MyBatis 是支持普通 SQL 查询,存储过程和高级映射的优秀持久层框架。mybatis主要是对JDBC进行封装,几乎消除了所有的JDBC代码编写;
导jar包
要使用mybatis框架必须先导入支持jar包;
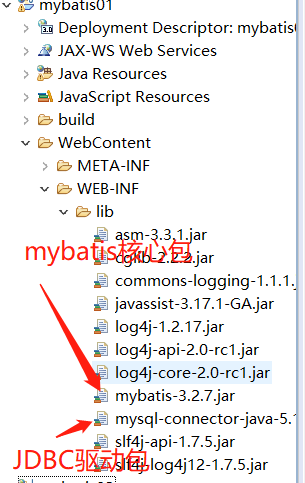
其他包用不到可以不导,但mybatis核心包和JDBC驱动包必须导入;
每 一 个 MyBatis 的 应 用 程 序 都 以 一 个 SqlSessionFactory 对 象 的 实 例 为 核 心 。 SqlSessionFactory 对 象 的 实 例 可 以 通 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对 象 来 获 得 。 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 对象可以从 XML 配置文件构建 SqlSessionFactory 对象。
String resource = "org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); sqlSessionFactory factory= new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
从上面的代码来看,是通过org/mybatis/example/mybatis-config.xml全局配置文件来实例化sqlSessionFactory这个对象的;
如何编写mybatis-config.xml全局配置文件?
mybatis-config.xml(因为通过路径名引用的,所以不一定叫这个名字,可以起其他名字,路径写对就行)包含对 MyBatis 系统的核心设置,包含获取数据库连接实例的数据源和决定事务范围和控制的事务管理器。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- default 写的是下面那个环境的id就表示当前该environment环境 --> <environments default="development"> <!-- 每个environment标签表示一个的环境 ,当前只写了一个环境--> <environment id="development"> <!-- 使用原生 JDBC 事务 --> <transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--POOLED表示当前环境使用连接池对象--> <dataSource type="POOLED"> <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="smallming"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments>
//mapper配置文件位置信息 <mappers> <mapper resource="com/bjsxt/mapper/FlowerMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
上面的configuration标签中嵌套了两个标签environments和mappers,environments表示数据库连接环境,记录了与数据库连接需要的信息。
那我们在JDBC编程中对数据库进行操作时,在与数据库连接后还需要编写查询语句对数据进行操作,其实在mybatis中就是将sql查询语句封装成Mapper XML文件;通过SQL 映射的 XML 文件是相当的简单。
如何编写Mapper XML文件?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!--引入DTD,规范XML文件格式--> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespqce 就相当于JDBC中dao层类的路径--> <mapper namespace="com.bjsxt.mapper.PeopleMapper">
<!--id相当于方法名 resultType表示返回的类型--> <select id="selAll" resultType="com.bjsxt.pojo.People"> select * from people </select> </mapper>
mybatis如何使用查询语句?
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.util.List; import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import com.bjsxt.pojo.People; import com.bjsxt.service.PeopleService; public class PeopleServiceImpl implements PeopleService{ @Override public List<People> show() throws IOException {
//读取mybatis-config.xml配置文件,和Mapper XML配置文件 InputStream is=Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis.xml");
//构建会话工厂 SqlSessionFactory factory=new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(is);
//获取连接数据库的连接对象 SqlSession session =factory.openSession();
//通过Sqlsession连接对象调用Mapper XML文件中配置的查询语句进行查询
//selectList方法的参数:就是mapper XML文件中配置的namespace类名和id方法名 List<People> list=session.selectList("com.bjsxt.mapper.PeopleMapper.selAll"); session.close(); return list; } }
三种查询方式:
1.selectList() 返回值为 List<resultType 属性控制>, 适用于返回结果有多个的查询
返回结果遍历:
List<Flower> list = session.selectList("a.b.selAll");
for (Flower flower : list) {
System.out.println(flower.toString());
}
2.selectOne() 返回值 Object,适用于返回结果只是变量或一行数据时
int count = session.selectOne("a.b.selById"); System.out.println(count);
3.selectMap() 返回值Map<key,resultType 控制>,适用于需要在查询结果中通过某列的值取到这行数据的需求
//返回以name为key,值为整条数据的map
Map<Object, Object> map = session.selectMap("a.b.c", "name");
System.out.println(map);
SQL语句如何传参?
传递单个参数:
在上面的例子中sql语句都是直接写好的,但在实际开发中肯定需要收到客户端发送的数据才知道要查询什么,这就需要通过传递参数来完成sql语句的编写。其实在xxxMapper.XML中的<select><delete>等标签都有一个parameterType属性用来表示参数的类型。
<select id="selById" resultType="com.bjsxt.pojo.People" parameterType="int"><!--表示参数类型为int类型--> select * from people where id=#{0} </select>
查询代码编写:
People p = session.selectOne("a.b.selById",1);
System.out.println(p);
sql语句获取参数:#{}获取参数内容,相当于JDBC的?占位符,然后传参
1,使用索引,从 0 开始 #{0}表示第一个参数
2,也可以使用#{param1}表示第一个参数
3,如果只有一个参数(基本数据类型或 String),mybatis对#{}里面内容没有要求只要写内容即可.
4,如果参数是对象#{属性名},(会根据属性名找到对象对应的getset方法的返回值)
5,如果参数是 map 写成#{key}
${} 与#{}功能基本一样,但${}不使用?。如果写数字,就是一个数字
多个参数传递:
上面的参数传递方法,只能传递单个参数,虽然可以通过传递对象和Map容器来包装多个参数,但是不够直观;
所以mybatis还提供了可以传递多个参数的方法:接口绑定实现参数传递
1,在与mapper xml文件的namespace表示的路径建立一个同名的接口(例如:namespace为com.mapper.PeopleMapper,则在com.mapper路径下建立名为PeopleMaper的接口)
2,在接口中写与mapper xml相同功能的方法()
例如mapper xml中有:
<select id="selByIdName" resultType="com.bjsxt.pojo.People" parameterType="int"><!--表示参数类型为int类型--> select * from people where id=#{0} and name=#{name} </select>
则在接口中写方法:
People selById(int id,String name);//id与方法名对应,parameterType与参数对应,resultType与返回值对应,如果返回值为列表,则与列表中的元素类型对应
3,在全局配置文件中设置接口扫描:
<mappers> <package name="com/bjsxt/mapper"/> </mappers>
4,调用接口方法
//通过sqlsession的实例化对象,的getMapper方法,传递参数为接口的classs对象,获取接口的对象
PelpleMapper mapper=session.getMapper(PeopleMapper.class);
//通过接口的对象,调用接口方法, List<People> list=mapper.selByIdName(id,name);
原理:接口其实是没办法创建对象的,所以getMapper其实是系统内部给接口创建代理实体类,所以调用的是实体类的方法,然后接口的实体类做的就是取调用mapper xml的实体类的对应方法,其实就是转了一个弯还是调用了原来的方法。通过这样的代理模式,使得程序员开发时逻辑更清晰,更方便。
typeAliases 别名
1.系统内置别名: 把类型全小写
<select id="selById" resultType="com.bjsxt.pojo.People" parameterType="map"><!--正确写法为Map,map为系统内置的别名--> select * from people where id=#{key} </select>
2.给某个类起别名(在全局配置中加typeAliases标签)
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias type="com.bjsxt.pojo.People" alias="peo"/>
</typeAliases>
起别名后的Mapper编写
<select id="selById" resultType="peo" parameterType="map"> select * from people where id=#{key} </select>
3.直接给某个包下所有类起别名,别名为类名,不区分大小写
<typeAliases> <package name="com.bjsxt.pojo" /> </typeAliases>
给类起别名后的Mapper编写
<select id="selById" resultType="people" parameterType="map"> select * from people where id=#{key} </select>
MyBatis 实现新增

<insert id="ins" parameterType="People"> insert into people values(default,#{name},#{age}) </insert>

int index1 = session.insert("a.b.ins", p); if(index1>0){ System.out.println("成功"); } else{ System.out.println("失败"); }
MyBatis 实现修改

<update id="upd" parameterType="People"> update people set name = #{name} where id = #{id} </update>

People peo = new People(); peo.setId(3); peo.setName("王五"); int index = session.update("a.b.upd", peo); if(index>0){ System.out.println("成功"); }else{ System.out.println("失败"); } session.commit();
.mybatis 实现删除

<delete id="del" parameterType="int"> delete from people where id = #{0} </delete

int del = session.delete("a.b.del",3); if(del>0){ System.out.println("成功"); }else{ System.out.println("失败"); } session.commit();
