IDE 集成开发环境(Integrated Development Environment )
VIM #经典的linux下的文本编辑器
Emacs #linux文本编辑器,比VIM更容易使用
Eclipse #Java IDE,支持python,C,C++
Visual Studio #微软开发的IDE,支持python ,C++,C#,java
notepad++
subline python开发的
pycharm 主要用于python开发的IDE
在python3中,已经不区分int和long int,统一为int
布尔 只有两种状态,分别是真(True)和假(False)
salary.isdigit() 计算机中,一切皆为对象。 世界万物,皆为对象,一切对象皆可分类
1 C:UsersEthan>python 2 Python 3.5.2 |Anaconda 4.2.0 (64-bit)| (default, Jul 5 2016, 11:41:13) [MSC v.1900 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32 3 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. 4 >>> name = "Ethan" 5 >>> age = "25" 6 >>> print("You name is",name,"and age is",age) 7 You name is Ethan and age is 25 8 9 >>> print("You name is" + name + "and age is" + age) 10 You name isEthanand age is25
1 C:UsersEthan>python 2 Python 3.5.2 |Anaconda 4.2.0 (64-bit)| (default, Jul 5 2016, 11:41:13) [MSC v.1900 64 bit (AMD64)] on win32 3 Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. 4 >>> range(3) 5 range(0, 3) 6 >>> for i in range(3): 7 ... print(i) 8 ... 9 0 10 1 11 2 12 13 for i in range(10): 14 .... #如果这里有break,那么for循环执行break以后,就不会执行else语句 15 else: #只要上面的for循环正常执行完毕,中间没被打断,就执行下面的else语句 16 ....
while 循环
while 条件: 语句 # 如果条件为真(True),则执行这条语句,否者不执行
终止循环的第一个方法:改变条件,终止循环。引入标志位。
flag = True while flag: print("锦江近西烟水绿,") print("新雨山头荔枝熟。") print("万里桥边多酒家,") print("游人爱向谁家宿?") 结果: 锦江近西烟水绿, 新雨山头荔枝熟。 万里桥边多酒家, 游人爱向谁家宿? 锦江近西烟水绿, 新雨山头荔枝熟。 万里桥边多酒家, 游人爱向谁家宿? ...
flag = True while flag: print("锦江近西烟水绿,") print("新雨山头荔枝熟。") print("万里桥边多酒家,") print("游人爱向谁家宿?") flag = False 结果: 锦江近西烟水绿, 新雨山头荔枝熟。 万里桥边多酒家, 游人爱向谁家宿?
例1:输出1到100的所有数字
1 a = 1 2 while a <= 100: 3 print("a:",a) 4 a += 1
例2:使用while循环求出1-100所有数的和
sum = 0 a = 1 while a <= 100: sum += a # sum = sum + a a += 1 # a = a + 1 print("sum:", sum) 结果: sum: 5050
终止循环的第二个方法:break
跳出整个循环
1 flag = True 2 print("***********") 3 while flag: 4 print("锦江近西烟水绿,") 5 print("新雨山头荔枝熟。") 6 break 7 print("万里桥边多酒家,") 8 print("游人爱向谁家宿?") 9 10 print("////////////////////////////////////") 11 12 结果: 13 *********** 14 锦江近西烟水绿, 15 新雨山头荔枝熟。 16 ////////////////////////////////////
例3:打印1~100所有的偶数
#方法一: i = 1 while i <= 100: if i % 2 == 0: print(str(i) + "是偶数") i += 1 # 方法二: flag = True a = 1 while flag: if a % 2 == 0: print(a,"是偶数") a += 1 if a >= 101: break # 方法三 a = 2 while a <= 100: print(a) a += 2
终止循环的第三个方法:continue
终止本次循环,继续下一次循环
flag = True print("********************") while flag: print("锦江近西烟水绿,") print("新雨山头荔枝熟。") continue print("万里桥边多酒家,") print("游人爱向谁家宿?") print("////////////////////////////////////") 结果: 锦江近西烟水绿, 新雨山头荔枝熟。 锦江近西烟水绿, 新雨山头荔枝熟。 ...
例4:使用while循环打印 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10
1 a = 0 2 while a < 10: 3 a += 1 4 if a == 7: # 当满足这个条件时,这个循环将有continue来操控,即continue后面的语句将不会被执行,继续下一次循环 5 continue 6 print(a)
例5:请输出1,2,3,4,5,95,96,97,98,99,100
1 a = 0 2 while a < 100: 3 a += 1 4 if a > 5 and a < 95: 5 continue 6 7 print(a)
while...else:
当while 循环正常执行完以后(中间没有被break 中止),会继续执行else后面的语句
1 a = 1 2 while a <= 5: 3 print("loop", a) 4 a += 1 5 else: 6 print("loop over") 7 8 结果: 9 loop 1 10 loop 2 11 loop 3 12 loop 4 13 loop 5 14 loop over
1 a = 1 2 while a <= 5: 3 print("loop", a) 4 if a == 3: 5 break 6 a += 1 7 else: 8 print("loop over") 9 10 结果: 11 loop 1 12 loop 2 13 loop 3
格式化输出
%:占位符
%s:字符串占位符
%d:数字占位符
1 """ 2 ------------ info of 王麻子 ----------- 3 Name : 王麻子 4 Age : 22 5 job : Teacher 6 Hobbie: basketball 7 ------------- end ----------------- 8 """ 9 10 name = input("请输入名字:") 11 age = input("请输入年龄:") 12 job = input("请输入工作:") 13 hobbie = input("请输入爱好:") 14 15 msg = '''------------ info of %s ----------- 16 name : %s 17 age : %s 18 job : %s 19 hobbie : %s 20 ''' % (name, name, age, job, hobbie) # 这行的 % 号就是把前面的字符串与拓号后面的变量关联起来 括号里面要一一对应 21 print(msg) 22 23 结果: 24 请输入名字:zcj 25 请输入年龄:24 26 请输入工作:student 27 请输入爱好:football 28 ------------ info of zcj ----------- 29 name : zcj 30 age : 24 31 job : student 32 hobbie : football
1 name = input("请输入名字:") 2 # age = input("请输入年龄:") 3 age = int(input("请输入年龄:")) 4 job = input("请输入工作:") 5 hobbie = input("请输入爱好:") 6 7 msg = '''------------ info of %s ----------- 8 name : %s 9 age : %d 10 job : %s 11 hobbie : %s 12 ''' % (name, name, age, job, hobbie) # 括号里面要一一对应 13 print(msg) 14 15 结果: 16 请输入名字:zcj 17 请输入年龄:24 18 请输入工作:student 19 请输入爱好:eating 20 ------------ info of zcj ----------- 21 name : zcj 22 age : 24 23 job : student 24 hobbie : eating
1 msg = "我是%s, 今年%d岁,当前学习进度是80%" % ('zcj', 24) 2 print(msg) 3 4 结果: 5 Traceback (most recent call last): 6 File "D:/python_learning/格式化输出.py", line 32, in <module> 7 msg = "我是%s, 今年%d岁,当前学习进度是80%" % ('zcj', 24) 8 ValueError: incomplete format
1 msg = "我是%s, 今年%d岁,当前学习进度是80%%" % ('zcj', 24) 2 print(msg) 3 4 结果: 5 我是zcj, 今年24岁,当前学习进度是80%
基本运算符
python中的运算可分为算术运算、比较运算、逻辑运算、赋值运算、成员运算、身份运算、位运算。
算术运算
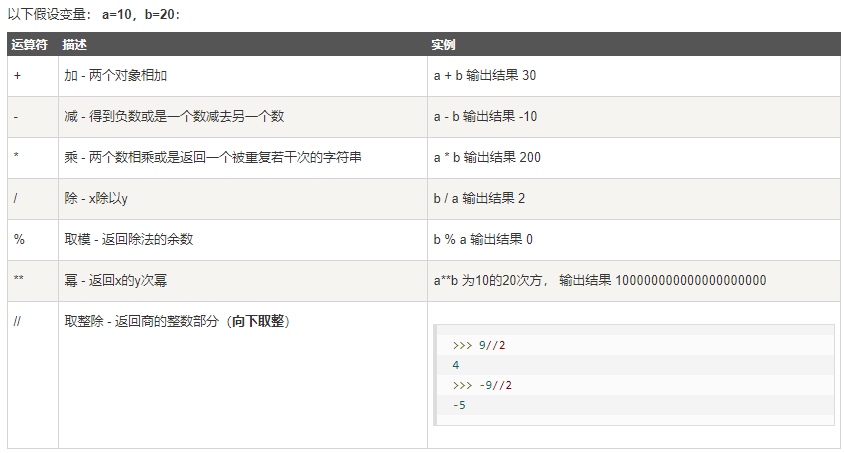
比较运算
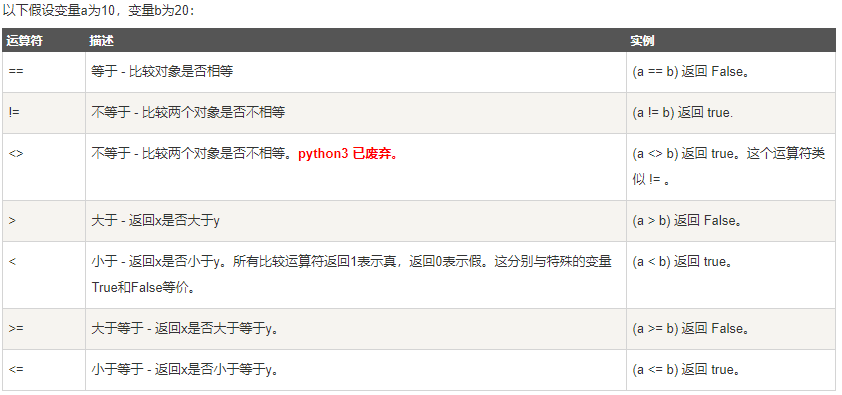
赋值运算
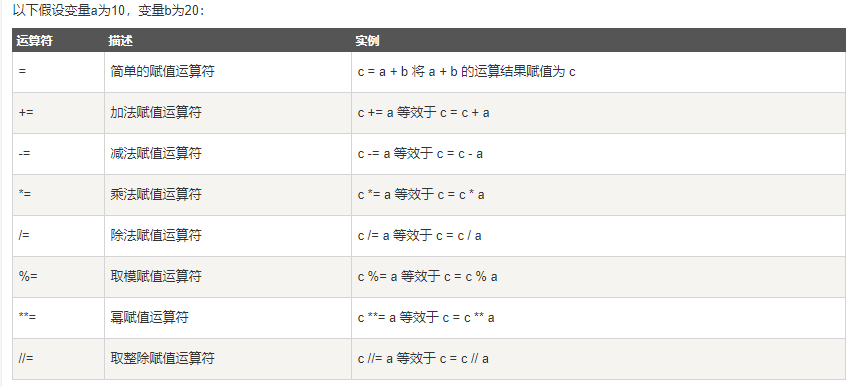
位运算符
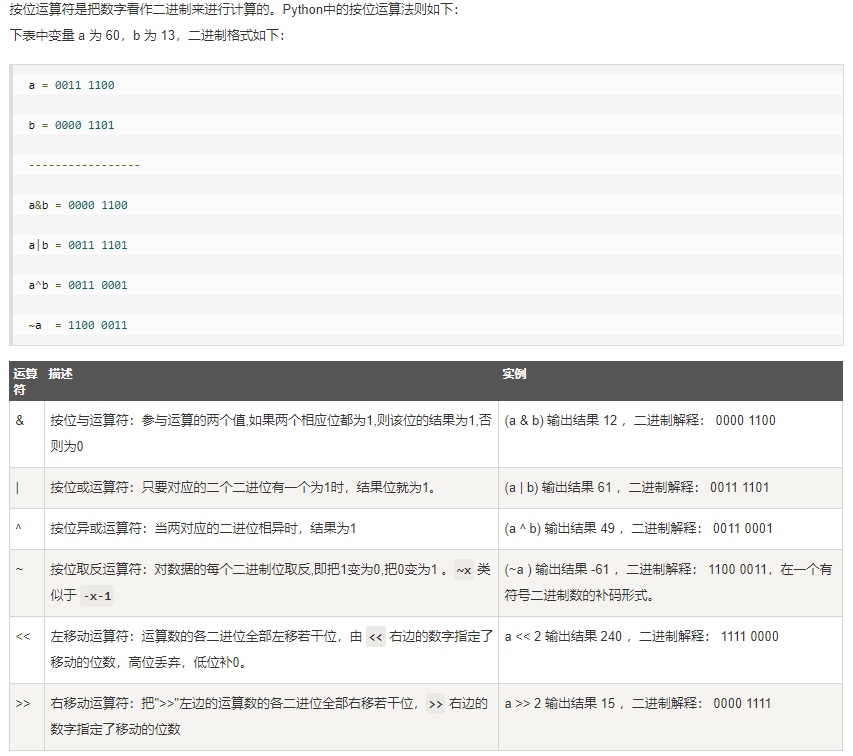
逻辑运算符
需要注意在没有()的情况下not 优先级高于 and,and优先级高于or,即优先级关系为( )>not>and>or,同一优先级从左往右计算。

1 >>> 3 > 4 or 4 < 3 and 1 == 1 2 False
3 >>> 1 < 2 and 3 < 4 or 1 > 2 4 True
5 >>> 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1 6 True
7 >>> 1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 < 8 8 False
9 >>> 1 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6 10 False
11 >>> not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6 12 False
1 >>> 1 or 2 2 1 3 >>> 3 or 2 4 3 5 >>> 0 or 11 6 11 7 >>> 5 or 0 8 5 9 >>> -1 or 44 10 -1 11 >>> -1 or 5 12 -1 13 >>> -1 or -5 14 -1 15 >>> -1 or 0 16 -1 17 >>> 0 or -1 18 -1
1 >>> 1 and 2 2 2 3 >>> 4 and 55 4 55 5 >>> -1 and 3 6 3 7 >>> -5 and 44 8 44 9 >>> -1 and -5 10 -5 11 >>> 0 and 5 12 0 13 >>> 0 and 99 14 0 15 >>> 2 and 100 16 100 17 >>> 9 and 0 18 0 19 >>> -1 and 0 20 0 21 >>> 0 and -5 22 0 23 >>> 1 and 2 or 3 and 4 24 2 25 >>> 1 > 2 and 3 or 6 26 6
1 >>> s = '00100' 2 >>> int(s) 3 100 4 >>> i = 100 5 >>> str(i) 6 '100' 7 >>> type(str(i)) 8 <class 'str'> 9 >>> 10 >>> j = 0 11 >>> bool(i) 12 True 13 >>> bool(j) 14 False 15 >>> int(True) 16 1
成员运算
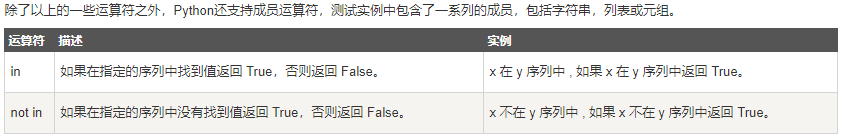
1 >>> a = [1, 2, 5, 44, 11] 2 >>> b = 10 3 >>> b in a 4 False 5 >>> b not in a 6 True 7 >>> s = 'safsasfascwa' 8 >>> s1 = 'f' 9 >>> s1 in s 10 True 11 >>> s1 not in s 12 False 13 >>>
优先级
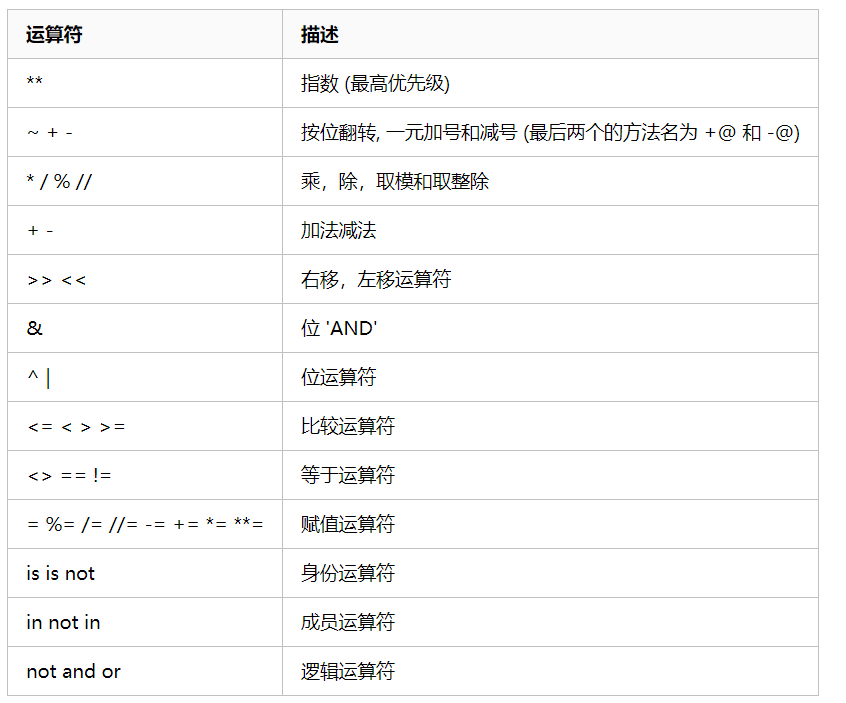
编码
GBK:一个英文用一个字节,一个中文用两个字节,所以:'a哈哈' 如果是GBK编码占5个字节
UTF-8: 一个英文用一个字节,一个中文用三个个字节,所以:'a嗯哼' 如果是UTF-8编码占7个字节。
8bit = 1byte 1024byte = 1KB 1024KB = 1MB 1024MB = 1GB 1024GB = 1TB 1024TB = 1PB 1024TB = 1EB 1024EB = 1ZB 1024ZB = 1YB 1024YB = 1NB 1024NB = 1DB