写在前面
好久没更新公众号和博客了,因为最近在研究新的方向,所以很少发文。
笔者接触编程只有一年,这一年间主要研究启发式算法在运筹学中的应用。但是由于编程基础薄弱,在进一步研究复杂运筹学问题时发现基础算法不过关导致写出的代码运行速度很慢,因此很苦恼。所以决定这个暑假补习一下基础算法,主要是刷一些简单的ACM入门题。偶尔会发一些刷题笔记(偶尔!)。和作者有类似目标的同学可以一起交流共勉!
目前在看的教程:
北京理工大学ACM冬季培训课程
算法竞赛入门经典/刘汝佳编著.-2版可以在这里下载->github
课程刷题点
Virtual Judge
刷题代码都会放在github上,欢迎一起学习进步!
今天做的是紫书,本来打算做习题,但想想反正都是做,不如还是做有答案的例题。做着做着就想,反正都是学习,不如参考一下答案…所以就水水的做了…
还要提一句,因为vjudge上UVA提交太慢了,有些代码就懒得等提交出结果了,所以不敢保证都是AC。不过以我的习惯,有些题就算是WA也懒得改了…
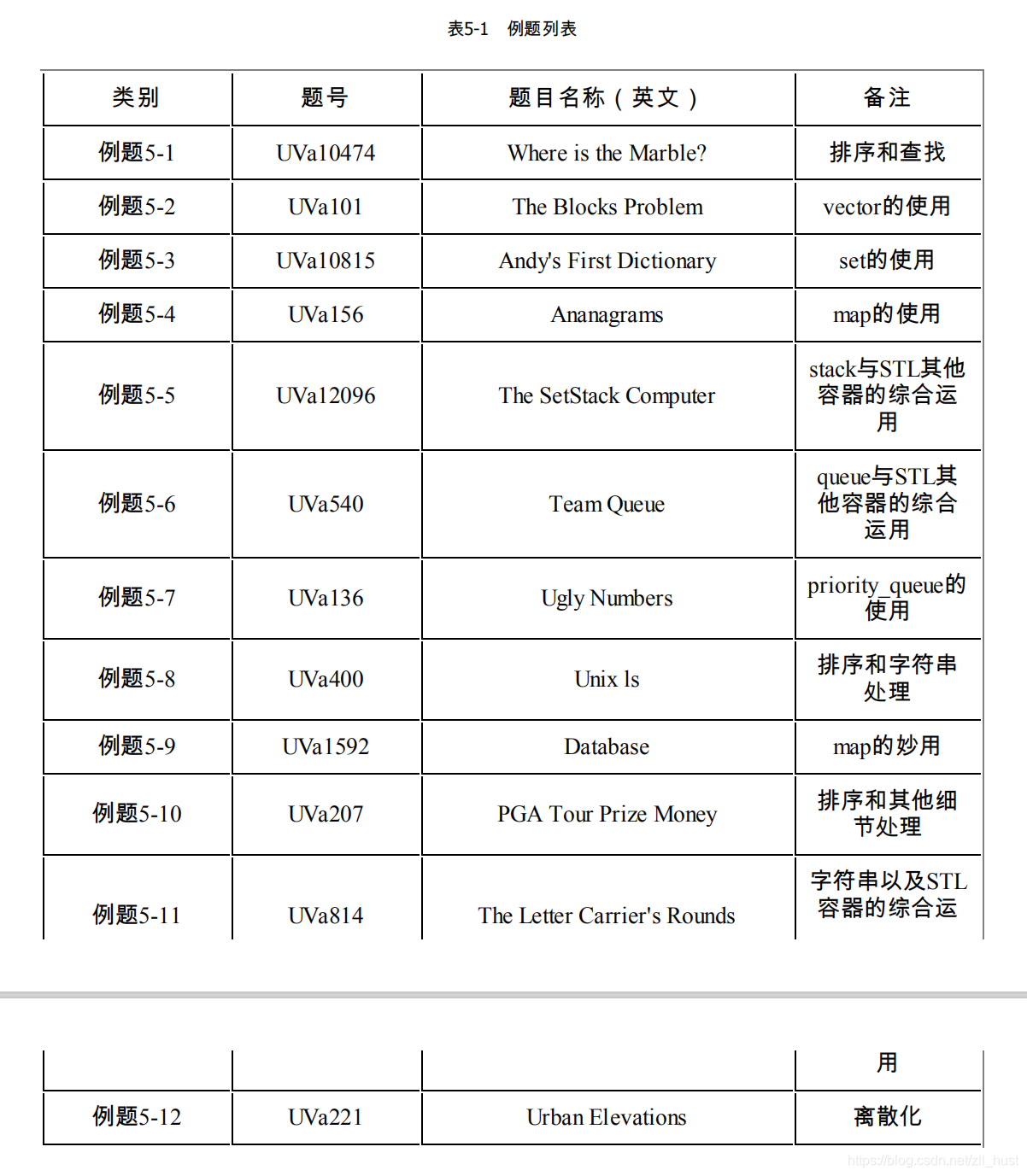
5 - 1 Where is the Marble

排序就好,通过lower_bound得到位置(input里有提是lower不是upper)。
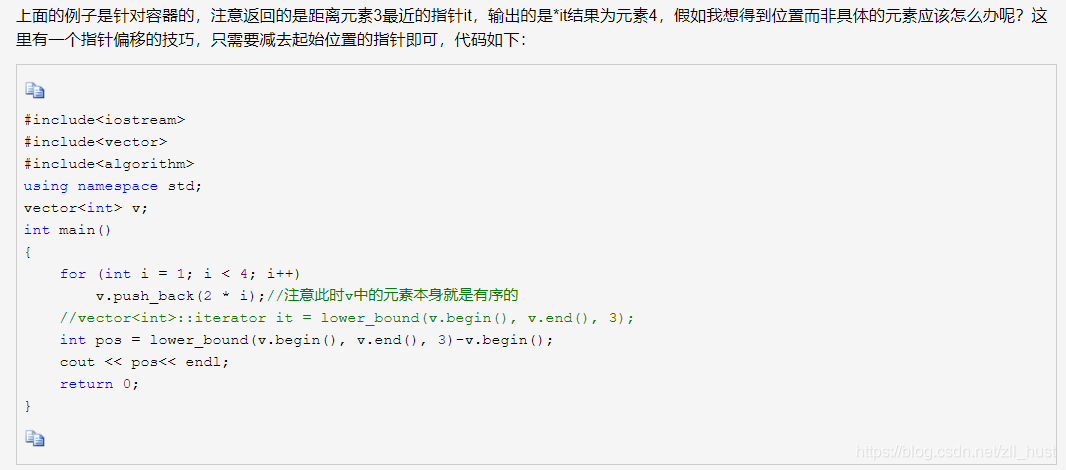
关于lower_bound这里找了一点资料,主要注意返回的是迭代器不是数组下标:

#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
// #define LOCAL
void swap(int& x, int& y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
int marbles[10005];
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n, m, kase;
kase = 1;
while (cin >> n >> m && n && m) {
printf("CASE# %d:
", kase++);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cin >> marbles[i];
sort(marbles, marbles + n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int mar;
cin >> mar;
int pos = lower_bound(marbles, marbles + n, mar) - marbles; // lowerbound返回的是指针,获得位置需要减去数组的初始位置
if (marbles[pos] == mar)
printf("%d found at %d
", mar, pos + 1);
else
printf("%d not found
", mar);
}
}
return 0;
}
5 - 2 The Blocks Problem

这题感觉没描述清楚,原题看了也没讲清楚,这里b到底是指木块还是柱子的位置?
这题还是有意思的,四个操作也可以简化,具体参考代码。因为没有搞懂,这里直接参考别人的答案。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
#define LOCAL
void swap(int &x, int &y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
string op1, op2;
vector<int> blocks[30]; // 二维数组存储方块编号
map<int, pair<int,int> > pos; // 存储每个编号对应位置
int n, a, b;
void showResult() { // 打印结果
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
printf("%d:", i); // 这里别打印空格
for (auto p : blocks[i]) printf(" %d", p);
puts("");
}
}
void clear(int a) { // 将a上面的都归位(不包含a)
int ia = pos[a].first, j = pos[a].second + 1;
for (; j < blocks[ia].size(); j ++) { // 考虑插入当前行
int k = blocks[ia][j]; // 要删除的值
blocks[k].push_back(k); // 归位
pos[k].first = k; pos[k].second = blocks[k].size()-1; // 更新位置
}
blocks[ia].erase(blocks[ia].begin()+pos[a].second+1, blocks[ia].end()); // 最后一块删除
}
void move(int a, int b) { // 将a和它上面的方块全移到含有b的柱子上
int ia = pos[a].first, left = pos[a].second, ib = pos[b].first;
for (int j = left; j < blocks[ia].size(); j ++) { // 开始移入
blocks[ib].push_back(blocks[ia][j]); // 移入b所在数组尾部
pos[blocks[ia][j]].first = ib; // 位置更新
pos[blocks[ia][j]].second = blocks[ib].size()-1;
}
blocks[ia].erase(blocks[ia].begin()+left, blocks[ia].end()); // 一块删除
}
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
cin >>n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {
blocks[i].push_back(i);
pos[i] = {i,0}; // 行列值位置
}
while (cin >>op1 && op1 != "quit") {
cin >>a >>op2 >>b;
if (pos[a].first == pos[b].first) continue; // 同一叠位置
if (op1 == "move") clear(a);
if (op2 == "onto") clear(b);
move(a,b);
}
showResult();
return 0;
}
5 - 3 Andy’s First Dictionary

保证单词不同,可以通过set。难点在筛选字符串,留下小写单词。可以用isalpha()函数和tolower()函数,用法比较简单就不多说了。
分割标点,书中用的方法是把标点整成空格,然后用stringstream输入。用着很舒服。
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
// #define LOCAL
void swap(int& x, int& y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
set<string>dir;
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
string words;
while (cin >> words) {
for (int i = 0; i < words.length(); i++) {
if (isalpha(words[i]))
words[i] = tolower(words[i]);
else
words[i] = ' ';
}
stringstream ss(words);
string buf;
while (ss >> buf)
dir.insert(buf);
}
for (auto word : dir)
cout << word << endl;
return 0;
}
5 - 4 Ananagrams

很巧今天看python课也讲到这个,好像叫“变位词”。对英文字母而言,判断两个词是否是变位词比较好的方法还是用桶。写的时候还是用了sort,方便嘛。
因为要关联原先输入的单词,还要判断单词是否出现过,可以用map连接排序单词和出现次数,用pair连接原单词和排序单词。因为pair不能用在map里面,就用vector存储pair。
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
// #define LOCAL
void swap(int &x, int &y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
map<string, int> table;
vector<pair<string, string> > words;
string standlize(const string &s)
{
string ans = s;
for (int i = 0; i < ans.length(); i++)
ans[i] = tolower(ans[i]);
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end()); // 之前没注意string是vector
return ans;
}
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
string str;
while (cin >> str && str != "#")
{
string word = standlize(str);
words.push_back(make_pair(str, word));
if(!table.count(word)) table[word] = 0;
table[word]++;
}
vector<string>ans;
for(int i = 0; i < words.size(); i++){
if(table[words[i].second] == 1)
ans.push_back(words[i].first);
}
sort(ans.begin(), ans.end());
for (auto word : ans)
cout << word << endl;
return 0;
}
5 - 5 The SetStack Computer

个人感觉这题非常有意思,算是对前面几种容器很好的综合运用,题目本身也挺有趣。
我一开始的想法是用struct表示题中的集合,用数字表示集合层数,vector表示集合个数。题中给了更好的方法。
typedef set<int> Set; // 题目要求的集合
map<Set, int> IDcache; // ID映射到集合
vector<Set> Setcache; // 根据ID提取集合
stack<int> s; // 题目中的栈,放置集合的ID
cache表示寄存器——英语不好的我注
给每个集合一个特定的ID,用ID表示集合。map构建ID到集合的映射,vector构建集合到ID的映射,操作起来就非常方便了。其中Set的lenth表示集合中的集合个数。
看看给出ID的方法:
int ID(Set x)
{
if (IDcache.count(x)) // 若集合已存在
return IDcache[x];
Setcache.push_back(x); // 添加新集合
return IDcache[x] = Setcache.size() - 1;
}
注意每一个new的Set都是不一样的,就算都是空的也是不一样的,在map中都各占一个ID,所以ID可以对应到Set。
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <queue>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define INT_MAX 0x7fffffff
#define INT_MIN 0x80000000
#define LOCAL
void swap(int &x, int &y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
typedef set<int> Set; // 题目要求的集合
map<Set, int> IDcache; // ID映射到集合
vector<Set> Setcache; // 根据ID提取集合
stack<int> s; // 题目中的栈,放置集合的ID
int ID(Set x)
{
if (IDcache.count(x)) // 若集合已存在
return IDcache[x];
Setcache.push_back(x); // 添加新集合
return IDcache[x] = Setcache.size() - 1;
}
#define ALL(x) x.begin(), x.end()
#define INS(x) inserter(x, x.begin())
int main()
{
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int n;
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
int m;
cin >> m;
while (m--)
{
string opr;
cin >> opr;
if (opr[0] == 'P')
s.push(ID(Set()));
else if (opr[0] == 'D')
s.push(s.top());
else
{
Set x1 = Setcache[s.top()];
s.pop();
Set x2 = Setcache[s.top()];
s.pop();
Set x;
if (opr[0] == 'U')
set_union(ALL(x1), ALL(x2), INS(x));
else if (opr[0] == 'I')
set_intersection(ALL(x1), ALL(x2), INS(x));
else if (opr[0] == 'A')
{
x = x2;
x.insert(ID(x1));
}
s.push(ID(x));
}
cout << Setcache[s.top()].size() << endl;
}
cout << "***" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
代码中在取交集并集是用了STL的函数,这里找了些资料,看完后大概就能明白了:



end。