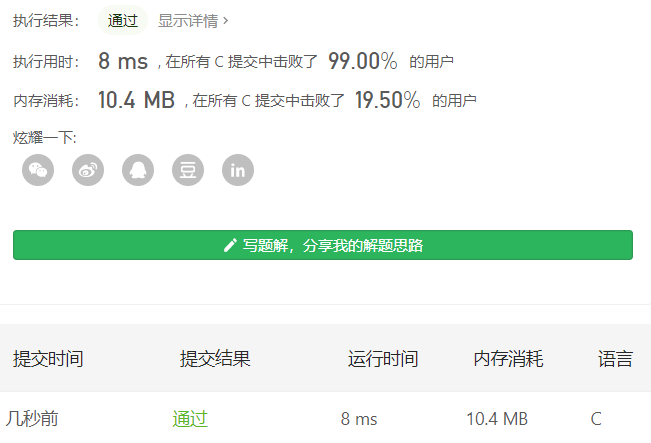
一、算法分析
1、子序列:在已知序列中去掉零个或多个元素后形成的序列(不能调换元素顺序)。
2、问题说明:已知两个序列X = <x1,x2,...,xm>, Y = <y1,y2,...,yn>,求其最长公共子序列Z。
3、分析:
假设Z = <z1, z2,...,zk>为所求的LSC
(1)若Xm = Yn时,则Zk = Xm = Yn为所求的LCS,且Zk-1是Xm-1与Yn-1的一个LCS;
(2)若Xm ≠ Yn,且Zk ≠Xm,则Z是Xm-1和Y的一个LCS(因为X中新增Xm后不影响Z);
(3)若Xm ≠ Yn,且Zk ≠Yn,则Z是X和Yn-1的一个LCS(因为Y中新增Yn后不影响Z);
由以上分析,可以推出递归表达式(转移矩阵):
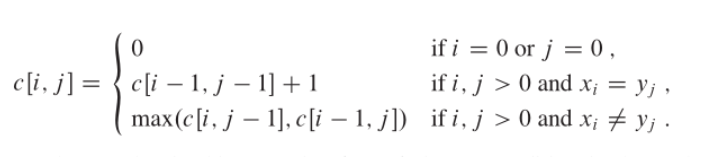
4、算法步骤:
(1)数据设置:需要遍历两个序列,判断新增的数据是否应当添加到LSC中,用二维数组进行记录;
(2)初始化:为了便于递归求解,需要设置初始值,当序列为有一个为空时,LCS为空;
(3)遍历序列(转移矩阵):判断Xi与Yj是否相等,若相等,则需要更新记录表;若不相等,则需要取LCS[Xi-1, Yj]与LCS[Xi, Yj-1]的较大值;其原因可见递归表达式推导分析。
5、LCS输出
(1)二维数组中,记录的是LCS的长度,并未记录公共子序列的内容,需要根据记录表进行反推;
(2)利用递归方法,从最外层开始判断Xi是否与Yj相等,相等则取值,不等则向内收缩;
二、代码实现
LSC过程:
int *lcsLength(void *x, void *y, int size, int xLen, int yLen, int(*comp)(void *, void *))
{
int i, j;
// LCS长度记录表: 利用一维数组记录,由于需要记录初始值,需要在原序列的长度上加一, c[i][j] = c[i * columnSize + j]
int *c = (int*)malloc((xLen + 1) * (yLen + 1) * sizeof(int));
// 初始化:分别初始化第一列、第一行
for (i = 1; i <= xLen; i++) {
c[i * (yLen + 1)] = 0;
}
for (j = 0; j <= yLen; j++) {
c[j] = 0;
}
// 遍历序列:
for (i = 1; i <= xLen; i++) {
for (j = 1; j <= yLen; j++) {
// 判断:Xi == Yj
if (comp(x + (i - 1) * size, y + (j - 1) * size) == 0) {
c[i * (yLen + 1) + j] = c[(i - 1) * (yLen + 1) + j - 1] + 1;
} else if (c[(i - 1) * (yLen + 1) + j] >= c[i * (yLen + 1) + j - 1]) { // 取当前相邻已有记录数据最大值
c[i * (yLen + 1) + j] = c[(i - 1) * (yLen + 1) + j];
} else {
c[i* (yLen + 1) + j] = c[i * (yLen + 1) + j - 1];
}
}
}
return c;
}
获取LCS:
void printfLcs(int *c, int columnSize, void *x, void *y, int size, int xLen, int yLen, int(*comp)(void *, void *), void(*ptr)(void *))
{
if (xLen == 0 || yLen == 0) {
return;
}
if (comp(x + (xLen - 1) * size, y + (yLen - 1) * size) == 0) {
printfLcs(c, columnSize, x, y, size, xLen - 1, yLen - 1, comp, ptr);
ptr(x + (xLen - 1) * size);
} else if (c[(xLen - 1) * (columnSize + 1) + yLen] >= c[xLen * (columnSize + 1) + yLen - 1]) {
printfLcs(c, columnSize, x, y, size, xLen - 1, yLen, comp, ptr);
} else {
printfLcs(c, columnSize, x, y, size, xLen, yLen - 1, comp, ptr);
}
}
三、测试结果
测试程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int *lcsLength(void *x, void *y, int size, int xLen, int yLen, int(*comp)(void *, void *))
{
// 具体实现参考上一小节
}
void printfLcs(int *c, int columnSize, void *x, void *y, int size, int xLen, int yLen, int(*comp)(void *, void *), void(*ptr)(void *))
{
// 具体实现参考上一小节
}
// 比较字符大小
int charLess(void *x, void *y)
{
return *(char *)y - *(char *)x;
}
// 输出字符
void charOutput(void *x)
{
printf("%c", *(char *)x);
}
// 打印LCS记录表
void printLcsTable(int *c, int m, int n)
{
printf("LSC table start:
");
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
printf(" %d ", c[i * n + j]);
}
printf("
");
}
printf("LSC table end.
");
}
int main(void)
{
char *x = "ABCBDAB";
char *y = "BDCABA";
int xLen = strlen(x);
int yLen = strlen(y);
int *c = lcsLength(x, y, sizeof(char), xLen, yLen, charLess);
printLcsTable(c, xLen + 1, yLen + 1);
printf("LSC: ");
printfLcs(c, 6, x, y, sizeof(char), xLen, yLen, charLess, charOutput);
while (1);
return 0;
}
测试结果:
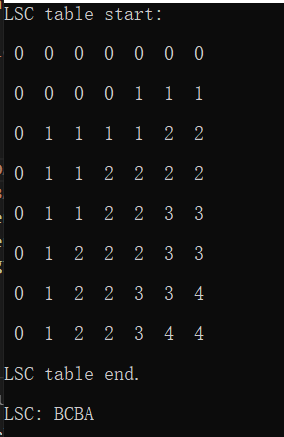
四、leetcode1143
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int longestCommonSubsequence(char * text1, char * text2)
{
// clsTab的行和列长度,对应序列长度+1
int rowLen = strlen(text1) + 1;
int columnLen = strlen(text2) + 1;
int *clsTab = (int *)malloc(rowLen * columnLen * sizeof(int));
// 初始化
for (int i = 0; i < rowLen; i++) {
clsTab[i * columnLen] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < columnLen; i++) {
clsTab[i] = 0;
}
// 填表从clsTab[1][1]开始,序列从0开始遍历
for (int i = 1; i < rowLen; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < columnLen; j++) {
// 序列索引与clsTab位置索引差一,因为在clsTab中的第一行和第一列添加了初始化为0
if (text1[i - 1] == text2[j - 1]) {
clsTab[i * columnLen + j] = clsTab[(i - 1) * columnLen + j - 1] + 1;
} else if (clsTab[(i - 1) * columnLen + j] >= clsTab[i * columnLen + j - 1]) {
clsTab[i * columnLen + j] = clsTab[(i - 1) * columnLen + j];
} else {
clsTab[i * columnLen + j] = clsTab[i * columnLen + j - 1];
}
}
}
return clsTab[rowLen * columnLen - 1];
}