CSharpGL(39)GLSL光照示例:鼠标拖动太阳(光源)观察平行光的漫反射和镜面反射效果
开始
一图抵千言。首先来看鼠标拖动太阳(光源)的情形。

然后是鼠标拖拽旋转模型的情形。
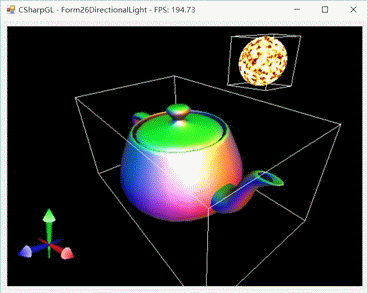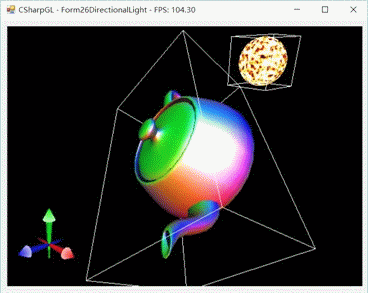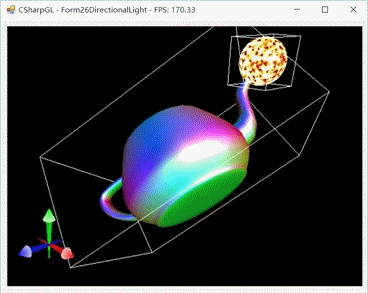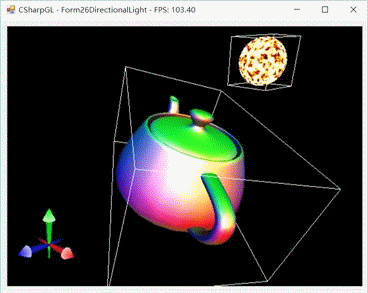
然后我们移动摄像机来从不同的角度看看。

现在太阳(光源)跑到比较远的位置去了,我们再移动它试试看。

本文就介绍平行光下是如何实现漫反射和镜面反射的。
本文shader核心部分来自红宝书第八版。
光照
只需记住一点,用GLSL实现光照效果时,都是根据顶点的位置、法线方向、光源位置(方向)、摄像机位置等等这些数据,根据物理学的反射规则计算出来的。当然,为了兼顾效果和效率,可能会对物理规则做一些简化处理。
Vertex shader
先看vertex shader。除了传递顶点的位置、颜色外,这里新增了传递法线(normal)的代码。顶点的变换可以通过mvp矩阵完成,而法线的变换则有所不同(说来话长,这里不要深究),所以单独提供一个normalMatrix供法线使用。
1 #version 330 core 2 3 uniform mat4 mvpMatrix; 4 uniform mat3 normalMatrix;// normal matrix is transpose(inverse(model matrix)) 5 6 in vec3 inPosition; 7 in vec3 inColor; 8 in vec3 inNormal; 9 10 out vec3 passNormal; 11 out vec3 passColor; 12 13 void main() 14 { 15 passNormal = normalize(normalMatrix * inNormal); 16 passColor = inColor; 17 gl_Position = mvpMatrix * vec4(inPosition, 1.0); 18 }
Fragment shader
这里是计算光照的地方。详情见注释。
1 #version 330 core 2 3 uniform vec3 ambientLight;// 环境光 4 uniform vec3 directionalLightColor; 5 uniform vec3 directionalLightDirection; 6 uniform vec3 halfVector; 7 uniform float shininess; 8 uniform float strength; 9 10 in vec3 passNormal; 11 in vec3 passColor; 12 13 out vec4 outColor; 14 15 void main() 16 { 17 // 根据光源方向与法线方向的夹角计算此处的漫反射的强度 18 float diffuse = max(0.0, dot(passNormal, directionalLightDirection)); 19 // 计算此处的镜面反射的强度 20 float specular = max(0.0, dot(passNormal, halfVector)); 21 22 if (diffuse == 0.0) { specular = 0.0; }// 若光源没有照射到此处,自然也不应该有镜面反射效果 23 else { specular = pow(specular, shininess); }// 指数式的剧烈变化,就是产生镜面高光的原理 24 25 vec3 scatteredLight = ambientLight + directionalLightColor * diffuse;// 漫反射光+环境光 26 vec3 reflectedLight = directionalLightColor * specular * strength;// 镜面反射光 27 28 vec3 rgb = min(passColor * scatteredLight + reflectedLight, vec3(1.0));// 最后的颜色 29 outColor = vec4(rgb, 1.0);// 搞定 30 }
渲染器
shader做好了,下面写一个渲染器。关于渲染器的详细介绍可参看(CSharpGL(34)以从零编写一个KleinBottle渲染器为例学习如何使用CSharpGL)由于制作光照效果需要模型自带法线值,而我手里的模型只有这个Teapot是有法线值的,又仅仅是个例子,就写死了用Teapot了。

1 class DirectonalLightRenderer : PickableRenderer 2 { 3 public vec3 AmbientLightColor { get; set; } 4 public vec3 DirectionalLightDirection { get; set; } 5 public vec3 DirectionalLightColor { get; set; } 6 //public vec3 HalfVector { get; set; } 7 public float Shininess { get; set; } 8 public float Strength { get; set; } 9 10 public static DirectonalLightRenderer Create() 11 { 12 var model = new Teapot(); 13 var shaderCodes = new ShaderCode[2]; 14 shaderCodes[0] = new ShaderCode(File.ReadAllText(@"shadersDirectionalLight.vert"), ShaderType.VertexShader); 15 shaderCodes[1] = new ShaderCode(File.ReadAllText(@"shadersDirectionalLight.frag"), ShaderType.FragmentShader); 16 var map = new AttributeMap(); 17 map.Add("inPosition", Teapot.strPosition); 18 map.Add("inColor", Teapot.strColor); 19 map.Add("inNormal", Teapot.strNormal); 20 21 var renderer = new DirectonalLightRenderer(model, shaderCodes, map, Teapot.strPosition); 22 renderer.ModelSize = model.Size; 23 return renderer; 24 } 25 26 private DirectonalLightRenderer(IBufferable model, ShaderCode[] shaderCodes, 27 AttributeMap attributeMap, string positionNameInIBufferable, 28 params GLState[] switches) 29 : base(model, shaderCodes, attributeMap, positionNameInIBufferable, switches) 30 { 31 this.AmbientLightColor = new vec3(0.2f); 32 this.DirectionalLightDirection = new vec3(1); 33 this.DirectionalLightColor = new vec3(1); 34 //this.HalfVector = new vec3(1); 35 this.Shininess = 10.0f; 36 this.Strength = 1.0f; 37 } 38 39 protected override void DoRender(RenderEventArgs arg) 40 { 41 this.SetUniform("ambientLight", this.AmbientLightColor); 42 this.SetUniform("directionalLightColor", this.DirectionalLightColor); 43 this.SetUniform("directionalLightDirection", this.DirectionalLightDirection.normalize()); 44 this.SetUniform("halfVector", this.DirectionalLightDirection.normalize()); 45 //this.SetUniform("halfVector", this.HalfVector.normalize()); 46 this.SetUniform("shininess", this.Shininess); 47 this.SetUniform("strength", this.Strength); 48 49 mat4 projection = arg.Camera.GetProjectionMatrix(); 50 mat4 view = arg.Camera.GetViewMatrix(); 51 mat4 model = this.GetModelMatrix().Value; 52 this.SetUniform("mvpMatrix", projection * view * model); 53 this.SetUniform("normalMatrix", glm.transpose(glm.inverse(model)).to_mat3()); 54 55 base.DoRender(arg); 56 } 57 }
这样其实就可以看到效果了,还可以通过属性面板控制光源的参数。
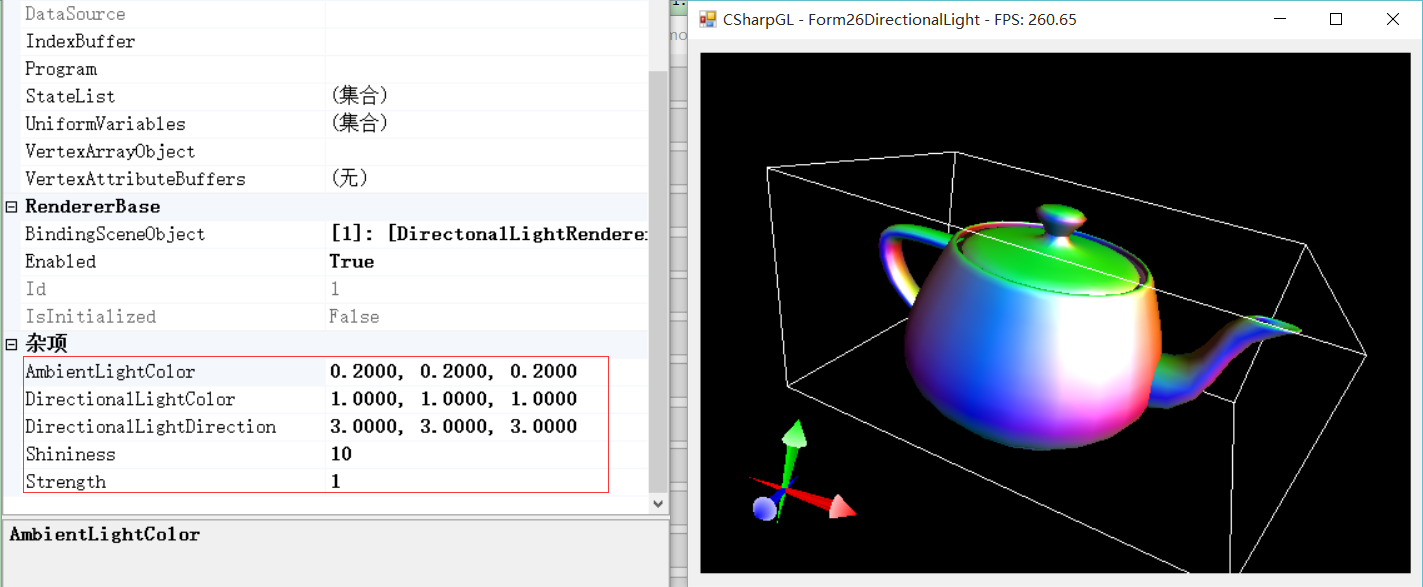
但是手动输入数值很不爽啊,没有一点点随心所欲的顺畅。于是后续的折腾就开始了。让我来画一个真正的太阳,然后通过鼠标拖动太阳,实时更新光源的位置(方向),看到本文开始的效果。
太阳(光源)
画太阳
其实太阳模型早就做过了,本质上就是利用一个noise方法模拟太阳表面的活动。外围辐射效果什么的,我先拉倒吧。
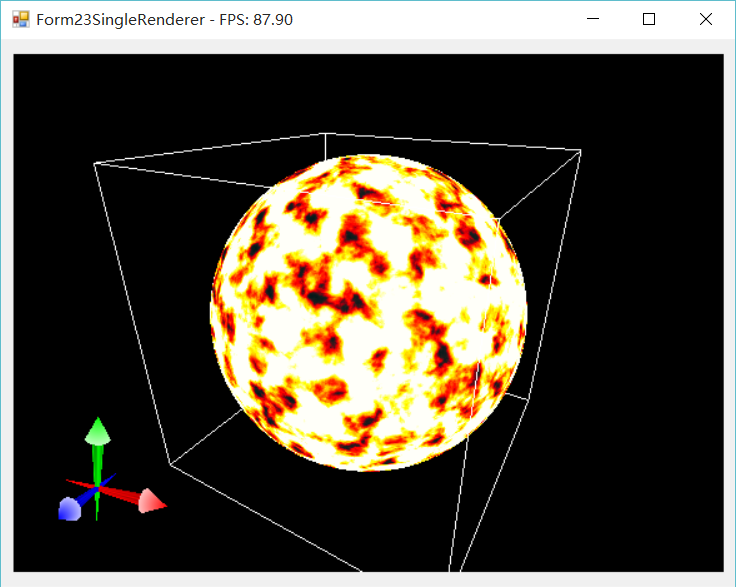
拖动太阳
把太阳放在那里很容易,如何用鼠标移动呢?
原理在(CSharpGL(20)用unProject和Project实现鼠标拖拽图元)已经整理出来了。只不过当时是单独修改模型内部的顶点位置,而现在需要整体移动模型,即修改模型的(RendererBase.WorldPosition)属性。
我的思路如下:假设有一个点在原点position = new vec3(0,0,0),我们像之前一样计算它在平移之后的位置newPosition,这是模型本身的变化,然后只需分别通过RendererBase.GetModelMatrix()的变换,就变成了在World Space里的变化,这个差别就是模型的位移。代码如下。
1 void IMouseHandler.canvas_MouseMove(object sender, MouseEventArgs e) 2 { 3 if (mouseDownFlag && ((e.Button & this.lastBindingMouseButtons) != MouseButtons.None)) 4 { 5 Point location = new Point(e.X, this.canvas.ClientRectangle.Height - e.Y - 1); 6 Point differenceOnScreen = new Point(location.X - this._lastPosition.X, location.Y - this._lastPosition.Y); 7 mat4 model = this.renderer.GetModelMatrix().Value; 8 mat4 view = this.camera.GetViewMatrix(); 9 mat4 projection = this.camera.GetProjectionMatrix(); 10 vec4 viewport; 11 { 12 int[] result = OpenGL.GetViewport(); 13 viewport = new vec4(result[0], result[1], result[2], result[3]); 14 } 15 var position = new vec3(0.0f);// imangine we have a point at (0, 0, 0). 16 vec3 windowPos = glm.project(position, view * model, projection, viewport); 17 var newWindowPos = new vec3(windowPos.x + differenceOnScreen.X, windowPos.y + differenceOnScreen.Y, windowPos.z); 18 vec3 newPosition = glm.unProject(newWindowPos, view * model, projection, viewport); 19 var worldPosition = new vec3(model * new vec4(position, 1.0f)); 20 var newWorldPosition = new vec3(model * new vec4(newPosition, 1.0f)); 21 this.renderer.WorldPosition += newWorldPosition - worldPosition; 22 23 this._lastPosition = location; 24 } 25 }
这样说似乎也不能彻底解释清楚,因为还需要先理解OpenGL里坐标变换的问题,这个问题可以参看(CSharpGL(27)讲讲清楚OpenGL坐标变换)
总结
整完收工。
