1、标准流(普通流/文档流)
标准流就是标签按照规定好的默认方式排列
(1)块级元素会独占一行,按照从上到下的方式排列
(2)行内元素会按照顺序,从左到右的顺序进行排列,遇到父元素则自动换行
(3)纵向排列标准流,横向排列用浮动
2、浮动的简单应用
(1)让多个块级元素水平排列在一行(这里将行内元素转换为了块级元素)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; } .myclass2{ background-color:black; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; } .myclass3{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; } </style> </head> <body> <span class="myclass1">1</span> <span class="myclass2">2</span> <span class="myclass3">3</span> </body> </html>
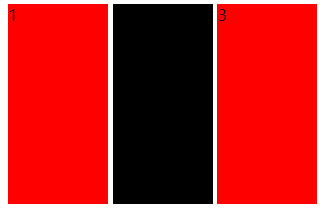
可以看出,块元素在显示的时候,他们之间会有空隙。
(2)添加浮动
<style type="text/css"> .myclass1{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } .myclass2{ background-color:black; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } .myclass3{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } </style>
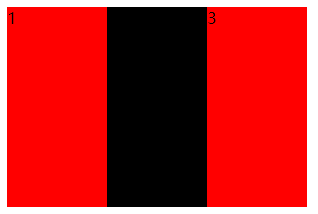
在标准流中不能实现的布局效果,在浮动中就可以很容易地完成,浮动可以改变标签的默认的排列方式。
3、浮动(左浮动与右浮动)
(1)左浮动
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } .myclass2{ background-color:black; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="myclass1"></div> <div class="myclass2"></div> </body> </html>

两个块元素本来是要每个div独占一行的,但是在添加了浮动以后就会合并到一行显示,因为设置的是左浮动,他们两个都是靠左排列的。
(2)一个左,一个右
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } .myclass2{ background-color:black; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: right; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="myclass1"></div> <div class="myclass2"></div> </body> </html> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: left; } .myclass2{ background-color:black; 100px; height: 200px; display:inline-block; float: right; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="myclass1"></div> <div class="myclass2"></div> </body> </html>

4、浮动的特性
(1)浮动元素会脱离标准流(不再保留原来的位置,也就是说其它元素可以占用浮动元素的位置)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1{ background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; float: left; } .myclass2{ background-color:black; 200px; height: 300px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="myclass1"></div> <div class="myclass2"></div> </body> </html>
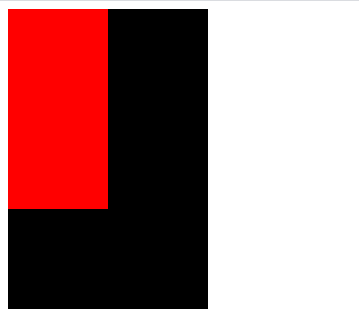
在对红色元素添加了浮动以后,他的位置是可以被其他的元素所占用的。
(2)浮动元素会在一行内显示并且元素顶部对齐
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1 { background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; float: left; } .myclass2 { float: left; background-color: black; 200px; height: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="myclass1"></div> <div class="myclass2"></div> </body> </html>

如果是标准流的话,他们是上下显示的,即一个div元素独占一行
(3)会具有行内块元素的特征
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .myclass1 { background-color: red; 100px; height: 200px; float: left; } .myclass2 { float: left; background-color: black; 200px; height: 200px; } </style> </head> <body> <span class="myclass1"></span> <span class="myclass2"></span> </body> </html>

一般情况下,行内元素转换为块元素需要添加属性,但是,在添加了浮动以后就可以自动转换为块元素。
4、浮动元素和标准父级搭配使用
一般情况下,先用标准流的父元素排列上下位置,之后内部子元素采取浮动的策略排列左右位置
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>test</title> <style type="text/css"> .bigbox { background-color: #ffffcc; 1100px; height: 400px; margin: 0 auto; } .left{ height: 400px; 300px; float: left; background-color: #fffcf5; } .right{ height: 400px; 600px; float: right; background-color: #e3dc89; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="bigbox"> <div class="left"></div> <div class="right"></div> </div> </body> </html>

这里面一共有三个盒子,其中父盒子包含两个子盒子。没有父元素的话,盒子是直接靠近浏览器的边缘排列的,但是有了父盒子以后就只能在父盒子里面,也就是说父盒子能够限制子盒子的位置。