们也已经完成kNN核心算法的函数,现在可以测试了,测试代码为:
def datingClassTest(): hoRatio=0.10 datingDataMat,datingLabels=file2matrix('datingTestSet.txt') normMat,ranges,minVals=autoNorm(datingDataMat) m=normMat.shape[0] numTestVecs=int(m*hoRatio) errorCount=0.0 for i in range(numTestVecs): classifierResult=classifyO(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],3) print "the classifier came back with:%d,the real answer is :%d" %(classifierResult,datingLabels[i]) if(classifierResult !=datingLabels[i]):errorCount+=1.0 print "the total error rate is: %f"%(errorCount/float(numTestVecs))
通过测试代码我们可以在回忆一下这个例子的整体过程:
- 读取txt文件,提取里面的数据到datingDataMat、datingLabels;
- 归一化数据,得到归一化的数据矩阵;
- 测试数据不止一个,这里需要一个循环,依次对每个测试数据进行分类。
代码中大家可能不太明白hoRatio是什么。注意,这里的测试数据并不是另外一批数据而是之前的数据集里的一部分,这样我们可以把算法得到的结果和原本的分类进行对比,查看算法的准确度。在这里,海伦提供的数据集又1000行,我们把前100行作为测试数据,后900行作为样本数据集,现在大家应该可以明白hoRatio是什么了吧。
在python命令提示符下重新加载kNN.py模块,并输入kNN.datingClassTest(),执行分类器测试程序,我们将得到下面的输出结果:
>>> kNN.datingClassTest() the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is :3 the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is :2 the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is :1 the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is :1 the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is :1 ... the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is :3 the classifier came back with:2,the real answer is :2 the classifier came back with:1,the real answer is :1 the classifier came back with:3,the real answer is :1 the total error rate is: 0.050000
---6.使用算法:构建完整可用系统
上面我们已经在数据上对分类器进行了测试,现在终于可以使用这个分类器为海伦来对人们分类。我们会给海伦一小段程序,通过改程序海伦会在约会网站上找到某个人并输入他的信息。程序会给出她对对方喜欢程度的预测值。
将下列代码加入到kNN.py并重新加载kNN.
1 def classifyPerson(): 2 resultList=['not at all','in small doses','in large doses'] 3 percentTats=float(raw_input("percentage of time apent playing video games?")) 4 ffMiles=float(raw_input("frequent flier miles earned per year?")) 5 iceCream=float(raw_input("liters of ice cream consumed per year?")) 6 datingDataMat,datingLabels=file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') 7 normMat,ranges,minVals=autoNorm(datingDataMat) 8 inArr=array([ffMiles,percentTats,iceCream]) 9 classifierResult=classifyO((inArr-minVals)/ranges,normMat,datingLabels,3) 10 print "You will probably like this person:",resultList[classifierResult-1]
为了解程序的十几运行效果,输入如下命令:
>>> kNN.classifyPerson() percentage of time apent playing video games?10 frequent flier miles earned per year?10000 liters of ice cream consumed per year?0.5 You will probably like this person: in small doses
总结:
整体的代码:
1 #!/usr/bin/python 2 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 3 from numpy import * #引入科学计算包numpy 4 import operator #经典python函数库,运算符模块 5 6 #算法核心 7 #inX:用户分类的输入向量,即将对其进行分类 8 #dataSet:训练样本集 9 #labels:标签向量 10 def classifyO(inX,dataSet,labels,k): 11 #距离计算 12 dataSetSize=dataSet.shape[0] #得到数组的行数,即知道有几个训练数据 13 diffMat=tile(inX,(dataSetSize,1))-dataSet #tile是numpy中的函数,tile将原来的一个数组,扩充成了4个一样的数组;diffMat得到目标与训练数值之间的差值 14 sqDiffMat=diffMat**2 #各个元素分别平方 15 sqDistances=sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1) 16 distances=sqDistances**0.5 #开方,得到距离 17 sortedDistIndicies=distances.argsort() #升序排列 18 #选择距离最小的k个点 19 classCount={} 20 for i in range(k): 21 voteIlabel=labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]] 22 classCount[voteIlabel]=classCount.get(voteIlabel,0)+1 23 #排序 24 sortedClassCount=sorted(classCount.iteritems(),key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True) 25 return sortedClassCount[0][0] 26 def file2matrix(filename): 27 fr=open(filename) 28 arrayOLines=fr.readlines() 29 numberOfLines=len(arrayOLines) 30 returnMat=zeros((numberOfLines,3)) 31 classLabelVector=[] 32 index=0 33 for line in arrayOLines: 34 line=line.strip() 35 listFromLine=line.split(' ') 36 returnMat[index,:]=listFromLine[0:3] 37 classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1])) 38 index+=1 39 return returnMat,classLabelVector 40 41 def autoNorm(dataSet): 42 minVals=dataSet.min(0) 43 maxVals=dataSet.max(0) 44 ranges=maxVals-minVals 45 normDataSet=zeros(shape(dataSet)) 46 m=dataSet.shape[0] 47 normDataSet=dataSet-tile(minVals,(m,1)) 48 normDataSet=normDataSet/tile(ranges,(m,1)) 49 return normDataSet,ranges,minVals 50 51 def datingClassTest(): 52 hoRatio=0.10 53 datingDataMat,datingLabels=file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') 54 normMat,ranges,minVals=autoNorm(datingDataMat) 55 m=normMat.shape[0] 56 numTestVecs=int(m*hoRatio) 57 errorCount=0.0 58 for i in range(numTestVecs): 59 classifierResult=classifyO(normMat[i,:],normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],datingLabels[numTestVecs:m],3) 60 print "the classifier came back with:%d,the real answer is :%d" %(classifierResult,datingLabels[i]) 61 if(classifierResult !=datingLabels[i]):errorCount+=1.0 62 print "the total error rate is: %f"%(errorCount/float(numTestVecs)) 63 64 def classifyPerson(): 65 resultList=['not at all','in small doses','in large doses'] 66 percentTats=float(raw_input("percentage of time apent playing video games?")) 67 ffMiles=float(raw_input("frequent flier miles earned per year?")) 68 iceCream=float(raw_input("liters of ice cream consumed per year?")) 69 datingDataMat,datingLabels=file2matrix('datingTestSet2.txt') 70 normMat,ranges,minVals=autoNorm(datingDataMat) 71 inArr=array([ffMiles,percentTats,iceCream]) 72 classifierResult=classifyO((inArr-minVals)/ranges,normMat,datingLabels,3) 73 print "You will probably like this person:",resultList[classifierResult-1]
运行一下代码:
>>>import kNN >>> kNN.classifyPerson() percentage of time apent playing video games?10 frequent flier miles earned per year?10000 liters of ice cream consumed per year?0.5 You will probably like this person: in small doses
最后的错误率为0.05。