At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite set of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers something about his set S:
- its elements were distinct integers from 1 to limit;
- the value of
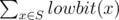 was equal to sum; here lowbit(x) equals 2k where k is the position of the first one in the binary representation of x. For example, lowbit(100102) = 102, lowbit(100012) = 12, lowbit(100002) = 100002 (binary representation).
was equal to sum; here lowbit(x) equals 2k where k is the position of the first one in the binary representation of x. For example, lowbit(100102) = 102, lowbit(100012) = 12, lowbit(100002) = 100002 (binary representation).
Can you help Picks and find any set S, that satisfies all the above conditions?
The first line contains two integers: sum, limit (1 ≤ sum, limit ≤ 105).
In the first line print an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), denoting the size of S. Then print the elements of set S in any order. If there are multiple answers, print any of them.
If it's impossible to find a suitable set, print -1.
5 5
2
4 5
In sample test 1: lowbit(4) = 4, lowbit(5) = 1, 4 + 1 = 5.
In sample test 2: lowbit(1) = 1, lowbit(2) = 2, lowbit(3) = 1, 1 + 2 + 1 = 4.
题意:就是给一个lowbit(x) x在二进制下 从左想右边数第一个为1的数的大小
x属于1到m 问你是否让着m中的某几个数的lowbit和为sum
题解:
我是预处理 lowbit值,然后从大的找,暴力跑就是了

///1085422276 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; typedef long long ll; #define mem(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define meminf(a) memset(a,127,sizeof(a)); #define inf 1000000007 #define mod 1000000007 inline ll read() { ll x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){ if(ch=='-')f=-1;ch=getchar(); } while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){ x=x*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar(); }return x*f; } //************************************************ const int maxn=100000+5; struct ss { int s,i; }b[maxn]; int cmp(ss s1,ss s2) { return s1.s<s2.s; } vector<int >G[maxn]; int a[maxn]; int main(){ int n=read(); int m=read(); set<int >s; int k=0; int sum=0,mn=0; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ if(i%2){ a[i]=1; } else { int tmp=i; int ans=1; while(tmp){ tmp/=2; ans*=2; if(tmp%2)break; } a[i]=ans; } sum+=a[i]; b[++k].i=i; b[k].s=a[i]; G[a[i]].push_back(i); mn=max(a[i],mn); } int A=0; if(sum<n){ cout<<-1<<endl;return 0; } int flag; for(int i=mn;i>=1;i--){ if(n>G[i].size()*i){ n-=G[i].size()*i; A+=G[i].size(); } else { flag=i; A+=n; break; } } cout<<A<<endl; for(int i=mn;i>flag;i--){ for(int j=0;j<G[i].size();j++){ cout<<G[i][j]<<" "; } } for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ cout<<G[1][i]<<" "; } return 0; }
