1.本节重点知识点用自己的话总结出来,可以配上图片,以及说明该知识点的重要性
1) 回归算法:

2) 线性回归:
(1)老师举了线性回归的应用:
①房价预测;
②销售额预测;
③贷款额度预测;

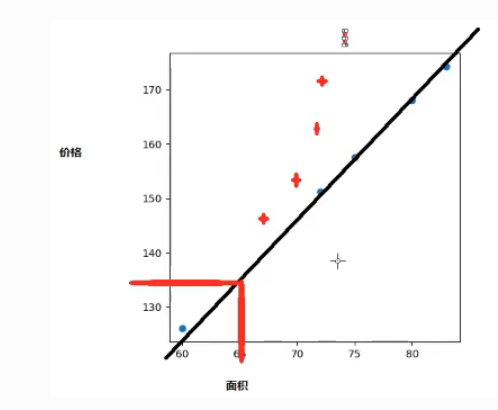
(2)在这个图中,线性回归的数据应该是连续型的,如果拿到的数据如上图的红色点,那就不符合线性回归模型。
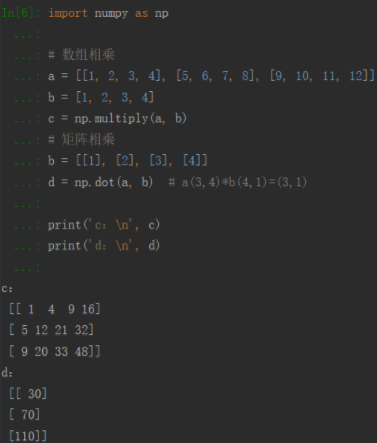
(3)这个知识点是用代码比较数据和矩阵相乘的结果
3) 机器学习
梯度下降代码:
# 梯度下降
import random
import time
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 产生数据
_xs = [0.1 * x for x in range(0, 10)]
_ys = [12 * i + 4 for i in _xs]
print(_xs)
print(_ys)
w = random.random()
b = random.random()
a1 = []
b1 = []
for i in range(100):
for x, y in zip(_xs, _ys):
o = w * x + b # 预测值
e = (o - y) # 误差
loss = e ** 2 # 损失
dw = 2 * e * x # 对w求导
db = 2 * e * 1 # 对d求导
# 梯度下降,0.1为学习率
w = w - 0.1 * dw
b = b - 0.1 * db
# 最终结果:loss越小越好,w接近12,b接近4
print('loss={0},w={1},b={2}'.format(loss, w, b))
a1.append(i)
b1.append(loss)
plt.plot(a1, b1)
plt.pause(0.1)
plt.show()
2.思考线性回归算法可以用来做什么?(大家尽量不要写重复)
如老师说的那般,线性回归算法可用迭代算法来减少误差,将损失函数最小化,也是基于已有的数据对新的数据进行预测,所以可用于:①预测某种产品的销量 ②根据每天地方的患病率,预测疫情的走向等等。
3.自主编写线性回归算法 ,数据可以自己造,或者从网上获取。(加分题)

代码:
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import explained_variance_score,mean_squared_error,median_absolute_error
# 数据读取与预处理
data = pd.read_csv('./Python智能/Python大作业/201706120047吴狄2.csv')
data2 = pd.read_csv('./Python智能/Python大作业/测试集2.csv')
x = data.iloc[1:,6:8]
y = data2.iloc[1:,2:3]
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.5,random_state=5)
# 构建逻辑回归模型
LR_model = LogisticRegression()
# 训练模型
LR_model.fit(x_train,y_train.astype('int'))
# 预测模型
pre = LR_model.predict(x_test)
print('模型的正确率:',LR_model.score(x_test,y_test.astype('int')))
LR_model =LogisticRegression().fit(x_train,y_train.astype('int'))