字节流
字节输出流OutputStream(抽象类)
常用方法:
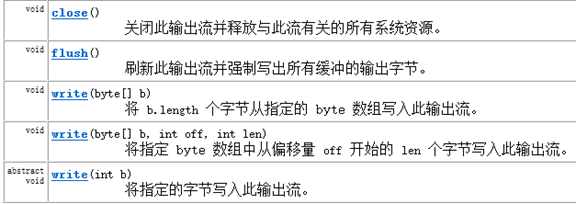
代码实例:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
2 //FileOutputStream的构造方法:如果文件存在,则覆盖,如果不存在,则创建
3 //
换行
4 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\bian.txt",true);
5 /*fos.write(49);
6 fos.write(48);
7 fos.write(48);*/
8 /*byte[] bytes={-65,-66,-67,-68};
9 fos.write(bytes,1,2);*/
10 fos.write("xuezhiqian
".getBytes()); //字符串转字节
11 /*new String(bytes);*/ //字节转字符串
12 fos.close();
13 }
FileOutputStream类(文件输出流,OutputStream的子类)

FileOutputStream类写入数据到文件中

代码实现:
1 public static void main(String[] args){
2 FileOutputStream fos=null;
3 try {
4 fos = new FileOutputStream("x:\test\bb.txt");
5 fos.write(12);
6 } catch (IOException e) {
7 throw new RuntimeException("输入失败");
8 }finally{
9 try {
10 if(fos!=null)
11 fos.close();
12 } catch (IOException e) {
13 throw new RuntimeException("关闭失败");
14 }
15 }
给文件中续写和换行
构造方法:

代码实现:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 2 //FileOutputStream的构造方法:如果文件存在,则覆盖,如果不存在,则创建 3 // 换行 4 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\bian.txt",true); 5 /*fos.write(49); 6 fos.write(48); 7 fos.write(48);*/ 8 /*byte[] bytes={-65,-66,-67,-68}; 9 fos.write(bytes,1,2);*/ 10 fos.write("xuezhiqian ".getBytes()); //字符串转字节 11 /*new String(bytes);*/ //字节转字符串 12 fos.close(); 13 }
IO异常的处理
代码实现:
1 public class FileOutputStreamDemo3 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 File file = new File("c:\file.txt");
4 //定义FileOutputStream的引用
5 FileOutputStream fos = null;
6 try {
7 //创建FileOutputStream对象
8 fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
9 //写出数据
10 fos.write("abcde".getBytes());
11 } catch (IOException e) {
12 System.out.println(e.toString() + "----");
13 throw new RuntimeException("文件写入失败,重试");
14
15 } finally {
16 //一定要判断fos是否为null,只有不为null时,才可以关闭资源
17 if (fos != null) {
18 try {
19 fos.close();
20 } catch (IOException e) {
21 throw new RuntimeException("关闭资源失败");
22 }
23 }
24 }
25 }
26 }
字节输入流InputStream
常用方法:

FileInputStream类

构造方法:

FileInputStream类读取数据read方法

代码实现:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
2 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\test.txt");
3 int len=0;
4 while((len=fis.read())!=-1){
5 System.out.println((char)len);
6 }
7 /*int a=fis.read();
8 System.out.println((char)a);
9 int b=fis.read();
10 System.out.println((char)b);
11 int c=fis.read();
12 System.out.println((char)c);
13 int d=fis.read();
14 System.out.println((char)d);
15 int e=fis.read();
16 System.out.println((char)e);
17 int f=fis.read();
18 System.out.println((char)f);*/
19 /*char ch=97;
20 System.out.println(ch);*/
21 fis.close();
22 }
23
24 }
读取数据read(byte[])方法

代码实现:
1 public class InputStreamDemo2 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\test.txt");
4 byte[] bytes=new byte[2];
5 int len=0;
6 while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
7 System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
8 }
9 /* //第一次读
10 int len=fis.read(bytes);
11 System.out.println(len);
12 System.out.println(new String(bytes));
13 //第二次读
14 len=fis.read(bytes);
15 System.out.println(len);
16 System.out.println(new String(bytes));
17 //第三次读
18 len=fis.read(bytes);
19 System.out.println(len);
20 System.out.println(new String(bytes));
21 //第4次读
22 len=fis.read(bytes);
23 System.out.println(len);
24 System.out.println(new String(bytes));*/
25 fis.close();
26 }
27
28 }
字节流复制文件
代码实现:
1 public class CopyDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 long time1=System.currentTimeMillis();
4 //1.明确数据源(要复制哪个文件)
5 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("C:\Program Files\java\eclipse.zip");
6 //2.明确目的地(要复制到哪个文件)
7 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\d\java.txt");
8 //3.复制
9 int len=0;
10 while((len=fis.read())!=-1){
11 fos.write(len);
12 }
13 long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
14 System.out.println(time2-time1);
15 //4.释放资源
16 fis.close();
17 fos.close();
18 }
19
20 }
缓冲数组方式复制文件
代码实现:
1 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
2 long time1=System.currentTimeMillis();
3 // 1.明确数据源
4 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("C:\Program Files\java\eclipse.zip");
5 //2.明确目的地
6 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\eclipse.zip");
7 //3.复制
8 int len=0;//获取读取字节的有效长度
9 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
10 while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
11 fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
12 }
13 long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
14 System.out.println(time2-time1);
15 //4.释放资源
16 fis.close();
17 fos.close();
18 }
19 }
字符流
字节流读取字符的问题
代码实现:
public class CharStreamDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//给文件中写中文
writeCNText();
//读取文件中的中文
readCNText();
}
//读取中文
public static void readCNText() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("c:\cn.txt");
int ch = 0;
while((ch = fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.println(ch);
}
}
//写中文
public static void writeCNText() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("c:\cn.txt");
fos.write("欢迎你".getBytes());
fos.close();
}
}
字符输入流Reader
基础方法:

代码实现:
1 public class ReaderDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
4 //通过字符数组的方式读
5 FileReader fr=new FileReader("x:\test\test.txt");
6 int len=0;
7 char[] ch=new char[1024];
8 while((len=fr.read(ch))!=-1){
9 System.out.println(new String(ch,0,len));
10 }
11 fr.close();
12 //method1(fr);
13 }
14 public static void method1(FileReader fr) throws IOException{
15 //通过一个字符一个字符的方法读
16 int len=0;
17 while((len=fr.read())!=-1){
18 System.out.print((char)len);
19 }
20 fr.close();
21 }
22
23 }
FileReader类
构造方法:

代码实现:
字符输出流Writer
基础方法:

FileWriter类
构造方法:

代码实现:
1 1 public class WriterDemo { 2 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 3 3 //写入中文字符 4 4 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("x:\test\test.txt"); 5 5 fw.write("段子手薛之谦");//被写在缓冲区 6 6 fw.flush();//可刷新多次 7 7 //fw.close();//具有一次刷新功能 8 8 } 9 9 10 10 }
flush()和close()的区别

close是在关闭之前刷新一次
flush是一边存一边刷
字符流复制文件
代码实现:
1 public class JpgCopy1 {
2 //字符流复制文件
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
4 //1.明确数据源
5 FileReader fr=new FileReader("X:\test\img1.jpg");
6 //2.明确目的地
7 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("x:\test\a\img1.jpg");
8 //3.复制
9 int len=0;
10 char[] ch=new char[1024];
11 while((len=fr.read(ch))!=-1){
12 fw.write(ch, 0, len);
13 }
14 //4.释放资源
15 fr.close();
16 fw.close();
17 }
18
19 }
转换流
OutputStreamWriter类(OutputStreamWriter 是字符流通向字节流的桥梁)

代码实现:
1 public class OutputStreamWriterDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\utf8.txt",true);
4 OutputStreamWriter osw=new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"utf-8");
5 osw.write("这是utf-8编码");
6 osw.close();
7 }
8
9 }
InputStreamReader类(InputStreamReader 是字节流通向字符流的桥梁)

代码实现:
1 public class InputStreamReaderDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
4 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\utf8.txt");
5 InputStreamReader isr=new InputStreamReader(fis,"utf-8");
6 char[] ch=new char[1024];
7 int len=0;
8 while((len=isr.read(ch))!=-1){
9 System.out.println(new String(ch,1,len-1));
10 }
11 isr.close();
12 }
13
14 }
转换流和子类区别
OutputStreamWriter:
|--FileWriter:
InputStreamReader:
|--FileReader;
OutputStreamWriter和InputStreamReader是字符和字节的桥梁:也可以称之为字符转换流。字符转换流原理:字节流+编码表。
FileWriter和FileReader:作为子类,仅作为操作字符文件的便捷类存在。当操作的字符文件,使用的是默认编码表时可以不用父类,
而直接用子类就完成操作了,简化了代码。
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("a.txt"));//默认字符集。
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("a.txt"),"GBK");//指定GBK字符集。
FileReader fr = new FileReader("a.txt");
这三句代码的功能是一样的,其中第三句最为便捷。
注意:一旦要指定其他编码时,绝对不能用子类,必须使用字符转换流。什么时候用子类呢?
条件:
1、操作的是文件。2、使用默认编码。
总结:
字节--->字符 : 看不懂的--->看的懂的。 需要读。输入流。 InputStreamReader
字符--->字节 : 看的懂的--->看不懂的。 需要写。输出流。 OutputStreamWriter
缓冲流
字节缓冲流
{
字节缓冲输出流BufferedOutputStream
字节缓冲输入流 BufferedInputStream
使用基本的流与高效的流完成复制文件
}
字符缓冲流
{
字符缓冲输出流 BufferedWriter
字符缓冲输入流 BufferedReader
使用字符缓冲流完成文本文件的复制
}
整体代码实现:
1 public class Demo01 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 //method1();
4 //method2();
5 copy();
6 }
7 //缓冲字符输出流
8 //bw.newLine();可以实现平台无关性
9 //win 换行
10 //Linux 换行
11 public static void method1() throws IOException{
12 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("x:\test\test.txt",true);
13 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
14 bw.write("你好吗".toCharArray());
15 bw.flush();
16 bw.newLine();//换行
17 bw.write("我不好");
18 bw.flush();
19 bw.newLine();
20 bw.write(100);
21 bw.close();
22 }
23 //缓冲字符输入流
24 public static void method2() throws IOException{
25 FileReader fr=new FileReader("x:\test\test.txt");
26 BufferedReader bfr=new BufferedReader(fr);
27 String line=null;
28 int count=0;
29 while((line=bfr.readLine())!=null){
30 count++;
31 System.out.println(count+" "+line);
32 }
33 /*System.out.println(bfr.readLine());
34 System.out.println(bfr.readLine());
35 System.out.println(bfr.readLine());
36 System.out.println(bfr.readLine());*/
37
38 bfr.close();
39 }
40 //缓冲字符流的复制
41 public static void copy() throws IOException{
42 //1.明确数据源
43 FileReader fr=new FileReader("x:\test\test.txt");
44 BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(fr);
45 //2.确定目的地
46 FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("x:\test\d\copy.txt");
47 BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(fw);
48 //3.复制
49 String line=null;
50 while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
51 bw.write(line);
52 bw.newLine();
53 bw.flush();
54
55 }
56 br.close();
57 bw.close();
58 }
59
60 }
1 public class Demo02 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 //method1();
4 method2();
5 }
6 //缓冲字节输出流
7 public static void method1() throws IOException{
8 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\test.txt",true);
9 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
10 //bos.write(100);
11 bos.write("你好啊".getBytes());
12 bos.close();
13 }
14 //缓冲字节输入流
15 public static void method2() throws IOException{
16 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\test.txt");
17 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
18 int len=0;
19 while((len=bis.read())!=-1){
20 System.out.print((char)len);
21 }
22 bis.close();
23 }
24
25 }
整体练习:
1 public class Demo01 {
2 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
3 method1();//31159
4 method2();//52
5 method3();//105
6 method4();//3
7 }
8 public static void method1() throws IOException {
9 //字节流read()
10 long time1=System.currentTimeMillis();
11 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar");
12 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\a\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar");
13 int len=0;
14 while((len=fis.read())!=-1){
15 fos.write(len);
16 }
17 long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
18 System.out.println(time2-time1);
19 fis.close();
20 fos.close();
21 }
22 public static void method2() throws IOException{
23 //字节流read(byte[])
24 long time1=System.currentTimeMillis();
25 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar");
26 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
27 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\kkk.jar");
28 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
29 int len=0;
30 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
31 while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
32 fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
33 }
34 long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
35 System.out.println(time2-time1);
36 fis.close();
37 fos.close();
38 }
39 //缓冲字节输出流
40 public static void method3() throws IOException{
41
42 long time1=System.currentTimeMillis();
43 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar");
44 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
45 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\ggg.jar");
46 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
47 int len=0;
48 while((len=bis.read())!=-1){
49 bos.write(len);
50 }
51 long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
52 System.out.println(time2-time1);
53 bis.close();
54 bos.close();
55 }
56 //缓冲字节输入流
57 public static void method4() throws IOException{
58 long time1=System.currentTimeMillis();
59 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("x:\test\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar");
60 BufferedInputStream bis=new BufferedInputStream(fis);
61 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("x:\test\mysql-connector-java-5.1.37-bin.jar");
62 BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
63 int len=0;
64 byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
65 while((len=bis.read(bytes))!=-1){
66 bos.write(bytes, 0, len);
67 }
68 long time2=System.currentTimeMillis();
69 System.out.println(time2-time1);
70 bis.close();
71 bos.close();
72 }
73
74 }