********2019-2020-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》第九周学习总结
教材学习内容总结
-
树的特点:
- 每个结点有零个或多个子结点;没有父结点的结点称为根结点;每一个非根结点有且只有一个父结点;除了根结点外,每个子结点可以分为多个不相交的子树
-
二叉树的前序、中序、后序、层序遍历(非递归方法):
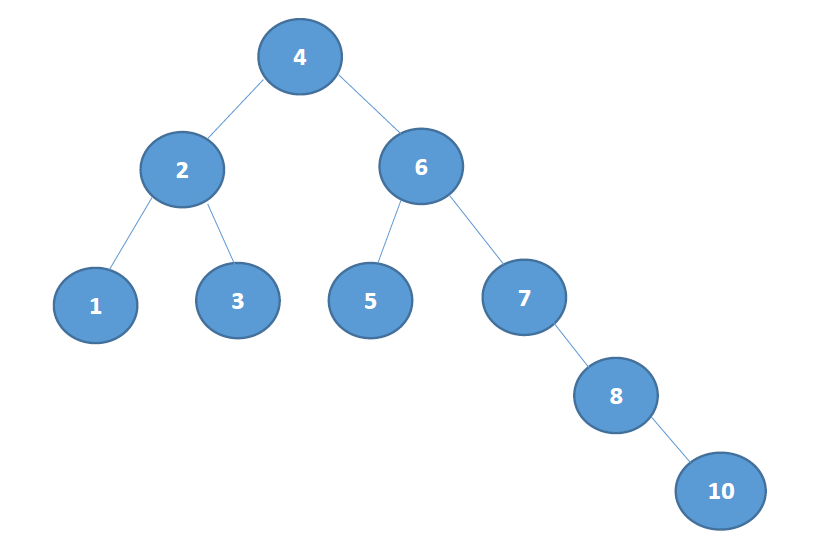
-
前序遍历:4 2 1 3 6 5 7 8 10
-
中序遍历:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10
-
后序遍历:1 3 2 5 10 8 7 6 4
-
层序遍历:4 2 6 1 3 5 7 8 10
前序遍历:
public void preOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
if (Node != null)
{
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
preOrder(Node.left);
preOrder(Node.right);
}
}
中序遍历:
public void midOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
if (Node != null)
{
midOrder(Node.left);
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
midOrder(Node.right);
}
}
后序遍历:
public void posOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
if (Node != null)
{
posOrder(Node.left);
posOrder(Node.right);
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
}
}
层序遍历(递归):
public void levelOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node) {
if (Node == null) {
return;
}
int depth = depth(Node);
for (int i = 1; i <= depth; i++) {
levelOrder(Node, i);
}
}
private void levelOrder(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node, int level) {
if (Node == null || level < 1) {
return;
}
if (level == 1) {
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
return;
}
// 左子树
levelOrder(Node.left, level - 1);
// 右子树
levelOrder(Node.right, level - 1);
}
public int depth(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node) {
if (Node == null) {
return 0;
}
int l = depth(Node.left);
int r = depth(Node.right);
if (l > r) {
return l + 1;
} else {
return r + 1;
}
}
前序遍历(非递归):
public void preOrder1(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node)
{
Stack<BinaryNode> stack = new Stack<>();
while(Node != null || !stack.empty())
{
while(Node != null)
{
System.out.print(Node.element + " ");
stack.push(Node);
Node = Node.left;
}
if(!stack.empty())
{
Node = stack.pop();
Node = Node.right;
}
}
}
层序遍历(非递归):
public void levelOrder1(BinaryNode<AnyType> Node) {
if (Node == null) {
return;
}
BinaryNode<AnyType> binaryNode;
Queue<BinaryNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(Node);
while (queue.size() != 0) {
binaryNode = queue.poll();
System.out.print(binaryNode.element + " ");
if (binaryNode.left != null) {
queue.offer(binaryNode.left);
}
if (binaryNode.right != null) {
queue.offer(binaryNode.right);
}
}
}
- 二叉树的重要性质:
- 在二叉树的第i层上最多有2 i-1 个节点
- 二叉树中如果深度为k,那么最多有2k-1个节点。(k>=1)
- n0=n2+1 n0表示度数为0的节点 n2表示度数为2的节点
- 在完全二叉树中,具有n个节点的完全二叉树的深度为[log2n]+1,其中[log2n]+1是向下取整。
- 若对含 n 个结点的完全二叉树从上到下且从左至右进行 1 至 n 的编号,则对完全二叉树中任意一个编号为 i 的结点:
- (1) 若 i=1,则该结点是二叉树的根,无双亲, 否则,编号为 [i/2] 的结点为其双亲结点;
- (2) 若 2i>n,则该结点无左孩子, 否则,编号为 2i 的结点为其左孩子结点;
- (3) 若 2i+1>n,则该结点无右孩子结点, 否则,编号为2i+1 的结点为其右孩子结点。
教材学习中的问题和解决过程
代码调试中的问题和解决过程
代码托管A
代码托管B
代码托管C
代码托管D
代码托管E
上周考试错题总结
1.In an ideal implementations of a stack and a queue, all operations are ______________________ .
A . O(1)
B . O(n)
C . O(n log n)
D . O(n2)
E . it depends on the operation
答案:B。在堆栈和队列的良好实现中,所有操作都需要固定的时间。
2.If a binary search tree is not __________, it may be less efficient than a linear structure.
A . complete
B . empty
C . balanced
D . None of the above
答案:C。如果二叉搜索树不平衡,它的效率可能低于线性结构。
3.It is possible to implement a stack and a queue in such a way that all operations take a constant amount of time.
A .true
B .false
答案: A
解析: 理想情况。
4.In a circular array-based implementation of a queue, the elements must all be shifted when the dequeue operation is called.
A .true
B .false
答案: B
解析:基于循环数组的队列实现无需移动元素。
结对及互评
点评
- 博客中值得学习的:
- 教材学习内容概括行强,简介明了。
- 有自己动手打新代码,加入了很多个人的理解。
- 内容很充实,很用心,比上次进步了很多。
- 博客格式正确,运用了很多不同的方法,排版精美。
- 希望能在课本内容总结以及问题&解决过程中加入自己的思考,使博客内容更加充实。
基于评分标准,我给本博客打分12分:
得分情况如下:
正确使用Markdown语法(加1分)
模板中的要素齐全(加1分)
教材学习中的问题和解决过程(加2分)
代码调试中的问题和解决过程(加2分)
其他加分(加6分)
进度条中记录学习时间与改进情况(1)
感想,体会不假大空(1)
有动手写新代码(1)
错题学习深入(1)
点评认真,能指出博客和代码中的问题(1)
结对学习情况真实可信(1)
点评过的同学博客和代码
- 本周结对学习情况:
- [20182316]
其他(感悟、思考等,可选)
我们遇到什么困难,也不要怕,微笑着面对他,消除恐惧的最好办法就是面对恐惧,坚持,才是胜利,加油,奥里给!!
参考资料
| 代码行数(新增/累积) | 博客量(新增/累积)|学习时间(新增/累积)|重要成长
---|---|---|---|---
目标 | 10000行 | 30篇 | 400小时 |
第一周 | 138/138 | 2/2 | 23/23 | 减少了鼠标的使用次数
第二周 | 749/887 | 1/4 | 25/48 |
第三周 | 765/1652 | 1/4 | 25/48 |
第四周 | 694/2346 | 1/6 | 20/87 |学会了类
第五周 | 1659/4005 | 1/8 | 21/108 |
第六周 | 531/4536 | 1/10 | 23/128 |
第七周 | 1523/6059 | 1/10 | 38/166 |
第八周 | 1736/7795 | 1/11 | 29/195 |
第九周 | 2866/10661 | 6/17 | 25/220 |