A. Laptops
题意:给两个数列,问是否存在i,j,是的a[i]<a[j] 而 b[i]>b[j]
题解:先把一维排序,就是问是否存在逆序对。我写了个树状数组。。。貌似从a小到大扫一遍保存遇到的b的最大值即可
代码:

1 var s,a,b,c:array[0..150000] of longint; 2 i,n,m,tot:longint; 3 procedure sort(l,r:longint); 4 var i,j,x,y:longint; 5 begin 6 i:=l;j:=r;x:=a[(i+j)>>1]; 7 repeat 8 while a[i]<x do inc(i); 9 while a[j]>x do dec(j); 10 if i<=j then 11 begin 12 y:=a[i];a[i]:=a[j];a[j]:=y; 13 y:=b[i];b[i]:=b[j];b[j]:=y; 14 inc(i);dec(j); 15 end; 16 until i>j; 17 if i<r then sort(i,r); 18 if j>l then sort(l,j); 19 end; 20 procedure init; 21 begin 22 readln(n); 23 for i:=1 to n do readln(a[i],b[i]); 24 sort(1,n); 25 tot:=0; 26 i:=0;tot:=0; 27 for i:=1 to n do 28 begin 29 if (i=1) or (a[i]<>a[i-1]) then 30 begin 31 inc(tot);c[tot]:=b[i]; 32 end; 33 if b[i]>c[tot] then c[tot]:=b[i]; 34 end; 35 end; 36 procedure add(x:longint); 37 begin 38 while x<=n do 39 begin 40 inc(s[x]); 41 inc(x,x and (-x)); 42 end; 43 end; 44 function sum(x:longint):longint; 45 var t:longint; 46 begin 47 t:=0; 48 while x>0 do 49 begin 50 inc(t,s[x]); 51 dec(x,x and (-x)); 52 end; 53 exit(t); 54 end; 55 56 function check:boolean; 57 begin 58 fillchar(s,sizeof(s),0); 59 for i:=tot downto 1 do 60 begin 61 if sum(c[i]-1)>0 then exit(true); 62 add(c[i]); 63 end; 64 exit(false); 65 end; 66 begin 67 init; 68 if check then writeln('Happy Alex') else writeln('Poor Alex'); 69 end.
B. Fedya and Maths
题意:求 (1^n+2^n+3^n+4^n) mod 5
题解:不难看出,4 mod 5=-1 3 mod 5=-2
i) 当n为奇数时 有 (1^n+2^n+3^n+4^n) mod 5=(1^n+(-1)^n+2^n+(-2)^n) mod 5=0 正好抵消
ii)当n为偶数时,(1^n+2^n+3^n+4^n) mod 5=(1+1+2^n+2^n) mod 5 =(2+2*(-1)^n/2) 所以又要分情况
① n/2为奇数时, 原式=2-2=0
② n/2为偶数时,原式=2+2=4
所以总结起来就是如果能被4整除,=4 else =0
代码:

1 var z:longint;s:ansistring; 2 begin 3 readln(s); 4 if length(s)>=2 then val(copy(s,length(s)-1,2),z) 5 else val(s,z); 6 if z mod 4=0 then writeln(4) 7 else writeln(0); 8 end.
C. Boredom
题意:给一个数列,你如果选了a[k],那么a[k]+1与a[k]-1都不能选了,选a[k]获得的收益为a[k]*a[k]出现的次数,求最大收益
题解:显然不能只选奇数或只选偶数 如 1 1 1 1 2 3 4 当然应该选1 和 4
所以我们应该DP,令f[i]表示选i 可以获得的最大收益,g[i]表示不选i 获得的最大收益,则:
f[i]=g[i-1]+w[i] g[i]=max(g[i-1],f[i-1])
代码:

1 var f,g,v,a:array[-1..150000] of int64; 2 i,n,x:longint; 3 function max(x,y:int64):int64; 4 begin 5 if x>y then exit(x) else exit(y); 6 end; 7 8 procedure init; 9 begin 10 readln(n); 11 for i:=1 to n do read(a[i]); 12 for i:=1 to n do inc(v[a[i]]); 13 end; 14 procedure main; 15 begin 16 fillchar(f,sizeof(f),0); 17 fillchar(g,sizeof(g),0); 18 for i:=1 to 100000 do 19 if v[i]=0 then begin f[i]:=f[i-1];g[i]:=g[i-1];end 20 else 21 begin 22 f[i]:=max(f[i-2],g[i-1])+i*v[i]; 23 g[i]:=max(g[i-1],f[i-1]); 24 end; 25 writeln(max(f[100000],g[100000])); 26 end; 27 28 begin 29 init; 30 if n=1 then writeln(a[1]) else main; 31 end.
D. A Lot of Games
题意:给你一些串,两个人轮流在一个字符串后面添加字母(初始为空),每个时刻都必须使当前的字符串为所有给定的字符串中的某个或多个的前缀。
无法填字母者输。游戏一共进行K次,每次的loser将下一次first,请问先手必胜还是后手必胜?
题解:我的想法是这样的,但是WA了,不知道哪里错了
先把所有的字符串建成一棵trie树,使用布尔变量来表示每个节点是必胜状态还是必败状态,可以通过一次dfs求出
定义0节点为初始节点,它的后继有 ab。。z然后分情况讨论:
i)如果0的后继中只有必败状态,那么first将一直输到第k轮
ii)如果0的后继中只有必胜状态,那么赢家依次是 first,second,first,second。。。最后赢家由k的就来决定
iii)如果0的后继中既有必胜状态又有必胜状态,那么first可以选择一直输到第k-1轮,然后赢掉第k场比赛
官方的题解是这样的:
To solve this problem we need the prefix tree(trie), which will have all the strings from the group. Next we will calculate the two DP: win[v] — Can player win if he makes a move now (players have word equal to prefix v in the prefix tree(trie)). lose[v] — Can player lose if he makes a move now (players have word equal to prefix v in the prefix tree(trie)).
if v is leaf of trie, then win[v] = false; lose[v] = true;
Else win[v] = (win[v] or (not win[i])); lose[v] = (lose[v] or (not lose[i])), such i — children of vertex v.
Let's look at a few cases:
If win[v] = false, then second player win (first player lose all games).
If win[v] = true и lose[v] = true, then first player win (he can change the state of the game in his favor).
If win[v] = true and lose[v] = false, then if  , then first player win, else second player win.
, then first player win, else second player win.
Asymptotics — 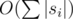 .
.
代码:
1.我的 WA了

1 const maxn=50000+100; 2 var s:ansistring; 3 f:array[0..maxn,0..30] of longint; 4 sg,flag:array[0..30*maxn] of boolean; 5 i,n,tot,k:longint; 6 can1,can2:boolean; 7 procedure insert; 8 var x,y,i:longint; 9 begin 10 readln(s);x:=0; 11 for i:=1 to length(s) do 12 begin 13 y:=ord(s[i])-ord('a')+1; 14 if f[x,y]=0 then 15 begin 16 inc(tot); 17 f[x,y]:=tot; 18 end; 19 x:=f[x,y]; 20 end; 21 flag[x]:=true; 22 end; 23 procedure init; 24 begin 25 readln(n,k);tot:=0; 26 for i:=1 to n do insert; 27 end; 28 procedure dfs(x:longint); 29 var can:boolean;i:longint; 30 begin 31 if flag[x] then begin sg[x]:=true;exit;end; 32 can:=false; 33 for i:=1 to 26 do 34 if f[x,i]<>0 then 35 begin 36 dfs(f[x,i]); 37 if not(sg[f[x,i]]) then can:=true; 38 end; 39 sg[x]:=can; 40 end; 41 function check:string; 42 begin 43 dfs(0); 44 can1:=false;can2:=false; 45 for i:=1 to 26 do 46 if f[0,i]<>0 then 47 if sg[f[0,i]] then can1:=true else can2:=true; 48 if can1 and can2 then exit('First'); 49 if can1 and not(can2) then 50 begin 51 if odd(k) then exit('First') else exit('Second'); 52 end; 53 if can2 and not(can1) then exit('Second'); 54 end; 55 begin 56 init; 57 writeln(check); 58 end.
2.官方标程

1 var 2 s : array [0..1000000] of ansistring; 3 f,g : array [0..1000000] of longint; 4 a : array [0..200000,'a'..'z'] of longint; 5 k,n,i,v : longint; 6 procedure give(x : longint); 7 begin 8 if x=1 then writeln('First') 9 else writeln('Second'); 10 end; 11 procedure dfs1(x : longint); 12 var 13 i : char; 14 v,s : longint; 15 begin 16 s:=0; 17 v:=0; 18 for i:='a' to 'z' do 19 if a[x,i]<>0 then dfs1(a[x,i]); 20 for i:='a' to 'z' do 21 if a[x,i]<>0 then begin inc(v); s:=s+f[a[x,i]]; end; 22 if v-s>0 then f[x]:=1 23 else f[x]:=0; 24 end; 25 procedure dfs2(x : longint); 26 var 27 i : char; 28 v,s : longint; 29 begin 30 v:=0; 31 s:=0; 32 for i:='a' to 'z' do 33 if a[x,i]<>0 then dfs2(a[x,i]); 34 for i:='a' to 'z' do 35 if a[x,i]<>0 then begin inc(v); s:=s+g[a[x,i]]; end; 36 if v=0 then g[x]:=1 37 else 38 if v-s>0 then g[x]:=1 39 else g[x]:=0; 40 end; 41 procedure add(s : ansistring); 42 var 43 vr,i : longint; 44 begin 45 vr:=1; 46 for i:=1 to length(s) do 47 begin 48 if a[vr,s[i]]=0 then begin inc(v); a[vr,s[i]]:=v; end; 49 vr:=a[vr,s[i]]; 50 end; 51 end; 52 begin 53 readln(n,k); 54 v:=1; 55 for i:=1 to n do readln(s[i]); 56 for i:=1 to n do add(s[i]); 57 dfs1(1); 58 dfs2(1); 59 if k=1 then give(f[1]) 60 else 61 if f[1]=0 then give(f[1]) 62 else 63 if g[1]=1 then give(f[1]) 64 else 65 if k mod 2=1 then give(1) 66 else give(0); 67 end.
E题是神题,看起来就不可做。。。
