灯塔(LightHouse)
Description
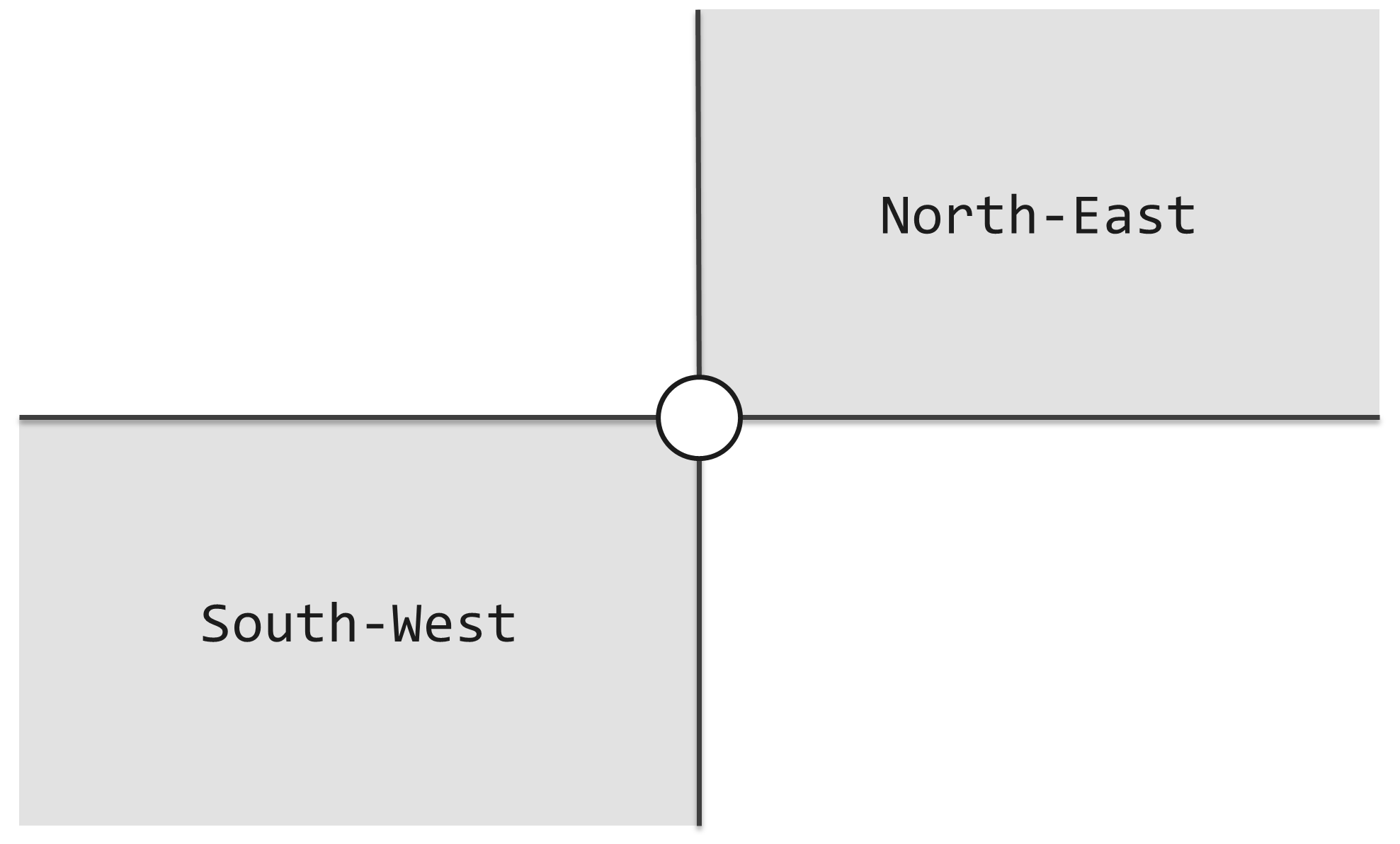
As shown in the following figure, If another lighthouse is in gray area, they can beacon each other.
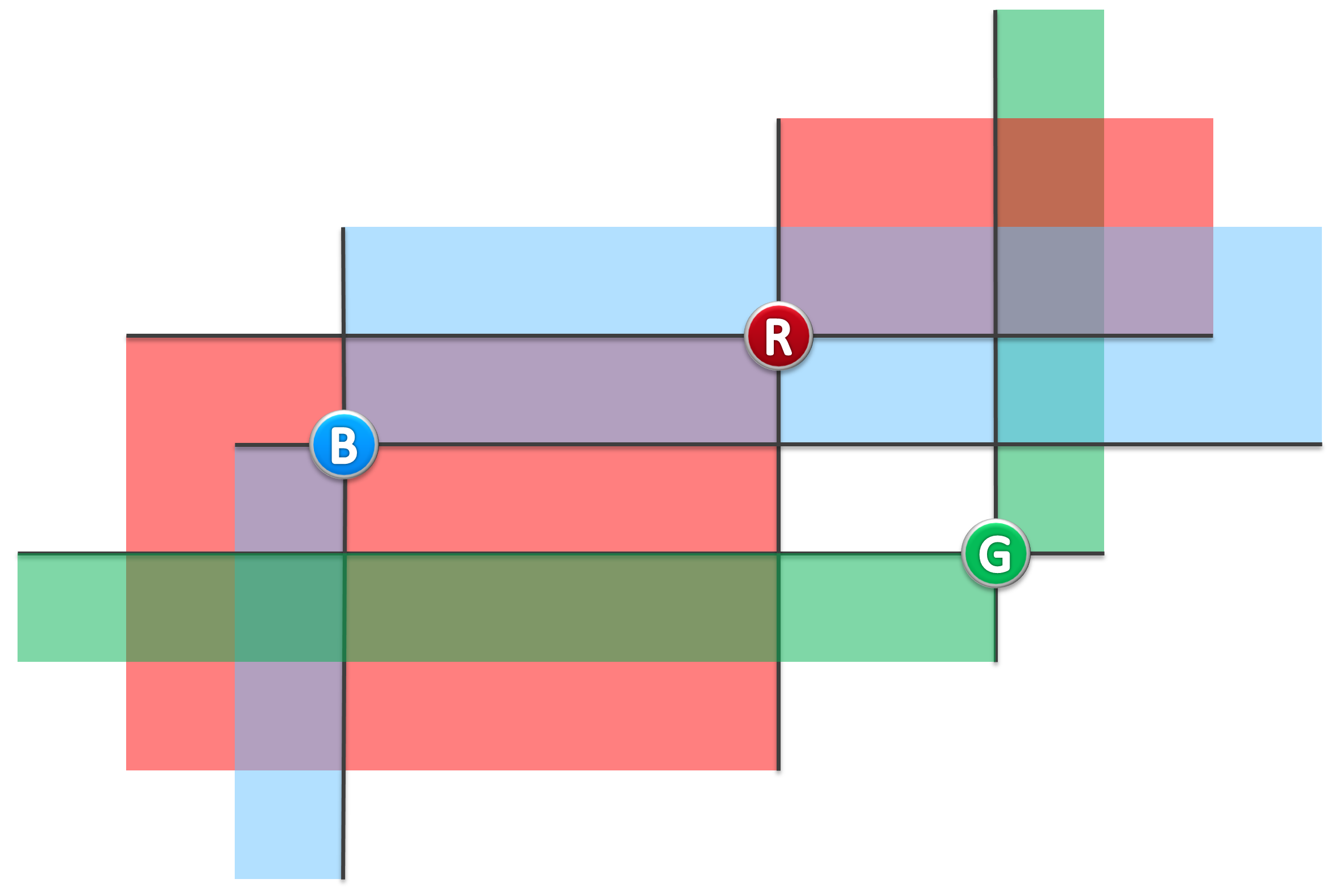
For example, in following figure, (B, R) is a pair of lighthouse which can beacon each other, while (B, G), (R, G) are NOT.
Input
1st line: N
2nd ~ (N + 1)th line: each line is X Y, means a lighthouse is on the point (X, Y).
Output
How many pairs of lighthourses can beacon each other
( For every lighthouses, X coordinates won't be the same , Y coordinates won't be the same )
Example
Input
3
2 2
4 3
5 1
Output
1
Restrictions
For 90% test cases: 1 <= n <= 3 * 105
For 95% test cases: 1 <= n <= 106
For all test cases: 1 <= n <= 4 * 106
For every lighthouses, X coordinates won't be the same , Y coordinates won't be the same.
1 <= x, y <= 10^8
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
Hints
The range of int is usually [-231, 231 - 1], it may be too small.
解题思路:将灯塔按照x轴由大到小排序,即将问题转化为求y的逆序对的个数。求解逆序对可以利用归并排序的思路实现。
如下图:在某次归并的时候,左右两个数组已经排好顺序,如果遇到a[i] > a[j],则,a[j] 与a[i] 到a[n]的所有元素均构成逆序对。

在归并排序的时候顺便统计一下逆序对的个数。
注意,要统计的逆序对个数可能很大。
代码如下

#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #define MAXN 4000005 #define ll long long using namespace std; struct node{ ll x; ll y; } tower[MAXN]; ll des[MAXN]; struct node des1[MAXN]; int N; ll num; void merg(int l, int mid, int r) { int i, j; int k; i = l; k = l; j = mid + 1; while(i <= mid && j <= r){ if(tower[i].x < tower[j].x){ des1[k].x = tower[i].x; des1[k++].y = tower[i++].y; } else{ des1[k].x = tower[j].x; des1[k++].y = tower[j++].y; } } while(i <= mid){ des1[k].x = tower[i].x; des1[k++].y = tower[i++].y; } while(j <= r){ des1[k].x = tower[j].x; des1[k++].y = tower[j++].y; } for (i = l; i <= r; i++){ tower[i].x = des1[i].x; tower[i].y = des1[i].y; } } void msort(int l, int r){ if(l >= r - 1) { if(tower[l].x > tower[r].x){ int x, y; x = tower[l].x; y = tower[l].y; tower[l].x = tower[r].x; tower[l].y = tower[r].y; tower[r].x = x; tower[r].y = y; } return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; msort(l, mid); msort(mid + 1, r); merg(l, mid, r); } void merge1(int l, int mid, int r) { int i, j; ll cnt = 0; int k = l; i = l; j = mid + 1; while(i <= mid && j <= r){ if(tower[i].y < tower[j].y){ des[k++] = tower[i++].y; cnt += r - j + 1; } else{ des[k++] = tower[j++].y; } } while(i <= mid) des[k++] = tower[i++].y; while(j <= r) des[k++] = tower[j++].y; for (i = l; i <= r; i++){ tower[i].y = des[i]; } num += cnt; } void get_num(int l, int r) { if(l >= r - 1){ if(tower[l].y < tower[r].y){ num++; } else{ int temp = tower[l].y; tower[l].y = tower[r].y; tower[r].y = temp; } return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; get_num(l, mid); get_num(mid + 1, r); merge1(l, mid, r); } int main() { scanf("%d", &N); num = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { scanf("%lld %lld", &tower[i].x, &tower[i].y); } msort(0, N - 1); get_num(0, N - 1); printf("%lld ", num); return 0; }
