0 前言
上周的一个练习,由于没来得及编写笔记,这里补充一下~
虽然CSS3中提供了overflow:scroll; 来实现滚动条,但是这里可以使用原生JS来编写一个,以达到练习组件编写的效果。
练习要点包括以下几点:
-
-
鼠标点击事件
-
鼠标滑轮事件
-
滚动条显示比例设计逻辑
感兴趣的朋友欢迎点击屏幕左上角的小猫咪进入我的github,或猛戳这里下载源码~
1 需求分析
-
需要支持鼠标点击响应:点击上下箭头时,能上下滚动文章内容。
-
需要支持鼠标拖拽响应:拖拽滚动条并上下滚动文章内容。此外应支持拖拽过快的状况,即鼠标超出滚动条区域范围依然能够上下滚动。
-
边界限制:当滚动条到达范围的边界的时候,必须能够停止,不得超出屏幕显示范围。
-
对于不在显示区域的文字部分需要隐藏。
- 这里我们只关心其实现逻辑,而不关注其展现形式上的美化。
效果如下:
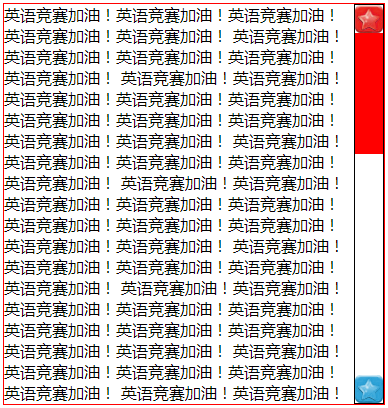
2 实现细节
2-1 HTML结构
结构上非常简单,两栏布局,内容文本区和滚动条区。
滚动条区采用ul-li结构实现,分别加载图片和使用一个div。
代码如下
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="UTF-8"> 5 <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> 6 <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> 7 <title>Scroll</title> 8 <link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css"> 9 </head> 10 <body> 11 <div class="container"> 12 <div class="content"> 13 区域文本内容。 14 </div> 15 <ul class="scroll"> 16 <li class="up"><img id="up_img" src="img/up.png" alt=""></li> 17 <li class="duration"><div class="bar"></div></li> 18 <li class="down"><img id="down_img" src="img/down.png" alt=""></li> 19 </ul> 20 </div> 21 <script src="index.js"></script> 22 </body> 23 </html>
2-2 CSS样式
几个要点:
-
在外层container上使用overflow:hidden隐藏超出区域范围的文本内容。
-
选择器的使用cursor:-webkit-grab;设置一个鼠标移入的形状控制。
- 若根据父子选择器的选择逻辑,则需要在父子标签之间添加空格,即表示选中子元素。
- 若不添加空格,则表示的是选中同一级标签,通过多个标签来缩小选中范围。
代码如下:
1 *{ 2 margin: 0; 3 padding: 0; 4 list-style: none; 5 } 6 body{ 7 overflow: hidden; 8 } 9 .container{ 10 width: 380px; 11 height: 400px; 12 margin: 100px auto; 13 border: 1px solid red; 14 position: relative; 15 overflow: hidden; 16 } 17 .container .content{ 18 width: 350px; 19 position: absolute; 20 left: 0; 21 top: 0; 22 } 23 .container .scroll{ 24 width: 28px; 25 height: 398px; 26 position: absolute; 27 border: 1px solid black; 28 right: 0; 29 top: 0; 30 } 31 .container .scroll li{ 32 width: 100%; 33 } 34 .container .scroll li.up{ 35 height: 28px; 36 cursor: pointer; 37 } 38 .container .scroll li.down{ 39 height: 28px; 40 cursor: pointer; 41 } 42 .container .scroll li img{ 43 height: 100%; 44 width: 100%; 45 } 46 .container .scroll li.duration{ 47 height: 342px; 48 width: 100%; 49 position: relative; 50 } 51 .container .scroll .duration .bar{ 52 position: absolute; 53 right: 0; 54 top: 0; 55 height: 27px; 56 width: 100%; 57 background-color: red; 58 cursor: -webkit-grab; 59 }
2-3 Javascript实现
2-3-1 模块调用入口
在html文档引入了JS代码以后,需要一个函数调用的入口,这里我采用的是以init()函数作为主入口。最外层是一个立即执行函数,保证这一组件内部的变量只可以被内部成员访问,避免变量污染的发生。
在入口函数init()中调用了三个函数,分别是控制拖拽的scrollDrage(ele_bar);控制点击事件的scrollClick(ele_bar);和控制滚轮事件的scrollWheel(ele_container , ele_bar);
(function(){ function init(){ scrollDrage(ele_bar); scrollClick(ele_bar); scrollWheel(ele_container , ele_bar); } init(); });
2-3-2 获取dom对象
由于需要对dom元素进行操作,因此首先需要先获取到与滚轮操作有关的对象:页面容器container、文本content、滚动条中间滑动部分duration、滑块bar
可以在初始时设置滑块bar的高度,这里采用相似变换的原理,计算其值并进行赋值即可。
滑块高度的计算公式为:
Math.floor((container.offsetHeight / content.offsetHeight) * duration.offsetHeight)
offsetHeight属性为获取还dom元素的height属性。
1 var ele_container = document.getElementsByClassName('container')[0]; 2 var ele_content = document.getElementsByClassName('content')[0]; 3 var ele_duration = document.getElementsByClassName('duration')[0]; 4 var ele_bar = document.getElementsByClassName('bar')[0]; 5 var percentH = Math.floor((ele_container.offsetHeight / ele_content.offsetHeight) * ele_duration.offsetHeight); 6 ele_bar.style.height = percentH + 'px
2-3-3 文本移动控制
文本移动控制的方法同样用到了相似变换的原理,并根据计算的高度,修改文本context的top值。
传入的参数为滑块bar对象,在鼠标事件中调用该方法。
注意:由于向下查看内容时,文本是向上移动的,因此这个top值需要设置为负值。
1 function contentMove(item){ 2 var percentHeight = item.offsetTop / (ele_duration.offsetHeight - item.offsetHeight); 3 var moveH = percentHeight * Math.floor(ele_content.offsetHeight - ele_container.offsetHeight); 4 ele_content.style.top = -moveH + 'px'; 5 }
2-3-4 鼠标拖拽事件
在这一部分有以下几点注意:
-
e = e||window.event 一般在获取事件对象e的时候要如此给一个初值,大体上是为了给firefox做一个兼容,细节上的讨论可以参考这篇文章。
-
e.preventDefault()这里是为了阻止事件的默认动作,比如提交表单等。
-
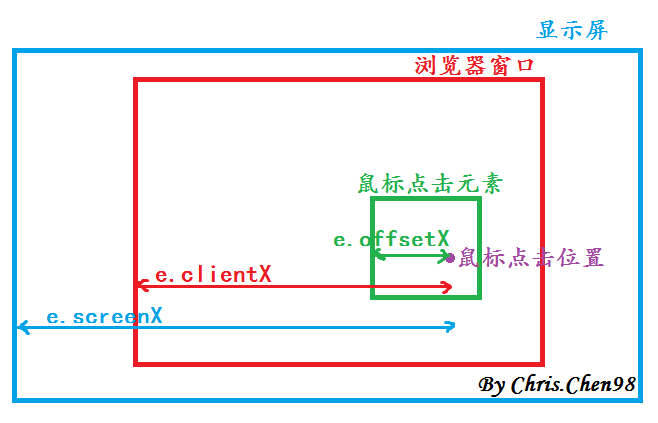
通过e.pageY来获取点击位置的y坐标。关于使用事件对象e来获取点击位置坐标的方法有screen,offset,page和client四种。
-
event.clientX、event.clientY
鼠标相对于浏览器窗口可视区域的X,Y坐标(窗口坐标),可视区域不包括工具栏和滚动条。IE事件和标准事件都定义了这2个属性
-
event.pageX、event.pageY
类似于event.clientX、event.clientY,但它们使用的是文档坐标而非窗口坐标。这2个属性不是标准属性,但得到了广泛支持。IE事件中没有这2个属性
-
event.offsetX、event.offsetY
鼠标相对于事件源元素(srcElement)的X,Y坐标,只有IE事件有这2个属性,标准事件没有对应的属性
-
event.screenX、event.screenY
鼠标相对于用户显示器屏幕左上角的X,Y坐标。标准事件和IE事件都定义了这2个属性
-
用一张图可以表示成下图所示
-
-
鼠标事件绑定的对象:需要确定鼠标事件的作用范围,因此必须明确鼠标事件所绑定的对象。对于mousedown事件,就需要绑定到bar滑块对象上;而mousemove和mouseup事件,则需要绑定在document对象上(即整个窗口)。这是为了避免鼠标移动过快,而导致鼠标移出滑块区域导致鼠标事件响应失效。
-
解除绑定:当mouseup时,需要解除mousemove的绑定,只需为mousemove赋值为null即可。
-
获取当前对象相对其父元素的top值:offsetTop,进而根据此值,来更新鼠标拖拽的滑块位置。
1 function scrollDrage(item){ 2 item.onmousedown = function(e){ 3 e = e || window.event; 4 e.preventDefault(); 5 var e_y = e.pageY; 6 document.onmousemove = function(e){ 7 var chay = e.pageY - e_y; 8 item.style.top = item.offsetTop + chay + 'px'; 9 e_y = e.pageY; 10 11 if(item.offsetTop <= 0){ 12 item.style.top = 0 + 'px'; 13 } 14 else if(item.offsetTop + item.offsetHeight >= ele_duration.offsetHeight){ 15 item.style.top = ele_duration.offsetHeight - item.offsetHeight + 'px'; 16 } 17 contentMove(item); 18 } 19 } 20 document.onmouseup = function(){ 21 document.onmousemove = null; 22 } 23 }
2-3-5 鼠标点击上下箭头移动事件
这里的要点有:
- e.target:
- target定义:
target 事件属性可返回事件的目标节点(触发该事件的节点),如生成事件的元素、文档或窗口。
-
- 语法:
event.target
event.target.nodeName //获取事件触发元素标签name(li,p...)
event.target.id //获取事件触发元素id
event.target.className //获取事件触发元素classname
event.target.innerHTML //获取事件触发元素的内容(li)
等等。
-
- 这里我用e.target.id来判断是上翻还是下翻页面。
- 边界判断:
这里仍要进行边界判断,比如offsetTop <= 0的情况和bar.offsetTop + bar.offsetHeight >= scroll.offsetHeight的情况需要直接赋予边界值,保证滑块不会从临界值超出范围。
1 function scrollClick(item){ 2 var ele_scroll = document.getElementsByClassName('scroll')[0]; 3 var speed = 5; 4 ele_scroll.onclick = function(e){ 5 // console.log(e.target.id); 6 if(e.target.id == 'up_img'){ 7 item.style.top = item.offsetTop - speed + 'px'; 8 if(item.offsetTop <= 0){ 9 item.style.top = 0 + 'px'; 10 } 11 } 12 else if(e.target.id == 'down_img'){ 13 item.style.top = item.offsetTop + speed + 'px'; 14 if(item.offsetTop + item.offsetHeight >= ele_duration.offsetHeight){ 15 item.style.top = ele_duration.offsetHeight - item.offsetHeight + 'px'; 16 } 17 } 18 contentMove(item); 19 } 20 }
2-3-6 鼠标滚轮控制
-
通过onmousewheel绑定滚轮事件,e.wheelDelta表示滚轮方向,为正向上,负向下。
-
同样要施加一个边界判断。其他流程与2-3-5完全类似。
1 function scrollWheel(container , item){ 2 var speed = 5; 3 container.onmousewheel = function(e){ 4 // console.log(e.wheelDelta); //上下滑动滑轮 5 if(e.wheelDelta > 0){ //向上滑动滑轮 6 item.style.top = item.offsetTop - speed + 'px'; 7 if(item.offsetTop <= 0){ 8 item.style.top = 0 + 'px'; 9 } 10 } 11 else{ 12 item.style.top = item.offsetTop + speed + 'px'; 13 if(item.offsetTop + item.offsetHeight >= ele_duration.offsetHeight){ 14 item.style.top = ele_duration.offsetHeight - item.offsetHeight + 'px'; 15 } 16 } 17 contentMove(item); 18 } 19 }
3 总结
通过练习基础组件的写法,达到基础巩固的目的。但还是不要忘记使用overflow:scroll;这种自动实现滚动条的方法。