堆:
树这种结构 本身在计算机科学领域 占有很重要的地位,这种数据结构之所以占有重要的地位,不仅仅是因为二分搜索树这样的一种结构, 是树本身这种形状可以产生很多拓展,对于不同的问题 ,我们可以稍微改变 或者 限制树这种数据结构的性质,从而产生不同的数据结构,高效的解决不同的问题,
从节开始,将会有四个章节介绍 四个不同的例子,它们分别是堆,线段树,字典树 以及 并查集 ,通过这些不同的树的结构,我们可以领会到 数据结构的灵活之处,
什么是优先队列:
优先队列(相对 高层的数据结构) 是 出队,入队和 顺序 无关,和 优先级 有关,其实用的最多是 谁优先出队,
优先队列的接口 和 普通队列是一样,只不过是在出队操作上 和 队首 元素上 是不同的,

优先队列的底层结构 实现也是可以由不同数据结构来构成, 这里提供的是三种类型的数据结(普通线性结构 , 顺序线性结构, 堆)
这里假设 优先级 是谁最大 ,

这里是用堆作为数据结构 作为优先队列的底层实现, 如果有时间也可以用 普通线性结构 或者顺序线性结构 来实现 优先队列 然后 再和 我们这里用堆实现的 优先队列 去比较性能,这有助于 对数据结果的学习!
堆的 基本结构:
在计算机的世界中,凡是时间复杂度 为 logn 的,那么差不多一定 和树这个结构有关系, 归并排序 和 快速排序 它们都是logn 级别的,(虽然没有直接使用树,但是它的递归过程 其实是个隐形 树 )
一个堆本身,其实也是一颗树,
二叉堆:
二叉堆 是一个特殊的树, 二叉堆 是一课完全二叉树,
满二叉树: 除最后一层无任何子节点外,每一层上的所有结点都有两个子结点的二叉树。
完全二叉树:完全二叉树是由满二叉树而引出来的。对于深度为K的,有n个结点的二叉树,当且仅当其每一个结点都与深度为K的满二叉树中编号从1至n的结点一一对应时称之为完全二叉树。
满二叉树:

完全二叉树: (其实就是一层一层的放,直到放不下了 )
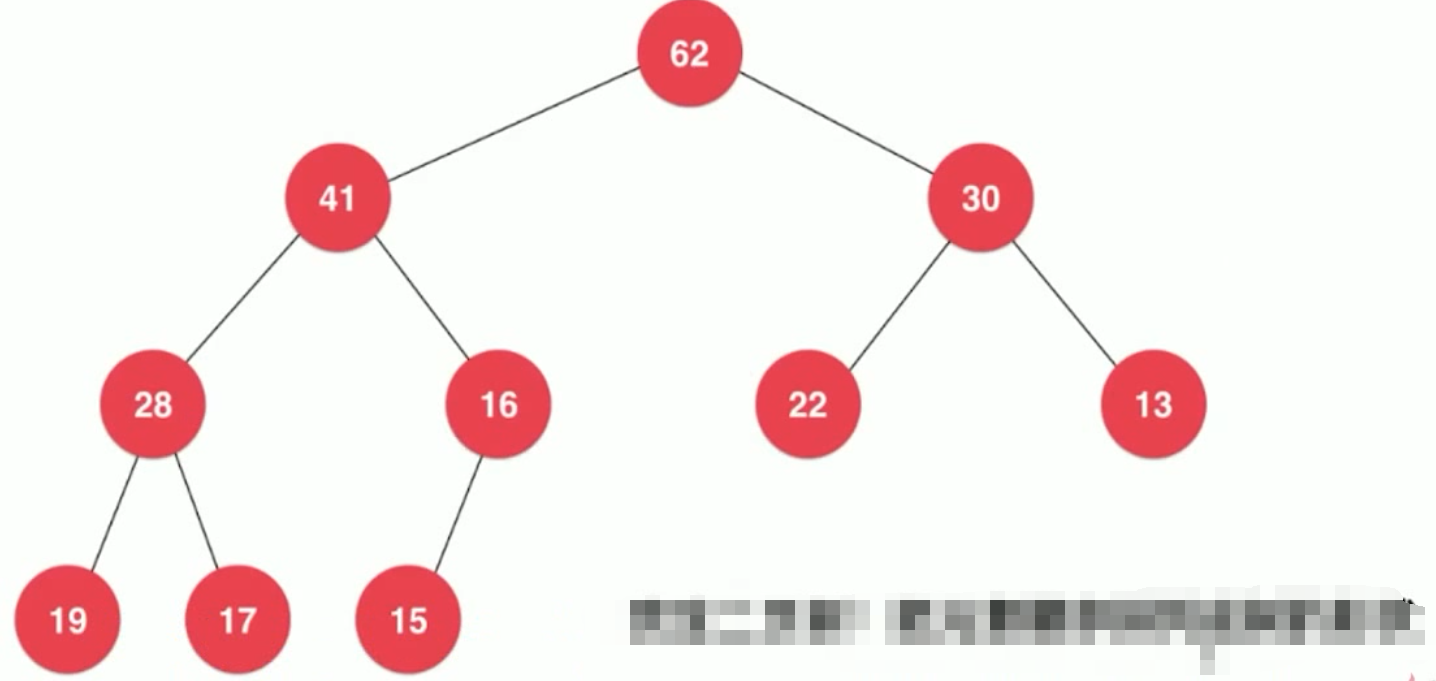
二叉堆 首先是个完全二叉树,除此之外,
它还有个特殊的性质: 堆中 每个节点的值总是 不大于 其父节点的值 (所有个节点值都大于它的孩子的值 )。 这个时候的堆,我们叫做 最大堆 (每个节点值 都大于 它的孩子的节点的值 ),相应也可以定义出最小堆 !
总结: 最大堆:首先是个 完全二叉树,然后,每个节点的值都大于它的孩子节点的值!
实现堆的 底层结构:
当然可以使用 二叉搜索树(使用Node ,left ,right),但是,因为堆是一层 一层的,我们可以使用数组 来实现堆,

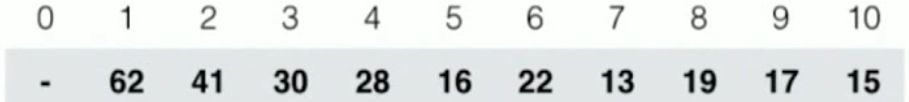
此时,如何寻找一个节点的 左右孩子呢?
其实是有规律的:
一个节点的左孩子的 索引 = 该节点 索引 * 2
一个节点的右孩子的索引 = 该节点 索引 * 2 + 1
而且:对于一个节点,它的父节点的索引= 该节点的 索引 / 2 (注:这里是整除 ,)
注: 上图中 根节点,我们都是从 1 开始标,这样有助于计算,但是,此时的数组中 索引 0 就空出来了, 不过从0 开始也可,只不过 索引关系会发生一点改变而已,
下面实现MaxHeap 最大堆:
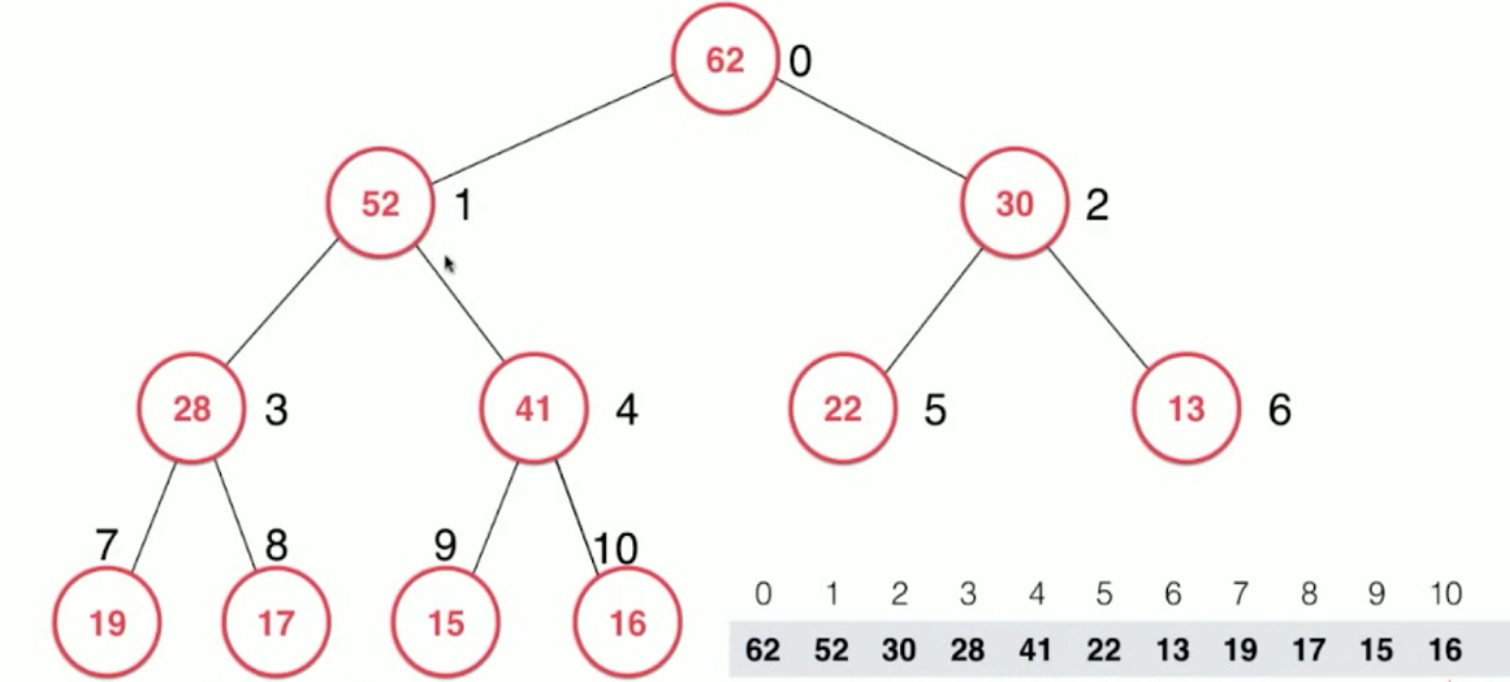
向堆中添加元素(sift up )时:
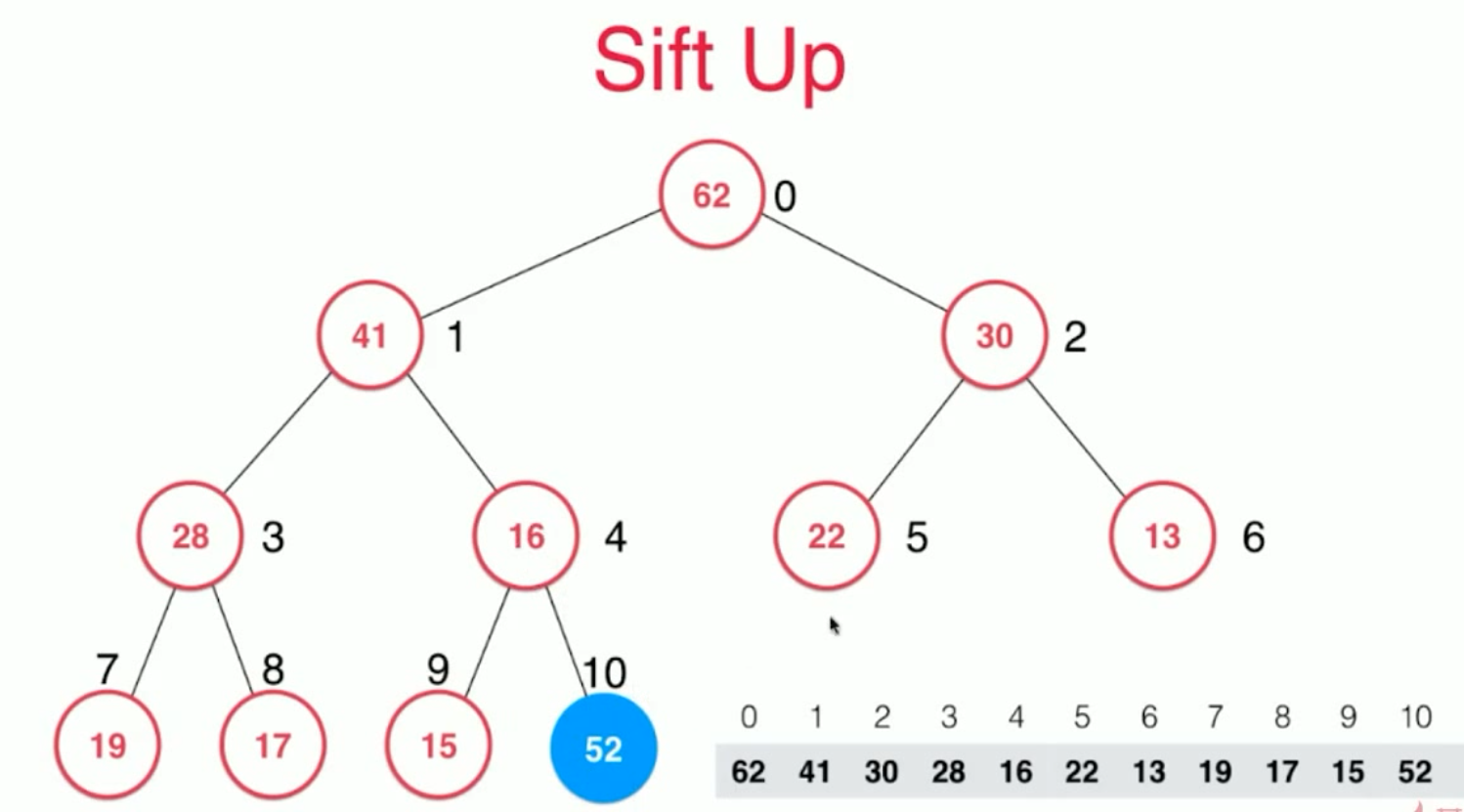
单单加进来,还不行,因为16 已经不大于 52了,所以此时还要进行调整,
调整方案就是 从添加的元素位置一路向上 找父亲节点进行比较, 大的上浮,
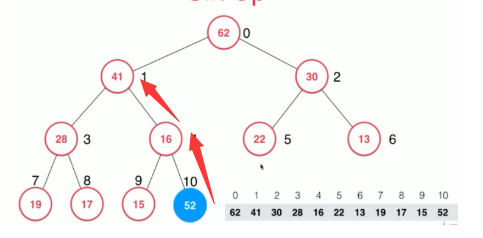
调整之后的方案:
向堆中取出元素(sift down )时:
此时,将堆顶 元素直接去掉,然后,还是将最后一层 最后一个放过去,
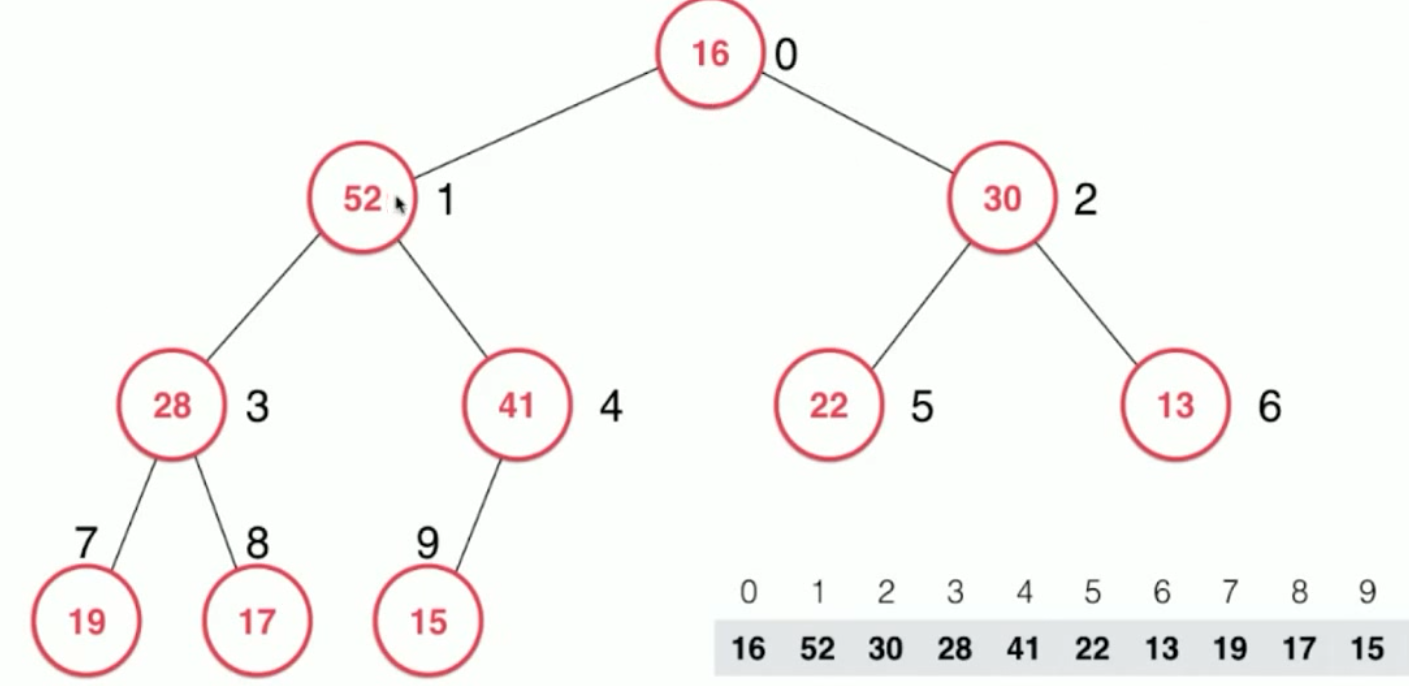
但是,此时是不满足 最大堆 的最大 性质的,所以还是需要进行调整,
这时候需要将 16 下沉 下来,每次它和 两个孩子大小进行比较,选择 较大的,(如果它比自己还大) 进行下沉交换 。
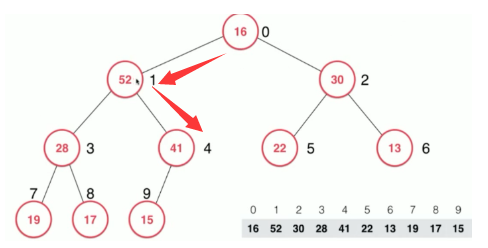
即:


1 package zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class MyArray<T> { 4 private T[] data; //数组 5 private int size; //数组实际大小, 6 //容量不用写,可以由data.length()得知 7 8 //满参构造函数 9 public MyArray(int capacity){ 10 // this.data = new int[capacity]; 11 // this.data = new T[capacity]; //不支持这样 12 this.data = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; //先new 出个 Object[] 类的,然后转为 T[] 13 this.size = 0; //开始时 实际大小size =0 14 } 15 //空参构造器 16 public MyArray(){ 17 this(10); //如果是空参的话,调用有参构造器。默认是10 18 } 19 20 //获取数组中的元素的个数 21 public int getSize(){ 22 return this.size; 23 } 24 25 //获取数组的容量 26 public int getCapacity(){ 27 return this.data.length; 28 } 29 30 //数组中是否为空 31 public boolean isEmpty(){ 32 return this.size ==0; 33 } 34 /////////////////////增//////////////////////////// 35 //向 数组的末尾添加一个新元素 36 public void addLast(T num){ 37 /* 38 if(size == this.data.length){ 39 //此时开辟的空间已经满了 40 //这里先抛出一个异常 41 throw new IllegalArgumentException("addLast failed.数组已经满了"); 42 } 43 this.data[size] = num; 44 size ++; //要维持数组 指针。 size 是当前数组中的个数。 45 */ 46 //此时其实可以直接复用 insert ()函数 47 insert(this.size,num); 48 } 49 // 向数组头添加元素 (直接复用 向指定位置添加元素的函数 ) 50 public void addFirst(T num){ 51 insert(0,num); 52 } 53 54 //向 指定数组位置添加一个新元素 55 public void insert(int idx,T num){ 56 if(this.size == this.data.length){ 57 // throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组已经放满了"); 58 /*此时对其扩容*/ 59 resize(2*this.data.length); 60 61 62 } 63 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size ) 64 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引非法"); 65 66 for(int i=this.size-1;i >= idx;--i){ 67 this.data[i+1] = this.data[i]; 68 } 69 this.data[idx] = num; 70 //更新size 71 this.size ++; 72 } 73 74 //////////////////////删/////////////////////////////////////// 75 //删除第一个 76 public T removeFirst(){ 77 return remove(0); //删除并将之返回出去 78 } 79 80 //删除最后一个 81 public T removeLast(){ 82 return remove(this.size-1); 83 } 84 85 //删除指定位置 的元素 86 public T remove(int idx){ //返回 删除的元素 87 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size -1) 88 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx错误!"); 89 T temp = this.data[idx]; 90 for (int i =idx;i<this.size - 1;i++){ 91 this.data[i] = this.data[i+1]; 92 } 93 this.size -- ; 94 95 //动态减少 当数组中的元素少于空间的一半的时候,就缩减空间。 96 if(this.size == this.data.length / 2){ 97 System.out.println("size = "+this.size); 98 99 resize(this.data.length/2); 100 } 101 return temp; 102 } 103 104 //删除 某个元素 不根据其位置 //它之所以返回void 是因为调用着已经知道的element ,所以没必要再返回出来了。 105 public void removeElement(T element){ 106 //首先要 寻找是否有 element 107 int idx = find(element); 108 if(idx == -1){ 109 throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有该元素"); 110 }else{ 111 remove(idx); 112 } 113 } 114 115 //////////////////////改/////////////////////////////////////// 116 //修改索引为 idx 的元素为 num 117 public void setByIndex(int idx,T num){ 118 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size) 119 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 120 121 this.data[idx] = num; 122 } 123 124 125 //////////////////////查/////////////////////////////////////// 126 //获取整个数组的概括 127 //重写 toString() 当打印arr 时候,就会调用该方法! 128 @Override 129 public String toString(){ 130 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); 131 res.append(String.format("Array:size = %d,capacity = %d ",this.size,this.data.length)); 132 res.append('['); 133 for (int i =0 ;i<this.size;i++){ 134 res.append(data[i]); 135 if(i != this.size -1) 136 res.append(", "); 137 } 138 res.append(']'); 139 return res.toString(); 140 } 141 //获取idx 索引位置的 元素 142 public T getByIndex(int idx){ 143 if (idx < 0 || idx >this.size) { 144 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引传入错误!"); 145 } 146 return this.data[idx]; 147 } 148 149 //////////////////////包含/////////////////////////////////////// 150 public boolean contains(T num){ 151 for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){ 152 if(this.data[i] == num){ 153 return true; 154 } 155 } 156 return false; 157 } 158 //////////////////////寻找//////////////////////////////////// 159 public int find(T num){ 160 //寻找数组中是否有 num ,如果有返回其索引,反之 返回-1 161 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 162 if(this.data[i] == num){ 163 return i; 164 } 165 } 166 return -1; 167 } 168 //////////////////////实现动态数组 resize()//////////////////////////////////// 169 private void resize(int new_capacity){ //之所以 用 private 是不让用户调用, 数组如果空间不足会自己扩展的。 170 T[] new_data =(T[]) new Object[new_capacity]; 171 172 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 173 new_data[i] = this.data[i]; 174 } 175 // 176 this.data = new_data; //此时新数组的size 不变 , 新数组的length 也不用变 177 } 178 }

1 package zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class MaxHeap<T extends Comparable<T>> { 4 private MyArray<T> arr; 5 6 // 构造函数 7 public MaxHeap(int capacity){ 8 // 已知容量 9 arr = new MyArray<>(capacity); 10 } 11 public MaxHeap(){ 12 arr = new MyArray<>(); 13 } 14 15 // 返回堆中的 元素个数 16 public int getSize(){ 17 return arr.getSize(); 18 } 19 // 堆中是否为空 20 public boolean isEmpty(){ 21 return arr.isEmpty(); 22 } 23 // 下面是三个 私有的辅助函数 24 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出左孩子的索引 (数组从0 就存值) 25 private int getIdx_left(int cur_idx){ 26 27 return (cur_idx + 1)*2; 28 } 29 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出右孩子的索引 30 private int getIdx_right(int cur_idx){ 31 32 return (cur_idx + 1)*2 - 1; 33 } 34 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出父亲节点的索引 35 private int getIdx_par(int cur_idx){ 36 if(cur_idx == 0){ 37 throw new IllegalArgumentException("根节点 没有父亲节点"); 38 } 39 return (cur_idx - 1) /2; 40 } 41 42 // 向堆中添加 元素 43 public void add(T t){ 44 arr.addLast(t); 45 if(arr.getSize() == 1){ 46 // 不需要调整位置了 47 return ; 48 } 49 // 调整位置 siftUp() 50 siftUp(arr.getSize() - 1); 51 } 52 private void siftUp(int cur_idx){ 53 int par_idx = getIdx_par(cur_idx); 54 55 while ( arr.getByIndex(cur_idx).compareTo( arr.getByIndex(par_idx) ) > 0 ){ 56 // 上浮 57 T temp = arr.getByIndex(cur_idx); 58 arr.setByIndex(cur_idx,arr.getByIndex(par_idx)); 59 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,temp); 60 61 cur_idx = par_idx; 62 if(cur_idx == 0) 63 break; 64 par_idx = getIdx_par(cur_idx); 65 } 66 } 67 68 // 从堆中 取出元素 (取出元素的时候,我们只取出 堆顶元素(最大的)) 69 public T removeMax(){ 70 if(arr.isEmpty()){ 71 return null; 72 } 73 T ret = arr.getByIndex(0); 74 arr.setByIndex(0,arr.getByIndex(arr.getSize() - 1)); 75 arr.remove(arr.getSize() - 1); 76 77 if(arr.getSize() == 1){ 78 // 此时不需要调整 79 return arr.getByIndex(0); 80 } 81 82 //进行 下沉调整 操作 83 siftDown(0); 84 return ret; 85 } 86 private void siftDown(int par_idx){ // 也可以不使用 递归 !!!(使用循环 ) 87 int left_idx = getIdx_left(par_idx); 88 int right_idx = getIdx_right(par_idx); 89 if(left_idx > arr.getSize() -1 || right_idx > arr.getSize() -1){ 90 return; 91 } 92 if(arr.getByIndex(par_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(left_idx)) > 0 && arr.getByIndex(par_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(left_idx)) >0 ){ 93 return; 94 } 95 if(arr.getByIndex(left_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(right_idx))> 0){ 96 // 向左 交换 97 T temp = arr.getByIndex(par_idx ); 98 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,arr.getByIndex(left_idx)); 99 arr.setByIndex(left_idx,temp); 100 siftDown(left_idx); 101 }else{ 102 // 向右 交换 103 T temp = arr.getByIndex(par_idx ); 104 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,arr.getByIndex(right_idx)); 105 arr.setByIndex(right_idx,temp); 106 siftDown(right_idx); 107 } 108 } 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 @Override 117 public String toString() { 118 return arr.toString(); 119 } 120 }

1 package zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 MaxHeap<Integer> heap = new MaxHeap<>(); 6 7 heap.add(62); 8 heap.add(52); 9 heap.add(30); 10 heap.add(28); 11 heap.add(41); 12 heap.add(22); 13 heap.add(13); 14 heap.add(19); 15 heap.add(17); 16 heap.add(15); 17 heap.add(16); 18 19 System.out.println(heap); 20 21 int ret1 = heap.removeMax(); 22 System.out.println(ret1); 23 System.out.println(heap); 24 25 int ret2 = heap.removeMax(); 26 System.out.println(ret2); 27 System.out.println(heap); 28 29 30 } 31 32 }
我们也可以发现,最大堆 对应的数组就是 从大到小的排序,这就是所谓的 堆排序算法的基本思想,
堆的时间复杂度:
它还是二叉树的 高度, 添加 和 删除 都是 O logn 级别的,
特殊之处是 因为 堆是个完全二叉树,所以它的最差情况 也是 O logn ,
堆上的另外两个 操作 replace 和 heapify:
1, replace:
![]()
我们可以通过 先 removeMax() 之后 ,然后 再 add() 一个新元素,时间复杂度 为 两次 log n 。
其实,可以直接将堆顶元素 替换以后,然后 siftDown ,这样的时间复杂度 为 一次 log n 。
2 ,heapify
将任意一个数组 整理成堆的形状,
现在任意来了一个数组,只要是我们合理的交换数组中的位置,它也可以是个堆的形状,
直观的想法是 扫描一下整个数组,把它 添加到我们实现的 堆里面就可以了,
不过这有个更快的做法:
我们假设 整个任意数组看做是个 完全二叉树,
如下:
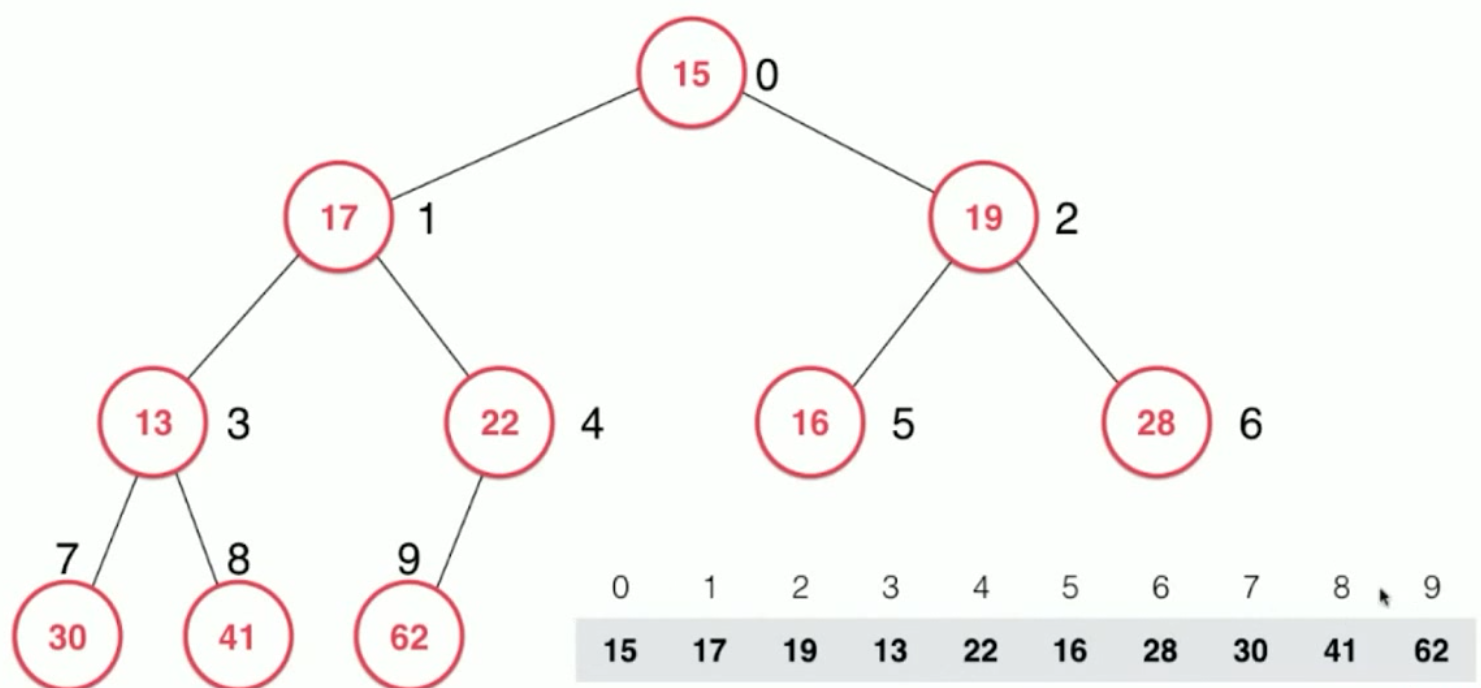
然后,从倒数第一个 非叶子结点 开始(每个非叶子结点都要走一遍 ),即上面的 22 结点, 不断的进行 siftDown(记得 每次都要下沉到底 ) 操作即可,
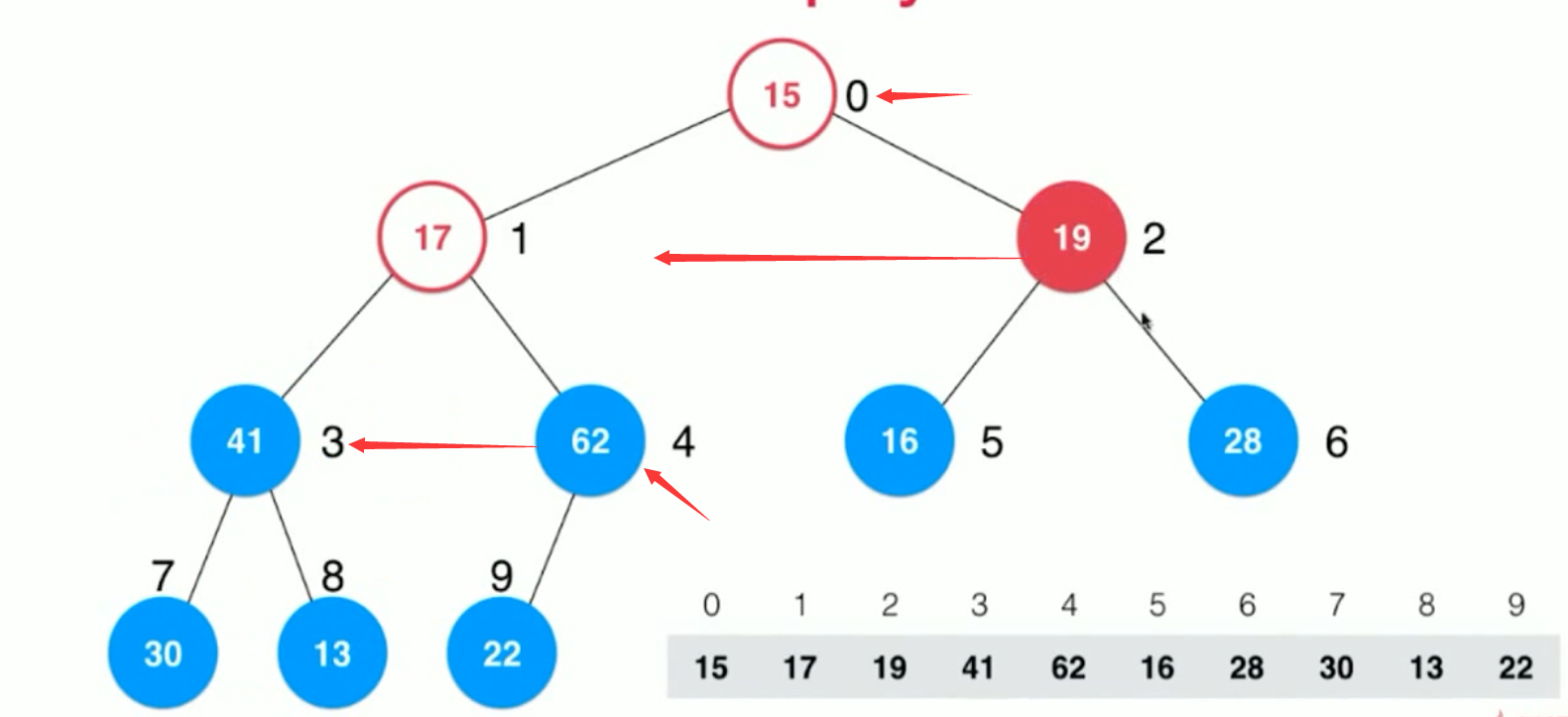
最终为:

这里的关键点是:
1,如何定位 到倒数第一个非叶子结点 所处的索引是 多少?
其实很简单,只需要 拿到最后一个索引,然后依据它计算它的父亲的索引即可,
这样之所以 快是,我们一上来 就抛弃了所有的叶子结点,(很多的哦),这比一个一个添加 要快
实际上,将n 个元素插入到 一个空堆中,算法的时间复杂度是 :O(n logn )
但是,上面的方法 算法时间复杂度是 O (n ) , 具体如何算出 不谈,

1 package zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class MyArray<T> { 4 private T[] data; //数组 5 private int size; //数组实际大小, 6 //容量不用写,可以由data.length()得知 7 8 //满参构造函数 9 public MyArray(int capacity){ 10 // this.data = new int[capacity]; 11 // this.data = new T[capacity]; //不支持这样 12 this.data = (T[]) new Object[capacity]; //先new 出个 Object[] 类的,然后转为 T[] 13 this.size = 0; //开始时 实际大小size =0 14 } 15 //空参构造器 16 public MyArray(){ 17 this(10); //如果是空参的话,调用有参构造器。默认是10 18 } 19 20 //获取数组中的元素的个数 21 public int getSize(){ 22 return this.size; 23 } 24 25 //获取数组的容量 26 public int getCapacity(){ 27 return this.data.length; 28 } 29 30 //数组中是否为空 31 public boolean isEmpty(){ 32 return this.size ==0; 33 } 34 /////////////////////增//////////////////////////// 35 //向 数组的末尾添加一个新元素 36 public void addLast(T num){ 37 /* 38 if(size == this.data.length){ 39 //此时开辟的空间已经满了 40 //这里先抛出一个异常 41 throw new IllegalArgumentException("addLast failed.数组已经满了"); 42 } 43 this.data[size] = num; 44 size ++; //要维持数组 指针。 size 是当前数组中的个数。 45 */ 46 //此时其实可以直接复用 insert ()函数 47 insert(this.size,num); 48 } 49 // 向数组头添加元素 (直接复用 向指定位置添加元素的函数 ) 50 public void addFirst(T num){ 51 insert(0,num); 52 } 53 54 //向 指定数组位置添加一个新元素 55 public void insert(int idx,T num){ 56 if(this.size == this.data.length){ 57 // throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组已经放满了"); 58 /*此时对其扩容*/ 59 resize(2*this.data.length); 60 61 62 } 63 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size ) 64 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引非法"); 65 66 for(int i=this.size-1;i >= idx;--i){ 67 this.data[i+1] = this.data[i]; 68 } 69 this.data[idx] = num; 70 //更新size 71 this.size ++; 72 } 73 74 //////////////////////删/////////////////////////////////////// 75 //删除第一个 76 public T removeFirst(){ 77 return remove(0); //删除并将之返回出去 78 } 79 80 //删除最后一个 81 public T removeLast(){ 82 return remove(this.size-1); 83 } 84 85 //删除指定位置 的元素 86 public T remove(int idx){ //返回 删除的元素 87 if(idx < 0 || idx > this.size -1) 88 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx错误!"); 89 T temp = this.data[idx]; 90 for (int i =idx;i<this.size - 1;i++){ 91 this.data[i] = this.data[i+1]; 92 } 93 this.size -- ; 94 95 //动态减少 当数组中的元素少于空间的一半的时候,就缩减空间。 96 if(this.size == this.data.length / 2){ 97 System.out.println("size = "+this.size); 98 99 resize(this.data.length/2); 100 } 101 return temp; 102 } 103 104 //删除 某个元素 不根据其位置 //它之所以返回void 是因为调用着已经知道的element ,所以没必要再返回出来了。 105 public void removeElement(T element){ 106 //首先要 寻找是否有 element 107 int idx = find(element); 108 if(idx == -1){ 109 throw new IllegalArgumentException("没有该元素"); 110 }else{ 111 remove(idx); 112 } 113 } 114 115 //////////////////////改/////////////////////////////////////// 116 //修改索引为 idx 的元素为 num 117 public void setByIndex(int idx,T num){ 118 if(idx <0 || idx > this.size) 119 throw new IllegalArgumentException("idx 错误!"); 120 121 this.data[idx] = num; 122 } 123 124 125 //////////////////////查/////////////////////////////////////// 126 //获取整个数组的概括 127 //重写 toString() 当打印arr 时候,就会调用该方法! 128 @Override 129 public String toString(){ 130 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(); 131 res.append(String.format("Array:size = %d,capacity = %d ",this.size,this.data.length)); 132 res.append('['); 133 for (int i =0 ;i<this.size;i++){ 134 res.append(data[i]); 135 if(i != this.size -1) 136 res.append(", "); 137 } 138 res.append(']'); 139 return res.toString(); 140 } 141 //获取idx 索引位置的 元素 142 public T getByIndex(int idx){ 143 if (idx < 0 || idx >this.size) { 144 throw new IllegalArgumentException("索引传入错误!"); 145 } 146 return this.data[idx]; 147 } 148 149 //////////////////////包含/////////////////////////////////////// 150 public boolean contains(T num){ 151 for (int i=0;i<this.size;i++){ 152 if(this.data[i] == num){ 153 return true; 154 } 155 } 156 return false; 157 } 158 //////////////////////寻找//////////////////////////////////// 159 public int find(T num){ 160 //寻找数组中是否有 num ,如果有返回其索引,反之 返回-1 161 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 162 if(this.data[i] == num){ 163 return i; 164 } 165 } 166 return -1; 167 } 168 //////////////////////实现动态数组 resize()//////////////////////////////////// 169 private void resize(int new_capacity){ //之所以 用 private 是不让用户调用, 数组如果空间不足会自己扩展的。 170 T[] new_data =(T[]) new Object[new_capacity]; 171 172 for (int i =0;i<this.size;i++){ 173 new_data[i] = this.data[i]; 174 } 175 // 176 this.data = new_data; //此时新数组的size 不变 , 新数组的length 也不用变 177 } 178 }

1 package zcb.demo03; 2 3 public class MaxHeap<T extends Comparable<T>> { 4 private MyArray<T> arr; 5 6 // 构造函数 7 public MaxHeap(int capacity){ 8 // 已知容量 9 arr = new MyArray<>(capacity); 10 } 11 public MaxHeap(){ 12 arr = new MyArray<>(); 13 } 14 15 // heapify 操作 (将任意一个数组 转化为 一个堆 ) 堆化 (构造函数) 16 public MaxHeap(T[] arr1){ 17 arr = new MyArray<>(); 18 // 首先将 arr1 数组中所有元素 放到 动态数组中 19 for (int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){ 20 arr.addLast(arr1[i]); 21 } 22 23 //从 倒数第一个 非叶子结点 开始每次都 siftDown 下 24 int idx = getIdx_par(arr.getSize() - 1); 25 for (int i=idx;i >= 0;i--){ 26 // 每次都 siftDown 即可 27 siftDown(i); 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 // ///////////////////////////////构造函数 /////////////////////////////////////////// 33 34 35 // 返回堆中的 元素个数 36 public int getSize(){ 37 return arr.getSize(); 38 } 39 // 堆中是否为空 40 public boolean isEmpty(){ 41 return arr.isEmpty(); 42 } 43 // 下面是三个 私有的辅助函数 44 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出左孩子的索引 (数组从0 就存值) 45 private int getIdx_left(int cur_idx){ 46 47 return (cur_idx + 1)*2; 48 } 49 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出右孩子的索引 50 private int getIdx_right(int cur_idx){ 51 52 return (cur_idx + 1)*2 - 1; 53 } 54 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出父亲节点的索引 55 private int getIdx_par(int cur_idx){ 56 if(cur_idx == 0){ 57 throw new IllegalArgumentException("根节点 没有父亲节点"); 58 } 59 return (cur_idx - 1) /2; 60 } 61 62 // 向堆中添加 元素 63 public void add(T t){ 64 arr.addLast(t); 65 if(arr.getSize() == 1){ 66 // 不需要调整位置了 67 return ; 68 } 69 // 调整位置 siftUp() 70 siftUp(arr.getSize() - 1); 71 } 72 private void siftUp(int cur_idx){ 73 int par_idx = getIdx_par(cur_idx); 74 75 while ( arr.getByIndex(cur_idx).compareTo( arr.getByIndex(par_idx) ) > 0 ){ 76 // 上浮 77 T temp = arr.getByIndex(cur_idx); 78 arr.setByIndex(cur_idx,arr.getByIndex(par_idx)); 79 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,temp); 80 81 cur_idx = par_idx; 82 if(cur_idx == 0) 83 break; 84 par_idx = getIdx_par(cur_idx); 85 } 86 } 87 88 // 从堆中 取出元素 (取出元素的时候,我们只取出 堆顶元素(最大的)) 89 public T removeMax(){ 90 if(arr.isEmpty()){ 91 return null; 92 } 93 T ret = arr.getByIndex(0); 94 arr.setByIndex(0,arr.getByIndex(arr.getSize() - 1)); 95 arr.remove(arr.getSize() - 1); 96 97 if(arr.getSize() == 1){ 98 // 此时不需要调整 99 return arr.getByIndex(0); 100 } 101 102 //进行 下沉调整 操作 103 siftDown(0); 104 return ret; 105 } 106 private void siftDown(int par_idx){ // 也可以不使用 递归 !!!(使用循环 ) 107 int left_idx = getIdx_left(par_idx); 108 int right_idx = getIdx_right(par_idx); 109 if(left_idx > arr.getSize() -1 || right_idx > arr.getSize() -1){ 110 return; 111 } 112 if(arr.getByIndex(par_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(left_idx)) > 0 && arr.getByIndex(par_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(left_idx)) >0 ){ 113 return; 114 } 115 if(arr.getByIndex(left_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(right_idx))> 0){ 116 // 向左 交换 117 T temp = arr.getByIndex(par_idx ); 118 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,arr.getByIndex(left_idx)); 119 arr.setByIndex(left_idx,temp); 120 siftDown(left_idx); 121 }else{ 122 // 向右 交换 123 T temp = arr.getByIndex(par_idx ); 124 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,arr.getByIndex(right_idx)); 125 arr.setByIndex(right_idx,temp); 126 siftDown(right_idx); 127 } 128 } 129 130 131 // replace 操作 (将堆顶的 元素替换为 t 并返回堆顶元素 ) 132 public T replace(T t){ 133 T ret = arr.getByIndex(0); 134 arr.setByIndex(0,t); 135 siftDown(0); 136 137 return ret; 138 } 139 140 @Override 141 public String toString() { 142 return arr.toString(); 143 } 144 }
其中 heapify 在构造函数中,

1 package zcb.demo03; 2 3 import java.util.ArrayList; 4 5 public class test { 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 // MaxHeap<Integer> heap = new MaxHeap<>(); 8 // heap.add(62); 9 // heap.add(52); 10 // heap.add(30); 11 // heap.add(28); 12 // heap.add(41); 13 // heap.add(22); 14 // heap.add(13); 15 // heap.add(19); 16 // heap.add(17); 17 // heap.add(15); 18 // heap.add(16); 19 // System.out.println(heap); 20 21 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 22 // int [] arr = {13,15,17,16,19,41,22,28,30,52,62}; 不可 23 Integer[] arr = {13,15,17,16,19,41,22,28,30,52,62}; 24 MaxHeap<Integer> heap = new MaxHeap<>(arr); 25 System.out.println(heap); 26 27 28 29 30 } 31 32 }
基于 堆 的优先队列:
优先队列 就是个队列, 接口还是之前的 Queue

1 package zcb.demo04; 2 3 public interface Queue <T> { 4 public abstract void enqueue(T t); //入队 5 public abstract T dequeue(); //出队 6 public abstract T getFront(); //队头 7 public abstract int getSize(); //得到队列中的实际长度 8 public abstract boolean isEmpty(); //是否为空。 9 }

1 package zcb.demo04; 2 3 import zcb.demo03.MyArray; 4 5 public class MaxHeap<T extends Comparable<T>> { 6 private MyArray<T> arr; 7 8 // 构造函数 9 public MaxHeap(int capacity){ 10 // 已知容量 11 arr = new MyArray<>(capacity); 12 } 13 public MaxHeap(){ 14 arr = new MyArray<>(); 15 } 16 17 // heapify 操作 (将任意一个数组 转化为 一个堆 ) 堆化 (构造函数) 18 public MaxHeap(T[] arr1){ 19 arr = new MyArray<>(); 20 // 首先将 arr1 数组中所有元素 放到 动态数组中 21 for (int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){ 22 arr.addLast(arr1[i]); 23 } 24 25 //从 倒数第一个 非叶子结点 开始每次都 siftDown 下 26 int idx = getIdx_par(arr.getSize() - 1); 27 for (int i=idx;i >= 0;i--){ 28 // 每次都 siftDown 即可 29 siftDown(i); 30 } 31 } 32 33 34 // ///////////////////////////////构造函数 /////////////////////////////////////////// 35 36 37 // 返回堆中的 元素个数 38 public int getSize(){ 39 return arr.getSize(); 40 } 41 // 堆中是否为空 42 public boolean isEmpty(){ 43 return arr.isEmpty(); 44 } 45 // 下面是三个 私有的辅助函数 46 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出左孩子的索引 (数组从0 就存值) 47 private int getIdx_left(int cur_idx){ 48 49 return (cur_idx + 1)*2; 50 } 51 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出右孩子的索引 52 private int getIdx_right(int cur_idx){ 53 54 return (cur_idx + 1)*2 - 1; 55 } 56 // 根据当前节点的索引 算出父亲节点的索引 57 private int getIdx_par(int cur_idx){ 58 if(cur_idx == 0){ 59 throw new IllegalArgumentException("根节点 没有父亲节点"); 60 } 61 return (cur_idx - 1) /2; 62 } 63 64 // 向堆中添加 元素 65 public void add(T t){ 66 arr.addLast(t); 67 if(arr.getSize() == 1){ 68 // 不需要调整位置了 69 return ; 70 } 71 // 调整位置 siftUp() 72 siftUp(arr.getSize() - 1); 73 } 74 private void siftUp(int cur_idx){ 75 int par_idx = getIdx_par(cur_idx); 76 77 while ( arr.getByIndex(cur_idx).compareTo( arr.getByIndex(par_idx) ) > 0 ){ 78 // 上浮 79 T temp = arr.getByIndex(cur_idx); 80 arr.setByIndex(cur_idx,arr.getByIndex(par_idx)); 81 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,temp); 82 83 cur_idx = par_idx; 84 if(cur_idx == 0) 85 break; 86 par_idx = getIdx_par(cur_idx); 87 } 88 } 89 90 // 从堆中 取出元素 (取出元素的时候,我们只取出 堆顶元素(最大的)) 91 public T removeMax(){ 92 if(arr.isEmpty()){ 93 return null; 94 } 95 T ret = arr.getByIndex(0); 96 arr.setByIndex(0,arr.getByIndex(arr.getSize() - 1)); 97 arr.remove(arr.getSize() - 1); 98 99 if(arr.getSize() == 1){ 100 // 此时不需要调整 101 return arr.getByIndex(0); 102 } 103 104 //进行 下沉调整 操作 105 siftDown(0); 106 return ret; 107 } 108 private void siftDown(int par_idx){ // 也可以不使用 递归 !!!(使用循环 ) 109 int left_idx = getIdx_left(par_idx); 110 int right_idx = getIdx_right(par_idx); 111 if(left_idx > arr.getSize() -1 || right_idx > arr.getSize() -1){ 112 return; 113 } 114 if(arr.getByIndex(par_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(left_idx)) > 0 && arr.getByIndex(par_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(left_idx)) >0 ){ 115 return; 116 } 117 if(arr.getByIndex(left_idx).compareTo(arr.getByIndex(right_idx))> 0){ 118 // 向左 交换 119 T temp = arr.getByIndex(par_idx ); 120 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,arr.getByIndex(left_idx)); 121 arr.setByIndex(left_idx,temp); 122 siftDown(left_idx); 123 }else{ 124 // 向右 交换 125 T temp = arr.getByIndex(par_idx ); 126 arr.setByIndex(par_idx,arr.getByIndex(right_idx)); 127 arr.setByIndex(right_idx,temp); 128 siftDown(right_idx); 129 } 130 } 131 132 // 查看 当前堆顶的 元素 133 public T getMax(){ 134 if(arr.isEmpty()) 135 return null; 136 return arr.getByIndex(0); 137 } 138 139 140 // replace 操作 (将堆顶的 元素替换为 t 并返回堆顶元素 ) 141 public T replace(T t){ 142 T ret = arr.getByIndex(0); 143 arr.setByIndex(0,t); 144 siftDown(0); 145 146 return ret; 147 } 148 149 @Override 150 public String toString() { 151 return arr.toString(); 152 } 153 }

1 package zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class PriorityQueue<T extends Comparable<T>> implements Queue<T> { 4 // 优先队列的底层结构是 最大堆 5 private MaxHeap<T> heap; 6 // 构造函数 7 public PriorityQueue(){ 8 heap = new MaxHeap<>(); 9 } 10 11 // Queue 中的接口方法 实现////////////////////// 12 public int getSize(){ 13 return heap.getSize(); 14 } 15 public boolean isEmpty(){ 16 return heap.isEmpty(); 17 } 18 19 // 查看优先队列 队首的 元素,其实就是底层结构中 堆顶的 元素 20 public T getFront(){ 21 return heap.getMax(); 22 } 23 24 // 优先队列 入队操作 25 public void enqueue(T t){ 26 heap.add(t); 27 } 28 // 优先队列 出队操作 29 public T dequeue(){ 30 return heap.removeMax(); 31 } 32 33 }

1 package zcb.demo04; 2 3 public class test { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 PriorityQueue<Integer> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>() ; 6 7 for (int i=0;i<10;i++){ 8 priorityQueue.enqueue(i*10); 9 } 10 System.out.println(priorityQueue.getFront()); 11 12 //////////////////////////////////////////////// 13 priorityQueue.dequeue(); 14 System.out.println(priorityQueue.getFront()); 15 16 /////////////////////////////////// 17 System.out.println(priorityQueue.getSize()); 18 19 /////////////////////////////////// 20 priorityQueue.enqueue(111); 21 System.out.println(priorityQueue.getFront() ); 22 23 } 24 }
优先队列的经典 问题 :
如何 在100 000 个元素中选出前100名? (这类问题 就是如何在 N个元素中 选出 M个元素),
我们可以使用 快速排序,它们时间复杂度是 nlogn ,然后再 选出前 M个,这也是可以接受的,
现在的问题是 有没有更好的方法来解决这类问题,
方法就是 使用 优先队列 ,它的时间复杂度是 nlogM ,
具体是 先将前M个 元素放入 优先队列,然后,再继续往里放,但是,优先队列 一直要维持 M个元素,
具体例子看下题:
优先队列的应用 Leetcode No.347. 前k个高频元素:
注:java 自带的priorityqueue 默认是最小堆~ 它的构造函数 可以传入一个比较器~

1 package zcb.demo04; 2 import java.util.LinkedList; 3 import java.util.List; 4 import java.util.TreeMap; 5 import java.util.PriorityQueue; 6 public class test { 7 public static void main(String[] args) { 8 // 输入: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 9 // 输出: [1,2] 10 int[] nums = {1,1,1,2,2,3}; 11 List<Integer>ret = Solution.topKFrequent(nums,2); 12 System.out.println(ret); 13 } 14 } 15 16 17 class Solution { 18 public static List<Integer> topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { 19 TreeMap<Integer,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(); 20 for (int num :nums){ 21 if(!map.containsKey(num)){ 22 map.put(num,1); 23 }else{ 24 map.put(num,map.get(num) + 1); 25 } 26 } 27 PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>( 28 (a,b) -> map.get(a) - map.get(b) 29 ); 30 for (int key:map.keySet()){ 31 if(pq.size() < k) 32 pq.add(key); 33 else if(map.get(key) > map.get(pq.peek()) ){ 34 pq.remove(); 35 pq.add(key); 36 } 37 } 38 39 LinkedList<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>(); 40 while (!pq.isEmpty()){ 41 res.addFirst(pq.remove()); 42 } 43 return res; 44 } 45 }
堆的扩展:
我们这里的基本上都是二叉堆,实际上计算机 的世界中有很多形式多样的堆,
d 叉堆,这里的d 是一个节点有d个孩子, 此时的 时间复杂度 更低(log d(n) ),但是,此时在做下沉(siftDown )的时候,便更复杂一些了,
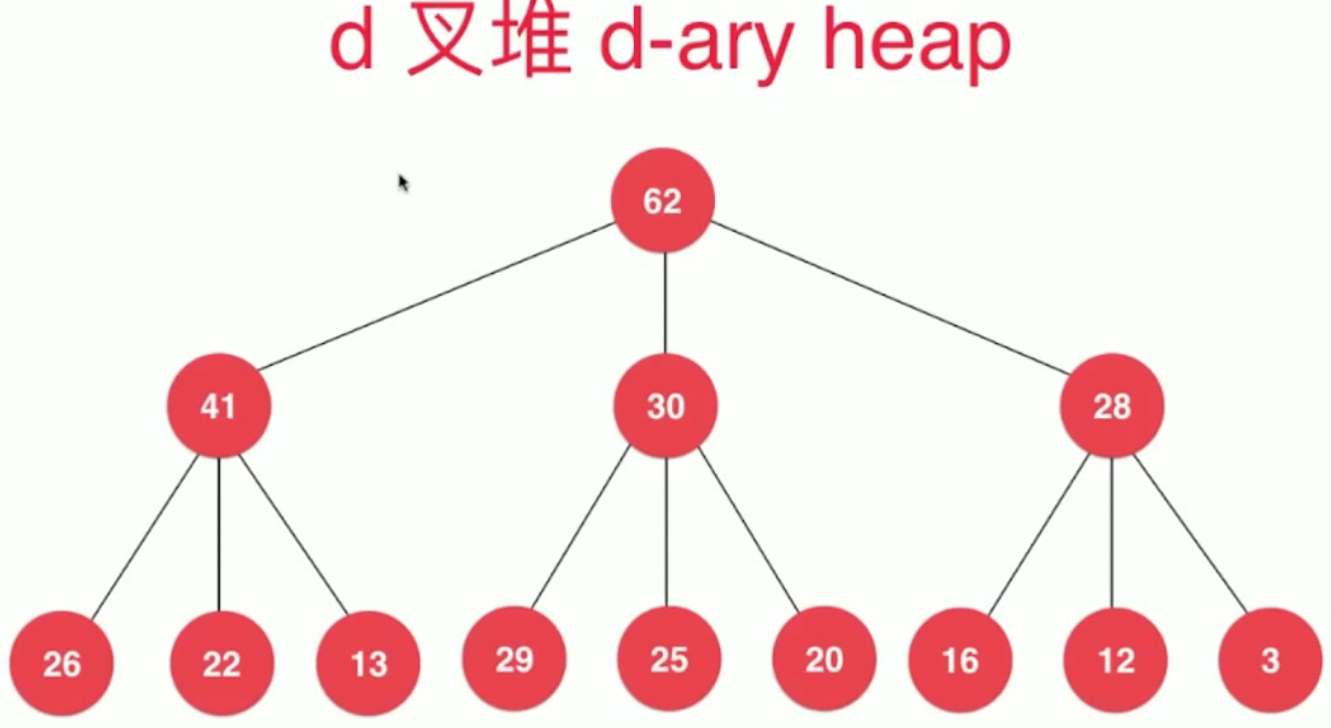
我们这里的堆 是 只能看到 堆首的 元素,不可以看到 堆中间的元素, 有时也是要看到堆中间的元素的, 即 索引堆, (也保存它的索引,通过索引可以便捷的 检索中间 的元素 并可以修改它 )
索引堆: https://www.cnblogs.com/dudududu/p/8574740.html
还有 二项堆,斐波那契堆 ,
