多线程技术
多线程基本概念_程序_进程_线程
·程序、进程、线程
程序:(program)是一个指令的集合
进程:Process,(正在执行中的程序)是一个静态的概念。进程是程序的异常静态执行过程,占用特定的地址空间,每个进程都是独立的,有3部分组成cup,data,code
缺点:内存的浪费,CPU的负担
线程:是进程中一个“单一的连续控制流程”。CPU调度的是线程

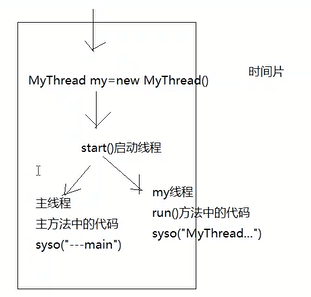
通过继承Thread类实现多线程
·实现多线程的步骤
1.继承Thread类
2.重写run()方法
3.通过start()方法启动线程
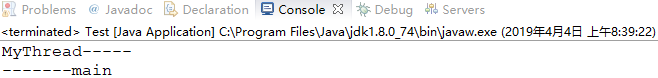
1 package com.zqf.threadproject; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 MyThread my = new MyThread(); 6 my.start(); //启动线程 7 System.out.println("-------main"); 8 } 9 }
1 package com.zqf.threadproject; 2 3 public class MyThread { 4 5 public void start() { 6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 7 //线程体 8 System.out.println("MyThread-----"); 9 } 10 }
通过实现Runnable接口实现多线程
·步骤
- 编写类实现Runnable接口
- 实现run()方法
- 通过Thread类的start()方法启动线程
1 package com.zqf.runnableproject; 2 3 public class test1 { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //创建线程类的对象 6 MyRunnable my=new MyRunnable(); 7 //start()方法是Thread类中的方法 8 Thread t = new Thread(my); 9 t.start(); //启动线程 10 //主线程中的循环 11 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 12 System.out.println("-------mian()"); 13 } 14 } 15 }
1 package com.zqf.runnableproject; 2 3 public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ //具备了多线程操作能力 4 5 @Override 6 public void run() { 7 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 8 System.out.println("MyRunnable.run()-----"+i); 9 } 10 } 11 }
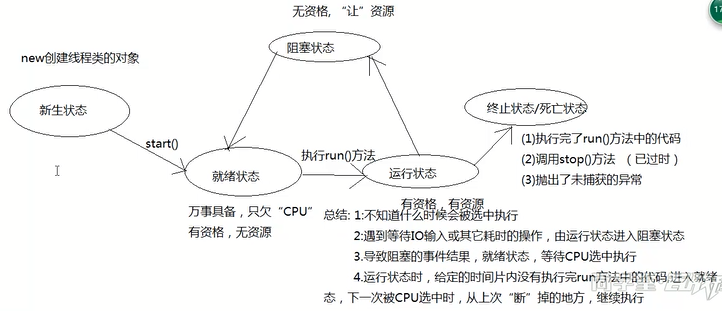
线程状态
获取线程基本信息的方法
·线程操作的常用方法
static Thread currentThread() 返回目前正在执行的线程
1 package com.zqf.threadmethodproject; 2 3 public class TestThreadMethod { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); //获取当前正在执行的线程对象 6 //toString()方法得到的内容为[线程名称,线程的优先级,线程组的名称] 7 System.out.println(t.toString()); 8 9 //创建线程类的对象 10 MyRunnable my =new MyRunnable(); 11 Thread t1 = new Thread(my); 12 Thread t2 = new Thread(my); 13 Thread t3 = new Thread(my); 14 15 //启动线程 16 t1.start(); 17 t2.start(); 18 t3.start(); 19 /**在Thread类中一定有一个静态变量int,用于统计创建线程的个数*/ 20 } 21 } 22 class MyRunnable implements Runnable{ //创建MyRunnable类实现Runnable接口 23 24 @Override 25 public void run() { 26 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); 27 System.out.println(t); 28 } 29 30 }
final String getName() 返回线程的名称

final boolean isAlibe() 判断线程是否处于活动状态
1 package com.zqf.threadmethodproject; 2 3 public class TestIsAliva { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //主线程 6 MyThread my =new MyThread(); 7 System.out.println("线程my处于新生状态的线程是否处于活动状态"); 8 my.start(); //启动线程 9 System.out.println("线程my处于就绪状态的线程是否处于活动状态:"+my.isAlive() 10 ); 11 //主线程中的循环 12 for(int i=0;i<10;i++){ 13 System.out.println("-------"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---------->"+i); 14 } 15 //主线程中的最后一句代码 16 System.out.println("my线程是否处于活动状态:"+my.isAlive()); 17 } 18 } 19 class MyThread extends Thread{ 20 public void run(){ 21 for(int i = 0;i<10;i++){ 22 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"---------->"+i); 23 } 24 } 25 }
多线程的安全问题
多线程的安全性问题:如300人买票5张票的问题
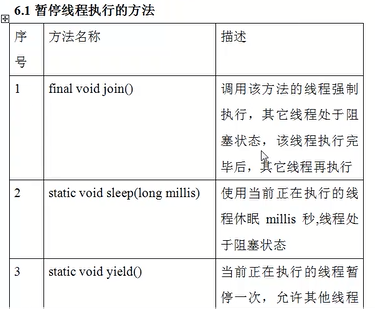
暂停线程执行sleep、yield、stop、join
线程的优先级问题
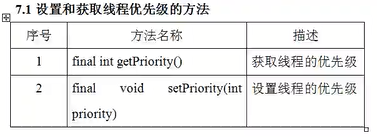
1 package com.zqf.threadpriority; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 System.out.println("最高优先级:"+Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); 6 System.out.println("最低优先级:"+Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); 7 System.out.println("默认优先级:"+Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); 8 //主线程的优先级 9 Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); 10 System.out.println("获取主线程的优先级:"+t.getPriority()); 11 Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyThread()); 12 System.out.println("新建的线程优先级:"+t2.getPriority()); 13 /** 14 * 优先级越高越有可能先被调用执行,但是不一定 15 * */ 16 t2.setPriority(6); 17 System.out.println("t2线程的优先级:"+t2.getPriority()); 18 //t2.setPriority(100); //由于超出了优先级,故会报错 19 } 20 } 21 class MyThread implements Runnable{ 22 public void run() { 23 } 24 }
线程同步 具体实现
·同步实现的方式
同步代码块
synchronized(obj){ } //obj称为同步监视器
·同步方法

死锁_死锁的解决办法
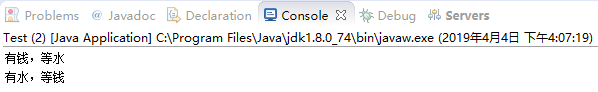
·产生死锁
1 package com.zqf.deadLockProject; 2 3 public class DeadLock extends Thread{ 4 private Object money; //钱 5 private Object water; //水 6 public boolean flag; //标识持有对象锁 7 public DeadLock(Object money, Object water) { 8 super(); 9 this.money = money; 10 this.water = water; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 if(flag){ //true时,持有“钱”的锁 16 synchronized(money){ 17 System.out.println("有钱,等水"); 18 try { 19 Thread.sleep(300); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 synchronized(water){} 25 System.out.println("有水,等钱"); 26 } 27 }else{ 28 synchronized(water){ 29 System.out.println("有水,等钱"); 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(300); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 synchronized(money){ 37 System.out.println("有钱,等水"); 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 } 42 }
1 package com.zqf.deadLockProject; 2 3 public class Test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //创建共享资源的对象 6 Object money= new Object(); 7 Object water = new Object(); 8 //创建线程类的对象 9 DeadLock d1 = new DeadLock(money,water); 10 DeadLock d2 = new DeadLock(money,water); 11 d1.flag= true; 12 d2.flag= false; 13 //启动线程 14 d1.start(); 15 d2.start(); 16 } 17 }
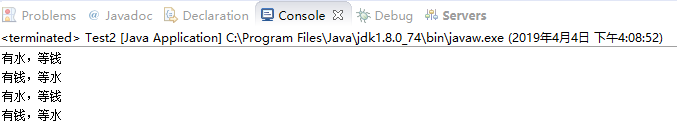
·解决死锁
1 package com.zqf.deadLockProject; 2 3 public class DeadLock2 extends Thread{ 4 private Object money; //钱 5 private Object water; //水 6 public boolean flag; //标识持有对象锁 7 public DeadLock2(Object money, Object water) { 8 super(); 9 this.money = money; 10 this.water = water; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 if(flag){ //true时,持有“钱”的锁 16 synchronized(money){ 17 System.out.println("有钱,等水"); 18 try { 19 Thread.sleep(300); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 synchronized(water){} 25 System.out.println("有水,等钱"); 26 } 27 }else{ 28 synchronized(water){ 29 System.out.println("有水,等钱"); 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(300); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 } 38 synchronized(money){ 39 System.out.println("有钱,等水"); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 }
1 package com.zqf.deadLockProject; 2 3 public class DeadLock2 extends Thread{ 4 private Object money; //钱 5 private Object water; //水 6 public boolean flag; //标识持有对象锁 7 public DeadLock2(Object money, Object water) { 8 super(); 9 this.money = money; 10 this.water = water; 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void run() { 15 if(flag){ //true时,持有“钱”的锁 16 synchronized(money){ 17 System.out.println("有钱,等水"); 18 try { 19 Thread.sleep(300); 20 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 21 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 } 24 synchronized(water){} 25 System.out.println("有水,等钱"); 26 } 27 }else{ 28 synchronized(water){ 29 System.out.println("有水,等钱"); 30 try { 31 Thread.sleep(300); 32 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 33 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 34 e.printStackTrace(); 35 } 36 37 } 38 synchronized(money){ 39 System.out.println("有钱,等水"); 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 }
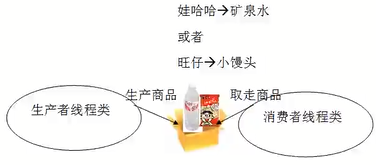
生产者消费者模式的实现
·生产者与消费者原理
·产生的问题
数据错乱