什么是委托?委托和事件是什么关系?
我的理解是委托朋友,事件是一个事情比如,中午12点要吃饭了,咱家搞忘了!还在继续嗨皮,我的朋友会叫我与他一起吃饭。
什么事反射?
可以获取.Net中的每个类型(类,结构,委托,结构,和枚举)包含所有,有了反射,可对每一个类型了如指掌
C#中的多个类基础?如何实现多重继承,如何派生?
C#中是没有类的多重继承这个概念.c#中类继承值能是一个,即子类派生于父类。
C#要使用多重继承必须要通过接口Interface来完成。
C#如果要实现派生,一种是隐藏基类,一种是使用abstract,还有一种是virtual。
什么是密封类?
就是不让这个类被继承
using 关键字的几种用途?
#waring和#error分别的用途是什么?
Asp.Net web应用程序和Asp.NET网站的区别是什么?
什么事委托?
咱家:在c/c++中使用过函数指针和类成员函数指针,所谓的函数指针和类成员函数指针,都是声明一种与函数指针或者类成员函数参数相同将其的名称挖掉,在用这个声明去接受这个这个函数,或者类成员函数,这个这个声明就存储了他的地址,就可以通过这个声明从而来操作这个函数;
为了方便识别咱家用c举了一个例子:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int cheng(int a, int b)
{
return a*b;
}
int chu(int a, int b)
{
return a / b;
}
void main()
{
int(*p)(int a, int b) = cheng;//存储函数指针的地址
printf("%d", p(15, 3));
system("pause");
}
我使用的编译工具是code::blocks,是纯c的编译环境
或许有些同志想说明明c#你玩什么C?
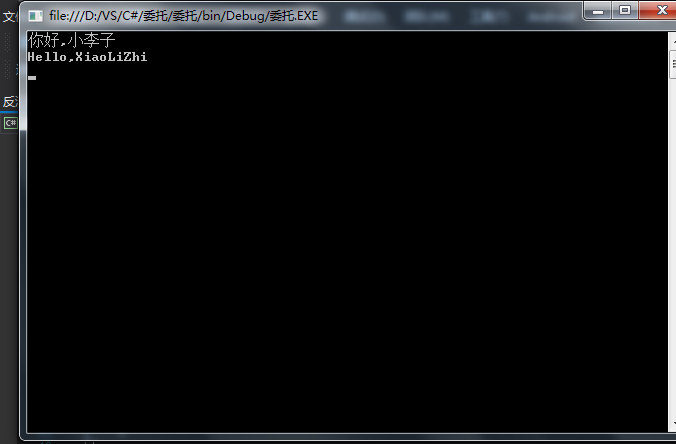
一、我只想说在我的理解中c#的委托像操作变量一样来操作函数,所以与c的相识,下面我们进入“正题”定义一个委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托
{
//声明委托类型
public delegate void SayDelegate(string name); //定义一个函数类型的委托
class ClassPeople
{
public void SayA(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("你好,{0}",name);
}
public void SayB(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}",name);
}
//注意此方法,他接受一个SayDelegate类型的方法做为参数
public void DoWork(string name,SayDelegate MakeSay)
{
MakeSay(name); //通过这个变量来操作函数
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ClassPeople p = new ClassPeople();
p.DoWork("小李子", p.A);
p.DoWork("XiaoLiZhi", p.B);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
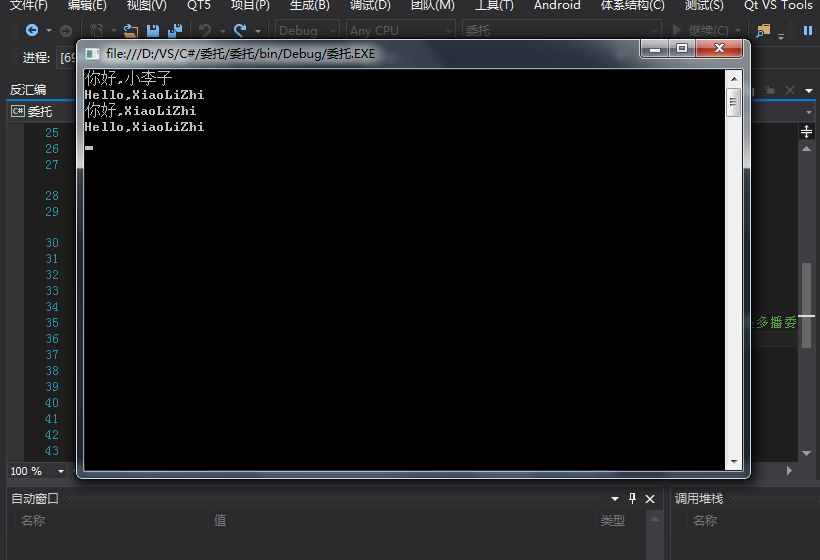
多播委托可以将多个相同的函数类型的赋值给一个委托,或者将多个方法帮定到一个委托,这就是多播委托
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托
{
//声明委托类型
public delegate void SayDelegate(string name);
class ClassPeople
{
public void A(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("你好,{0}",name);
}
public void B(string name)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}",name);
}
//注意此方法,他接受一个SayDelegate类型的方法做为参数
public void DoWork(string name,SayDelegate MakeSay)
{
MakeSay(name);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ClassPeople p = new ClassPeople();
p.DoWork("小李子", p.A);
p.DoWork("XiaoLiZhi", p.B);
//多播委托可以将多个相同类型的赋值给一个委托,或者将多个方法帮定到一个委托,这就是多播委托
SayDelegate delegate1 = p.A;
delegate1 += p.B; //将多个相同类型赋值到一个委托中
p.DoWork("XiaoLiZhi",delegate1);
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}
二、委托和事件
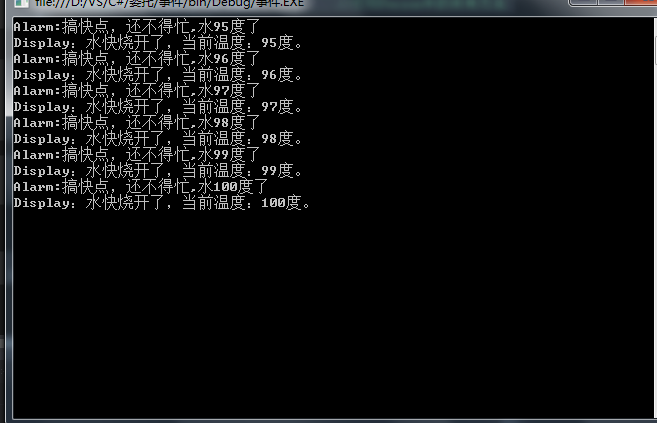
下面我将使用烧水的事件和委托来为同志们演示哈,书上的我高级太高端了,也太复杂了,我也看个半懂,我使用’循环来判断是否触发这个事件‘循环要比快定时器简单些,如果是定时器我又要看哈书懒得看。应该要详细演示,所以使用了多个事件,一个警告的,一个提示开了的。
event <委托类型> 事件名
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 事件
{
class Program
{
//烧水类
class Heater
{
private int temperature; //传递温度
public delegate void BoilHeater(int arg); //声明委托
public event BoilHeater BoilEvent; //声明事件
//烧水的
public void BoliWater()
{
for(int i=0;i<=100;i++)
{
temperature = i;
if (temperature >= 95)
{
if (BoilEvent != null) //如果没有对象注册
{
BoilEvent(temperature); //触发事件调用委托
}
}
}
}
}
//超过95度后报警
public class Alarm
{
public static void MakeAlert(int arg)
{
Console.WriteLine("Alarm:搞快点,还不得忙,水{0}度了", arg);
}
}
//显示的
public class Show
{
public void ShowMsg(int arg) //使用了静态的
{
Console.WriteLine("Display:水快烧开了,当前温度:{0}度。", arg);
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Heater headter = new Heater();
headter.BoilEvent += Alarm.MakeAlert; //将烧水的加入事件
headter.BoilEvent += (new Show()).ShowMsg; //应为没有使用static所以需要new对象,不这儿new可以在外面new了一样的,我比较懒你懂的
//事件添加好了,启动烧水的了
headter.BoliWater(); //启动烧水的
Console.Read();
}
}
}
三 、反射
下面的话是咱家抄的书上的
反射(Reflection)是,NET中的重要机制,通过反射,可以对运行时获的.NET中的每一个类型(包括类,结构,委托,接口,和枚举等)的成员,包括方法,属性,事件,已经构造函数等,还可以获得每个成员的名称,限定符和参数等,有了反射,即可对每个类型了了如指掌,只要获得了构造函数的信息,即可直接创建对象,即使对这个对象的类型在编译时还不知道,咱家抄袭的话是不是感觉很牛逼,好像网上同志的解释:是简单的说反射是为了动态地运行时加载,而静态代码是在编译时就确定好了。也就是说当你的程序需要在运行时再做一些晚绑定,动态加载或检查对象等操作时,你就需要用到反射啦,不过我感觉w某某好像没说过也,我估计怕是遇到了个假的w某某,开玩笑的,估计是他老人家忘了。
下面进入正题Assembly.Load
Assembly.LoadFile
Assembly.LoadFrom
Type对象的Assembly方法
MemberInfo-成员
ConstructorInfo-结构
FieldInfo-字段
MethodInfo-方法
PropertyInfo-属性
EventInfo-事件
第一个要生成类库,所以必须的使用”类库“创建程序生成 ”反射类库.dll“把dll引用到第二个程序中实现反射
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 反射类库
{
class Person
{
public Person() //空的构造
{
}
public Person(string name) //有参的构造
{
this.name = name;
}
private string name;
public string Name //将字段可以传出或者设置
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public void SayHello()
{
if (name == null)
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello World!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}", name);
}
}
}
}
实现反射
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 反射
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//我们可以通过Assembly的信息来获取程序的类,实例等编程需要用到的信息
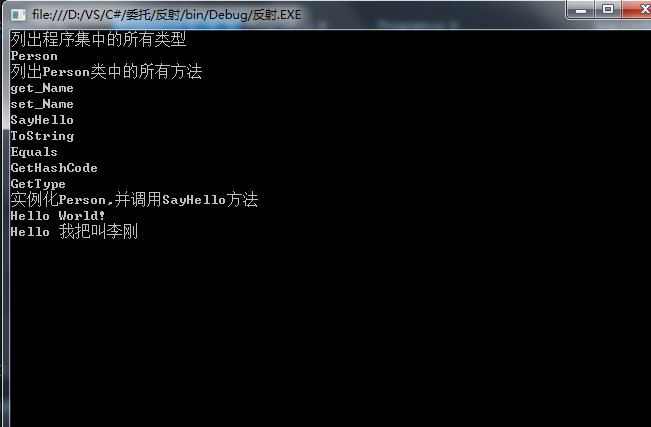
Console.WriteLine("列出程序集中的所有类型");
Assembly ass = Assembly.LoadFrom("反射类库.dll");
//c#中通过Type类可以访问任意数据类型信息
Type Person = null;
Type[] mytypes = ass.GetTypes();
foreach (Type item in mytypes)
{
Console.WriteLine(item.Name);
if(item.Name=="Person") //如果名称与Person
{
Person = item; //将反”射类库中.dll“中的Person赋值当当前的Person
}
}
Console.WriteLine("列出Person类中的所有方法");
//MeberInfo获取成员属性信息,并对成员提供访问
//GetMethods返回当前所有的public方法
MemberInfo[] mif = Person.GetMethods();
foreach (MemberInfo item in mif)
{
Console.WriteLine(item.Name); //打印Person中的所有方法
}
Console.WriteLine("实例化Person,并调用SayHello方法");
//Activator在远程或本地创建实例
//CreateInstance 使用指定类型默认构造
object obj = Activator.CreateInstance(Person); //没有传参的构造
object objName = Activator.CreateInstance(Person, "我把叫李刚");//有传参的构造
MethodInfo MsSayHello = Person.GetMethod("SayHello");
MsSayHello.Invoke(obj, null); //空的实例传参数
MsSayHello.Invoke(objName, null); //带参数构造实例
Console.Read();
}
}
}
结果如下
四、多继承
请允许我偷哈懒扣了2张图

下面实现一个派生类的接口继承
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 派生类的接口继承
{
class Program
{
interface IFace
{
void Say();
void Hello();
}
//派生类继承接口 接口可以被多次继承
class FacetoFace : IFace
{
public void Say()
{
Console.WriteLine("这是继承IFace的Say方法");
}
public void Hello()
{
Console.WriteLine("IFace Hello World!");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
FacetoFace facetoface = new FacetoFace();
facetoface.Say();
facetoface.Hello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}

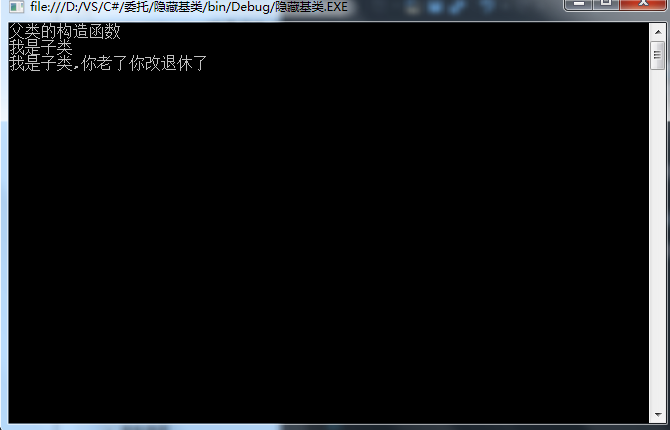
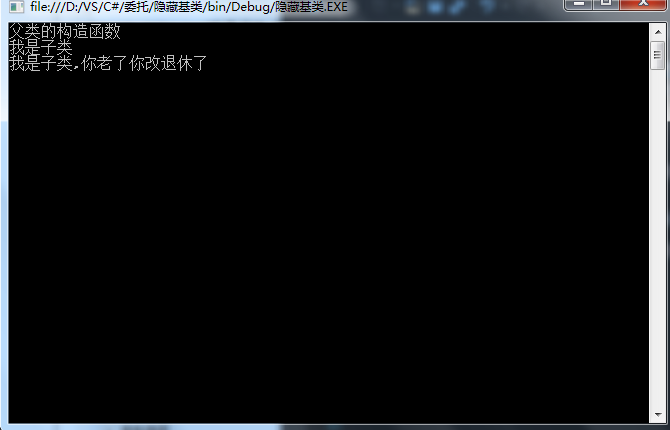
五、隐藏基类
有的时候同一个功能需要重新在派生类中实现新的逻辑,而不想用基类的方法
即隐藏掉父类的成员方法,c#使用new修改师傅来实现隐藏基类成员
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 隐藏基类
{
public class Parent
{
public Parent()
{
Console.WriteLine("父类的构造函数");
}
public void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是父类");
}
}
public class Child:Parent
{
public Child()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是子类");
}
public new void SayHello() //添加了new
{
Console.WriteLine("我是子类,你老了你改退休了");
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Child child = new Child();
child.SayHello();
Console.Read();
}
}
}
六、使用abstract多态
//c#中通过把类或者方法声明位abstract来实现抽象类和抽象方法,抽象类不能实例化,
//抽象方法没有具体执行代码,必须在非抽象的派生类中重写
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace abstract派生类
{
class Program
{
public abstract class Parent
{
public Parent()
{
Console.WriteLine("父类的构造函数");
}
abstract public void SayHello();
}
public class Child : Parent
{
public Child()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是子类");
}
public override void SayHello()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是子类,你老了你改退休了");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Child child = new Child();
child.SayHello();
}
}
}
七、使用virtual派生对象
//如果不想把类声明位抽象类,单有想实现方法在基中不具体实现,而是在派生类中重新实现功能,该怎么办呢?
//可以通过把方法声明位虚函数virtual的形式来实现方法的重写,可以不重写调用virtual的方法
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 使用virtual多态
{
public class Parent
{
public Parent()
{
Console.WriteLine("父类的构造函数");
}
public virtual void SayHello1()
{
}
public virtual void SayHello2(string name)
{
//虚函数必须方法主题,抽象方法可以不需要
//打起 "{}"表示声明了也可以不写也可以写
//我这儿还是写了
Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}!", name);
}
}
public class Child : Parent
{
public Child()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是子类");
}
public override void SayHello1() //实现了多态重写了接口
{
Console.WriteLine("我是子类,你老了你改退休了");
}
public void Hello() //这儿实现了调用虚方法
{
SayHello2("张三");
}
}
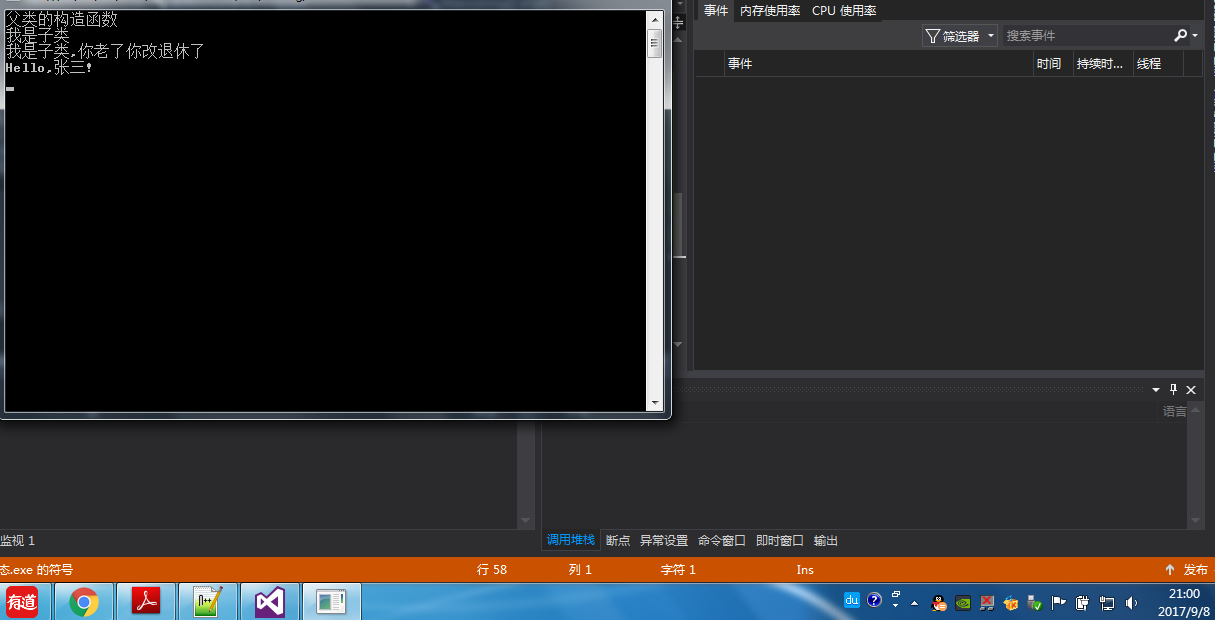
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Child child = new Child();
child.SayHello1();
child.Hello();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
八、密封类
//如果所有的类都可以被继承,那么继承的泛滥,类的层次结构体系
//变得非常庞大,大类之间的关系杂乱无章,对类的理解和使用都会变得困难
//所以提供了密封类的概念(sealed class)的改了,帮助开发人员来解决这一问题。
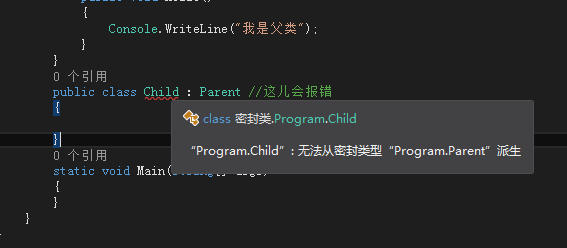
//使用sealed修饰符,这个可以放在该类被其他类继承,如果继承那么久会报错
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 密封类
{
class Program
{
sealed class Parent
{
public Parent()
{
Console.WriteLine("父类构造函数");
}
public void Hello()
{
Console.WriteLine("我是父类");
}
}
//public class Child:Parent //这儿会报错
//{
//}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
}
}
}
九、using 关键字的几种用途?
一共有3种
第一种:using 命名空间的名字; 引用命名空间
例如:using System;
第二种:using别名


第三种:释放资源

十、#waring和#error分别的用途是什么?

十一、Asp.Net web应用程序和Asp.NET网站的区别是什么?

咱家后面偷懒了,所以你懂的,这是我第三次写”博客“,如果有问题,”请指教“
如果想骂我