1. 配置
尽管在Prometheus服务器的设计中存在关于推和啦的激烈争论,以及使用拉的慎重决定,但是在一些合法的情况下,推更合适。
这个导出程序应该只在非常特定的用例中使用,如前所述,我们应该注意一些常见的陷阱。一个可能的问题是缺乏高可用性,使其成为单点故障。这也会影响可伸缩性,因为容纳更多度量/客户端的唯一方法是垂直伸缩实例(添加更多资源)或分片(为不同的逻辑组拥有不同迪菲Pushgateway实例)。通过使用Pushgateway,Prometheus不会直接获取应用程序实例,这就防止了up指标成为健康状况的代理
要推送一个度量,您需要使用一下URL路径定义向Pushgateway端点发送一个HTTP POST请求。
http://<pushgateway_address>:<push_port>/metrics/job/<job_name>/[<label_value1>]/[<label_nameN>]/[<label_valueN>]
在这里,<job_name>将成为被推送的指标标签作业的值,而<label_name>/<label_value>对将成为额外的标签/值对。请记住,在手动删除之前,或者在没有配置持久性的情况下重启之前,指标都是可用的。
Pushgateway是一个中心点,等于把推送过来的度量值收集一下。然后Prometheus从它这里拉取值。在标签冲突中,普罗米修斯将源标签分别重命名为exports_instance和exports_job。为了避免这种行为,在挂作业定义中应该使用honor_tags: ture ,以确保流行的标签来自Pushgateway。

2.部署
tar xfvz pushgateway-1.4.2.linux-amd64.tar.gz
mv mv pushgateway-1.4.2.linux-amd64/pushgateway /usr/bin
vim /etc/systemd/system/pushgateway.service
[Unit]
Description=pushgateway
Documentation=https://github.com/prometheus/pushgateway
After=network.target
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/bin/pushgateway
Restart=on-failure
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
systemctl daemon-reload
systemctl enable pushgateway.service
systemctl start pushgateway.service # 默认监听在9091端口
3.向pushgateway发送指标
一旦Pushgateway运行,你就可以开始发送指标。大多数Prometheus客户端库都支持向Pushgateway发送指标,以暴露它们以进行抓取。查看网关如何工作的最简单方法是使用curl等命令行工具来发送指标。让我们向网关推送一个指标。
echo 'batchjob1_user_counter 2' | curl --data-binary @- http://localhost:9091/metrics/job/batchjob1
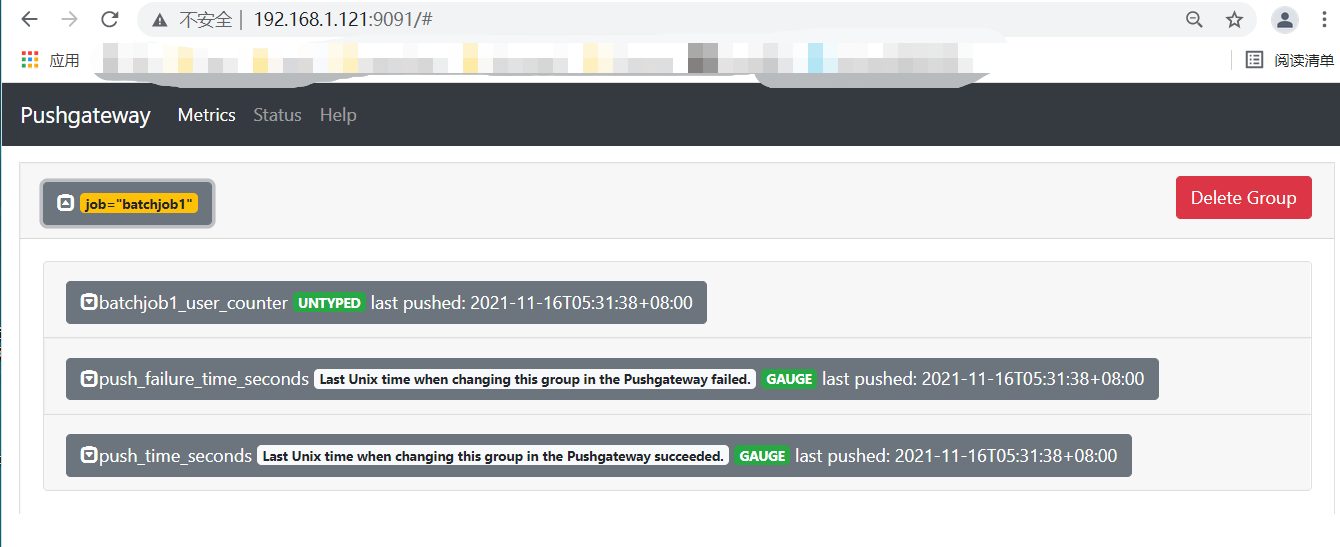
我们将指标推送到路径/metrics。URL使用标签组成,这是/metrics/job/
/metrics/job/<jobname>{/<label>/<label>}
让我们在URL中为指标添加一个instance标签
echo 'batchjob1_user_counter 2' | curl --data-binary @- http://localhost:9091/metrics/job/batchjob1/instance/sidekiq_server
[info]你不能将/作为标签值或作业名称的一部分使用,即使是转义。这是因为解码序列无法确定转义的内容,详细信息请参考Go URL 文档。
在上面的示例中,我们通过echo将指标batch1_user_counter2从作业batchjob1发送到网关。这将为作业batchjbo1创建一个新的指标组,其instance标签为sidekiq_server。指标组是指标的集合,你可以在分组中添加和删除指标,甚至可以删除整个组。由于网关是缓存而不是聚合器,因此指标组将保持运行,直到网关停止或删除它们为止。
这个计数器是我们可以发送的最简单的指标,我们将它命名batchjob1_user_counter,并为其赋值2.
我们可以通过将标签括在{}中来为推送的指标添加标签。
echo 'batchjob1_user_counter{job_id="123ABC"} 2' | curl --data-binary @-
http://localhost:9091/metrics/job/batchjob1/instance/sidekiq_server
4.在pushgateway上查看指标
curl http://localhost:9091/metrics
5.删除pushgateway中的指标
指标保存在网关中(假设未设置持久性),直到网关重启或者指标被删除。我们可以使用pushgateway API删除指标,这里再次使用curl作为示例。
curl -x DELETE localhost:9091/metrics/job/batchjob1
这将删除作业batchjob1的所有指标。你可以使用更精细的路径来进一步限制选择,例如,仅删除特定实例中的那些指标。
curl -x DELETE localhost:9091/metrics/job/batchjob1/instance/sidekiq_server
[info]还可以使用仪表板上的”Delete Group“按钮从pushgateway中删除整个指标组。
6.抓取Pushgateway
Pushgateway只是指标的临时停靠站。我们现在需要将他们放入Prometheus服务器。为此,需要创建一个作业。
- job_name: pushgateway
honor_labels: true
file_sd_configs:
- files:
- targets/pushgateway/*.json
refresh_interval: 5m
Pushgateway目标:
cd /etc/prometheus/targets
mkdir pushgateway
cd pushgateway
vim test1.json
[{
"targets": ["192.168.1.121:9091"]
}]
然后我们指定了honor_labels选项并将器设置为true。正如之前所了解的,当Prometheus抓取目标时,他将附加抓取作业的名称(此处为Pushgateway),以及填充了目标的主机或IP地址的instance标签。通过pushgateway,指标已经有了job和instance标签,用于指示指标的来源。我们希望在Prometheus中保留这些信息,而不是在抓取网关时由服务器进行重写。
如果honor_labels设置为true,那么Prometheus将使用pushgateway上的job和instance标签。如果设置为false,那么它将重命名这些值,在它们前面加上exported_前缀,并在服务器上为这些标签附加新值。