代码思路:
|
1、读取数据 |
read_scv | |
|
2、预测模型函数:①sigmoid函数②预测函数 |
#sigmoid函数 def sigmoid(z): return 1/(1+np.exp(-z)) #计算预测模型的函数 def model(X,theta): return sigmoid(np.dot(X,theta.T)) |
 |
|
3、目标函数(似然函数) |
#计算目标值的函数(对数似然) def cost(X,Y,theta): h=model(X,theta) left=np.multiply(-Y,np.log(h)) right=np.multiply(1-Y,np.log(1-h)) return np.sum(left-right)/(len(X)) |
 |
|
4、计算梯度的函数: |
#计算梯度的函数 def gradient(X,Y,theta): grad=np.zeros(theta.shape) error=(model(X,theta0)-Y).ravel() for j in range(len(theta.ravel())): term=np.multiply(error,X[:,j]) grad[j]=np.sum(term) / len(X) return grad |
 |
|
5、梯度下降的函数(更新梯度值): |
#对X,Y数据重新打乱(小批量梯度下降有用) |

|
| 6、测试 |
#训练数据 theta0=np.array([0.0,0.0,0.0]) X_train.insert(0,'ones',1) X=X_train.as_matrix() Y=Y_train.as_matrix() print(cost(X,Y,theta0)) print(gradient(X,Y,theta0)) |
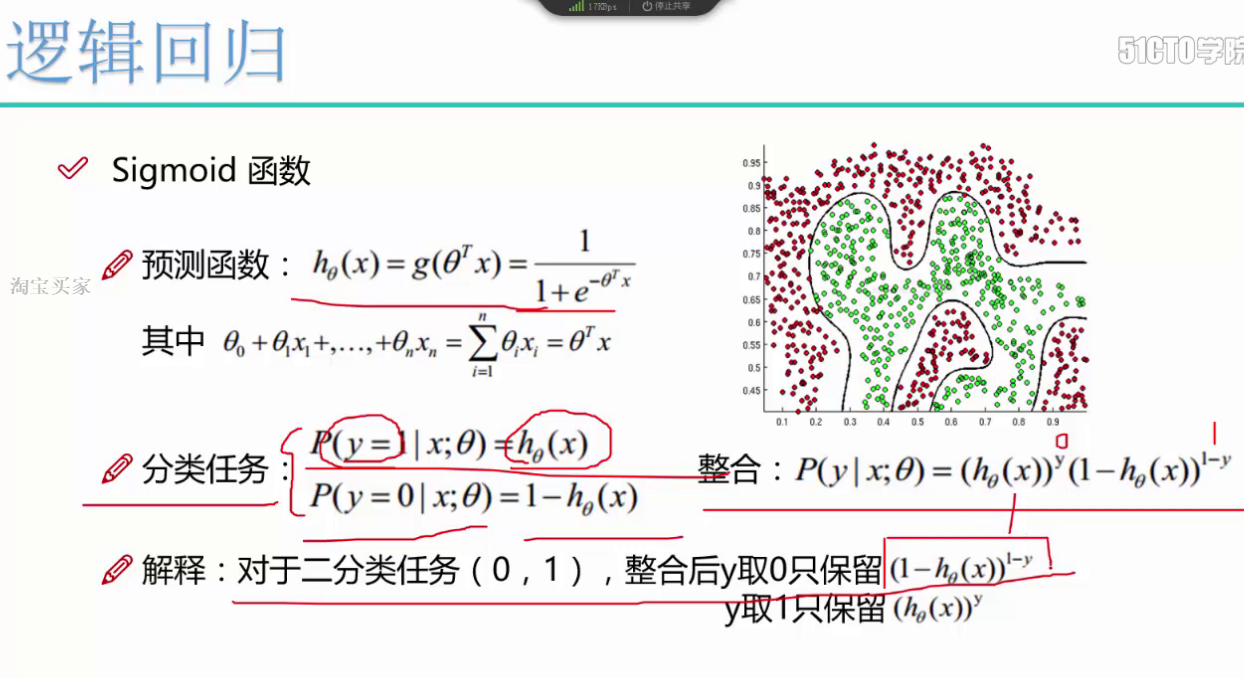
1、sigmoid函数:(也是预测函数)

2、逻辑回归过程:(目标函数)

(将目标函数转化成对数似然函数)

3、求导过程:

