在Spark中一个appliation可能包含多个job,每个job都是由SparkContext#runJob(。。。)触发的,一个Job下包含1个或多个Stage,Job的最后一个stage为ResultStage,其余的stage都为ShuffleMapStage。ResultStage会生成一组ResultTask,ResultTask在计算完成之后会将结果返回给Drive;而ShuffleMapStage会生成一组ShuffleMapTask,ShuffleMapTask则是在计算完成之后将结果(根据RDD的Partitioner)划分到不同的buckets中。
Spark代码如何被解析为RDD?
1)spark程序(dataframe,dataset,spark.sql(),rdd)经过catalyst优化解析后,把spark的程序都转化为了层级关联的rdd,经过DAG划分为的stage时,实际上就是根据rddshuffle的依赖关系来划分的(依赖关系分为窄依赖、宽依赖,如果遇到两个RDD(父子)依赖是宽依赖,那么会把RDD拆分为2个Stage,父类RDD在一个Stage,子类在一个Stage),并且map,reduce等算子转化为RDD时,将算子的实现函数(“闭包”或者“自定义函数、自定义类”)赋值到对应的RDD#f属性下。
2)在DAGScheduler#submitMissingTasks中会把stage划分为两种task:ShuffleMapTask,ResultTask,这两个Task会被传递给Executor,Executor会使用TaskRunner来运行它们。
在运行时,会调用ShuffleMapTask,ResultTask#runTask()方法,该方法内部都有rdd.iterator(...)的调用代码,rdd#iterator(..,)内部调用了rdd.compute(...)。如果RDDA的子是RDDB,RDDB的子是RDDC,执行时:
--------RDDA'compute.
---------------RDDB'compute.
----------------------RDDC'compute。
如果使用SparkSQL(dataset,dataframe,spark.sql(''))编写的代码经过catalyst优化解析后的代码后你会发现,实际上它就是把代码解析后层级关联RDD。
taskBinary中序列化的就是解析后RDD和(RDD依赖关系、ResultStage的话会把ResultTask的最后一个算子实现函数),其中非ResultTask的RDD属性中包含了算子业务函数,在算子转化为RDD时,会将算子的实现函数(“闭包”或者“自定义函数、自定义类”)赋值到对应的RDD#f属性下,并被RDD#compute()使用。
- 如果是“闭包”一般就是把一些常量定义到函数内部;
- 如果是“自定义函数、自定义类”可能会引用了外部包中的子函数,这时候在TaskRunner运行时会通过反射把jar加载到当前线程中,供调用使用。
算子如何转化为RDD(map算子为例)?
RDD有很多种:MapPartitoinRDD,ShuffleRDD等,但是每一种rdd都有一个compute()和iterator()方法,这个compute()方法就是循环某个partition下所有数据并调用“程序员调用算子时编写的算子内部业务代码函数”。
以RDD的map算子为例来分析,RDD#map()内部是把map算子转化为MapPartitionRDD,
/** * Return a new RDD by applying a function to all elements of this RDD. */ def map[U: ClassTag](f: T => U): RDD[U] = withScope { val cleanF = sc.clean(f) new MapPartitionsRDD[U, T](this, (context, pid, iter) => iter.map(cleanF)) }
备注:一般我们调用RDD的map算子时会实现 f 函数。
其中MapPartitionRDD的触发依赖iterator()、compute()。compute的实现就是循环RDD下某个partition下所有元素并执行 f() 函数,RDD#map()的 f() 函数被封装传递给MapPartitionRDD。
/** * An RDD that applies the provided function to every partition of the parent RDD. * * @param prev the parent RDD. * @param f The function used to map a tuple of (TaskContext, partition index, input iterator) to * an output iterator. * @param preservesPartitioning Whether the input function preserves the partitioner, which should * be `false` unless `prev` is a pair RDD and the input function * doesn't modify the keys. * @param isFromBarrier Indicates whether this RDD is transformed from an RDDBarrier, a stage * containing at least one RDDBarrier shall be turned into a barrier stage. * @param isOrderSensitive whether or not the function is order-sensitive. If it's order * sensitive, it may return totally different result when the input order * is changed. Mostly stateful functions are order-sensitive. */ private[spark] class MapPartitionsRDD[U: ClassTag, T: ClassTag]( var prev: RDD[T], f: (TaskContext, Int, Iterator[T]) => Iterator[U], // (TaskContext, partition index, iterator) preservesPartitioning: Boolean = false, isFromBarrier: Boolean = false, isOrderSensitive: Boolean = false) extends RDD[U](prev) { override val partitioner = if (preservesPartitioning) firstParent[T].partitioner else None override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = firstParent[T].partitions override def compute(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[U] = f(context, split.index, firstParent[T].iterator(split, context)) override def clearDependencies() { super.clearDependencies() prev = null } @transient protected lazy override val isBarrier_ : Boolean = isFromBarrier || dependencies.exists(_.rdd.isBarrier()) override protected def getOutputDeterministicLevel = { if (isOrderSensitive && prev.outputDeterministicLevel == DeterministicLevel.UNORDERED) { DeterministicLevel.INDETERMINATE } else { super.getOutputDeterministicLevel } } }
MapPartitionRDD的父类RDD类中定义了iterator()函数:
/** * Internal method to this RDD; will read from cache if applicable, or otherwise compute it. * This should ''not'' be called by users directly, but is available for implementors of custom * subclasses of RDD. */ final def iterator(split: Partition, context: TaskContext): Iterator[T] = { if (storageLevel != StorageLevel.NONE) { getOrCompute(split, context) // 会调用compute() } else { computeOrReadCheckpoint(split, context) // 会调用compute() } }
ShuflleMapTask和ResultTask
ShuffleMapTask类
ShuffleMapTask将RDD的元素分为多个存储桶(基于 ShuffleDependency 中指定的分区器)。
https://github.com/apache/spark/blob/branch-2.4/core/src/main/scala/org/apache/spark/scheduler/ShuffleMapTask.scala
private[spark] class ShuffleMapTask( stageId: Int, stageAttemptId: Int, taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]], partition: Partition, @transient private var locs: Seq[TaskLocation], localProperties: Properties, serializedTaskMetrics: Array[Byte], jobId: Option[Int] = None, appId: Option[String] = None, appAttemptId: Option[String] = None, isBarrier: Boolean = false) extends Task[MapStatus](stageId, stageAttemptId, partition.index, localProperties, serializedTaskMetrics, jobId, appId, appAttemptId, isBarrier) with Logging { /** A constructor used only in test suites. This does not require passing in an RDD. */ def this(partitionId: Int) { this(0, 0, null, new Partition { override def index: Int = 0 }, null, new Properties, null) } @transient private val preferredLocs: Seq[TaskLocation] = { if (locs == null) Nil else locs.toSet.toSeq } override def runTask(context: TaskContext): MapStatus = { // Deserialize the RDD using the broadcast variable. val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime } else 0L val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() val (rdd, dep) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])](ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) _executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime _executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime } else 0L var writer: ShuffleWriter[Any, Any] = null try { val manager = SparkEnv.get.shuffleManager writer = manager.getWriter[Any, Any](dep.shuffleHandle, partitionId, context) writer.write(rdd.iterator(partition, context).asInstanceOf[Iterator[_ <: Product2[Any, Any]]]) writer.stop(success = true).get } catch { case e: Exception => try { if (writer != null) { writer.stop(success = false) } } catch { case e: Exception => log.debug("Could not stop writer", e) } throw e } } override def preferredLocations: Seq[TaskLocation] = preferredLocs override def toString: String = "ShuffleMapTask(%d, %d)".format(stageId, partitionId) }
@param stageId 此Task所属Stage的ID(id of the stage this task belongs to)
@param stageAttemptId 此Task所属Stage的尝试ID (attempt id of the stage this task belongs to)
@param taskBinary RDD和ShuffleDependency的广播版本。反序列化后,类型应为(RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _])。(broadcast version of the RDD and the ShuffleDependency. Once deserialized,the type should be (RDD[_], ShuffleDependency[_, _, _]))
@param partition 与此Task关联的RDD分区(partition of the RDD this task is associated with)
@param locs 区域调度的首选Task执行位置 (preferred task execution locations for locality scheduling)
@param localProperties 用户在driver端设置的线程本地属性的副本。 (copy of thread-local properties set by the user on the driver side.)
@param serializedTaskMetrics 在driver端创建并序列化并发送到executor端的“TaskMetrics”。 (a `TaskMetrics` that is created and serialized on the driver side and sent to executor side.)
以下参数是可选的:
@param jobId 此Task所属Job的id(id of the job this task belongs to)
@param appId 此Task所属application的id(id of the app this task belongs to)
@param appAttemptId 此Task所属application的尝试id(attempt id of the app this task belongs to)
@param isBarrier 此Task是否属于屏障Stage。Spark必须同时启动所有Task以进入屏障Stage(whether this task belongs to a barrier stage. Spark must launch all the tasks at the same time for a barrier stage.)
TaskMetrics就是对task的执行信息的一个描述类
class TaskMetrics private[spark] () extends Serializable { // Each metric is internally represented as an accumulator private val _executorDeserializeTime = new LongAccumulator // executor端反序列化耗时 private val _executorDeserializeCpuTime = new LongAccumulator // executor端反序列化CPU耗时 private val _executorRunTime = new LongAccumulator // executor端运行时间 private val _executorCpuTime = new LongAccumulator // executor端CPU耗时 private val _resultSize = new LongAccumulator // 结果大小 private val _jvmGCTime = new LongAccumulator // JVM GC耗时 private val _resultSerializationTime = new LongAccumulator // 结果序列化耗时 private val _memoryBytesSpilled = new LongAccumulator // 溢出的内存字节 private val _diskBytesSpilled = new LongAccumulator // 溢出的磁盘字节 private val _peakExecutionMemory = new LongAccumulator // 峰值执行内存 private val _updatedBlockStatuses = new CollectionAccumulator[(BlockId, BlockStatus)] // 修改的block状态信息集合 }
ResultTask类
将输出发送回Driver应用程序的Task。
https://github.com/apache/spark/blob/branch-2.4/core/src/main/scala/org/apache/spark/scheduler/ResultTask.scala
private[spark] class ResultTask[T, U]( stageId: Int, stageAttemptId: Int, taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]], partition: Partition, locs: Seq[TaskLocation], val outputId: Int, localProperties: Properties, serializedTaskMetrics: Array[Byte], jobId: Option[Int] = None, appId: Option[String] = None, appAttemptId: Option[String] = None, isBarrier: Boolean = false) extends Task[U](stageId, stageAttemptId, partition.index, localProperties, serializedTaskMetrics, jobId, appId, appAttemptId, isBarrier) with Serializable { @transient private[this] val preferredLocs: Seq[TaskLocation] = { if (locs == null) Nil else locs.toSet.toSeq } override def runTask(context: TaskContext): U = { // Deserialize the RDD and the func using the broadcast variables. val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime } else 0L val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() val (rdd, func) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U)](ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) _executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime _executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime } else 0L func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context)) } // This is only callable on the driver side. override def preferredLocations: Seq[TaskLocation] = preferredLocs override def toString: String = "ResultTask(" + stageId + ", " + partitionId + ")" }
断点监控Task序列化携带信息
使用RDD来编写一个测试程序:
package com.dx.test; import org.apache.spark.SparkConf; import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaRDD; import org.apache.spark.api.java.JavaSparkContext; import org.apache.spark.api.java.function.Function; import org.apache.spark.broadcast.Broadcast; import org.apache.spark.sql.Row; import org.apache.spark.sql.RowFactory; import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.encoders.ExpressionEncoder; import org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.encoders.RowEncoder; import org.apache.spark.sql.types.DataTypes; import org.apache.spark.sql.types.StructType; import java.util.Map; public class TestBroadcast { public static void main(String[] args) { SparkConf conf = new SparkConf(); conf.setMaster("local[*]"); conf.setAppName("test application"); JavaSparkContext javaSparkContext = new JavaSparkContext(conf); Map<String, String> resource = new java.util.HashMap<String, String>(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { resource.put(String.valueOf(i), String.valueOf(i)); } final Broadcast<Map<String, String>> broadcastMap = javaSparkContext.broadcast(resource); StructType resulStructType = new StructType(); resulStructType = resulStructType.add("int_id", DataTypes.StringType, false); resulStructType = resulStructType.add("job_result", DataTypes.StringType, true); ExpressionEncoder<Row> resultEncoder = RowEncoder.apply(resulStructType); JavaRDD<String> sourceDataset = javaSparkContext.textFile("E:\test2"); JavaRDD<Row> dataset = sourceDataset.map(new Function<String, Row>() { public Row call(String line) throws Exception { String[] fields = line.split(","); int int_id = Integer.valueOf(fields[1]); Map<String, String> resources = broadcastMap.getValue(); String job_result = resources.get(int_id); Object[] values = new Object[2]; values[0] = int_id; values[1] = job_result; return RowFactory.create(values); } }); dataset.saveAsTextFile("E:\test3"); } }
端点设置到DAGScheduler#submitMissingTasks(stage: Stage, jobId: Int)

/** Called when stage's parents are available and we can now do its task. */ private def submitMissingTasks(stage: Stage, jobId: Int) { logDebug("submitMissingTasks(" + stage + ")") // First figure out the indexes of partition ids to compute. val partitionsToCompute: Seq[Int] = stage.findMissingPartitions() // Use the scheduling pool, job group, description, etc. from an ActiveJob associated // with this Stage val properties = jobIdToActiveJob(jobId).properties runningStages += stage // SparkListenerStageSubmitted should be posted before testing whether tasks are // serializable. If tasks are not serializable, a SparkListenerStageCompleted event // will be posted, which should always come after a corresponding SparkListenerStageSubmitted // event. stage match { case s: ShuffleMapStage => outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart(stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.numPartitions - 1) case s: ResultStage => outputCommitCoordinator.stageStart( stage = s.id, maxPartitionId = s.rdd.partitions.length - 1) } val taskIdToLocations: Map[Int, Seq[TaskLocation]] = try { stage match { case s: ShuffleMapStage => partitionsToCompute.map { id => (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, id))}.toMap case s: ResultStage => partitionsToCompute.map { id => val p = s.partitions(id) (id, getPreferredLocs(stage.rdd, p)) }.toMap } } catch { case NonFatal(e) => stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size) listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties)) abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e ${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e)) runningStages -= stage return } stage.makeNewStageAttempt(partitionsToCompute.size, taskIdToLocations.values.toSeq) // If there are tasks to execute, record the submission time of the stage. Otherwise, // post the even without the submission time, which indicates that this stage was // skipped. if (partitionsToCompute.nonEmpty) { stage.latestInfo.submissionTime = Some(clock.getTimeMillis()) } listenerBus.post(SparkListenerStageSubmitted(stage.latestInfo, properties)) // TODO: Maybe we can keep the taskBinary in Stage to avoid serializing it multiple times. // Broadcasted binary for the task, used to dispatch tasks to executors. Note that we broadcast // the serialized copy of the RDD and for each task we will deserialize it, which means each // task gets a different copy of the RDD. This provides stronger isolation between tasks that // might modify state of objects referenced in their closures. This is necessary in Hadoop // where the JobConf/Configuration object is not thread-safe. var taskBinary: Broadcast[Array[Byte]] = null var partitions: Array[Partition] = null try { // For ShuffleMapTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, shuffleDep). // For ResultTask, serialize and broadcast (rdd, func). var taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = null // taskBinaryBytes and partitions are both effected by the checkpoint status. We need // this synchronization in case another concurrent job is checkpointing this RDD, so we get a // consistent view of both variables. RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { taskBinaryBytes = stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => JavaUtils.bufferToArray( closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef)) case stage: ResultStage => JavaUtils.bufferToArray(closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef)) } partitions = stage.rdd.partitions } taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes) } catch { // In the case of a failure during serialization, abort the stage. case e: NotSerializableException => abortStage(stage, "Task not serializable: " + e.toString, Some(e)) runningStages -= stage // Abort execution return case e: Throwable => abortStage(stage, s"Task serialization failed: $e ${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e)) runningStages -= stage // Abort execution return } val tasks: Seq[Task[_]] = try { val serializedTaskMetrics = closureSerializer.serialize(stage.latestInfo.taskMetrics).array() stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => stage.pendingPartitions.clear() partitionsToCompute.map { id => val locs = taskIdToLocations(id) val part = partitions(id) stage.pendingPartitions += id new ShuffleMapTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, taskBinary, part, locs, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier()) } case stage: ResultStage => partitionsToCompute.map { id => val p: Int = stage.partitions(id) val part = partitions(p) val locs = taskIdToLocations(id) new ResultTask(stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, taskBinary, part, locs, id, properties, serializedTaskMetrics, Option(jobId), Option(sc.applicationId), sc.applicationAttemptId, stage.rdd.isBarrier()) } } } catch { case NonFatal(e) => abortStage(stage, s"Task creation failed: $e ${Utils.exceptionString(e)}", Some(e)) runningStages -= stage return } if (tasks.size > 0) { logInfo(s"Submitting ${tasks.size} missing tasks from $stage (${stage.rdd}) (first 15 " + s"tasks are for partitions ${tasks.take(15).map(_.partitionId)})") taskScheduler.submitTasks(new TaskSet( tasks.toArray, stage.id, stage.latestInfo.attemptNumber, jobId, properties)) } else { // Because we posted SparkListenerStageSubmitted earlier, we should mark // the stage as completed here in case there are no tasks to run markStageAsFinished(stage, None) stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => logDebug(s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; " + s"(available: ${stage.isAvailable}," + s"available outputs: ${stage.numAvailableOutputs}," + s"partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})") markMapStageJobsAsFinished(stage) case stage : ResultStage => logDebug(s"Stage ${stage} is actually done; (partitions: ${stage.numPartitions})") } submitWaitingChildStages(stage) } }
中的
if (tasks.size > 0) { // 断点
IDEA下Debug运行 TestBroadcast ,之后能拿到断点:
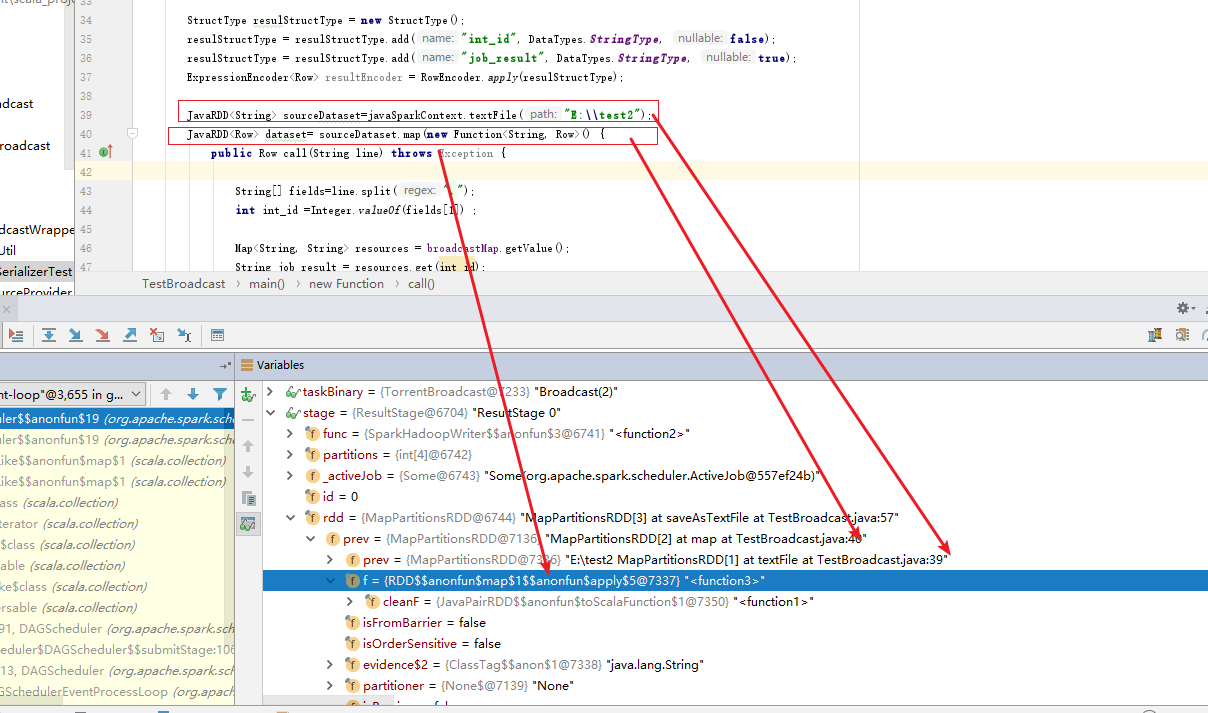
从Stage下可以看到stage#rdd属性,该rdd就是当前stage中包含执行逻辑代码的解析结果。stage 里边就是一层的rdd,不管是spark sql,dataframe,dataset还是rdd编程,最终程序都被解析(spark sql,dataframe,dataset经过catalyst解析后)为RDD,每个rdd包含了都有可以接收实现函数,比如map算子被转化为 MapPartitionRDD,转化后,把实现函数转化为 mapPartitionRDD实例的一个属性函数。
一个rdd,在执行过程中属性列表
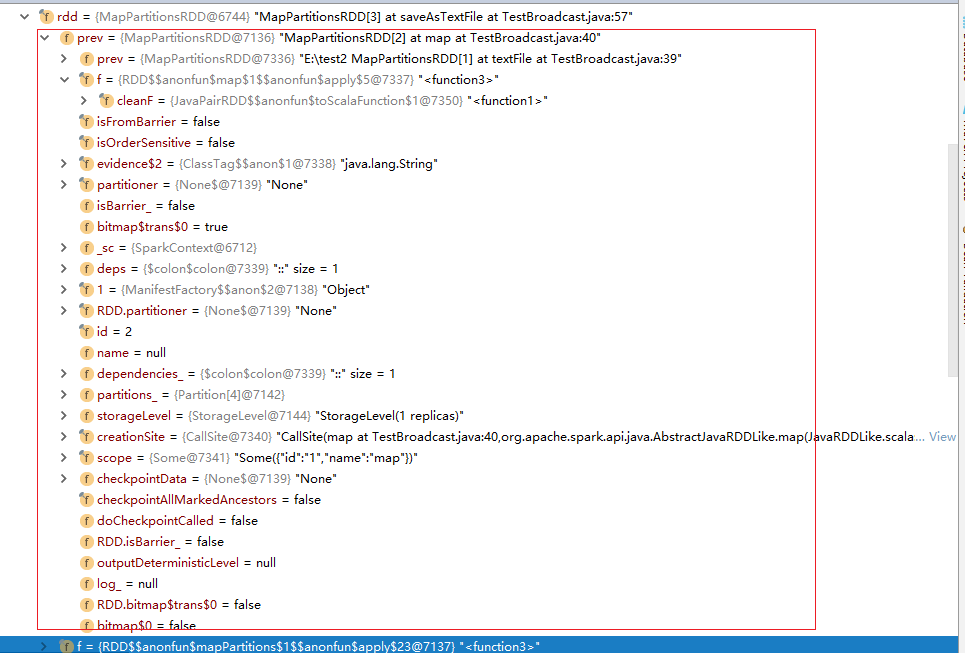
其中f就是我们的实现的函数,该函数被当做RDD的一个属性
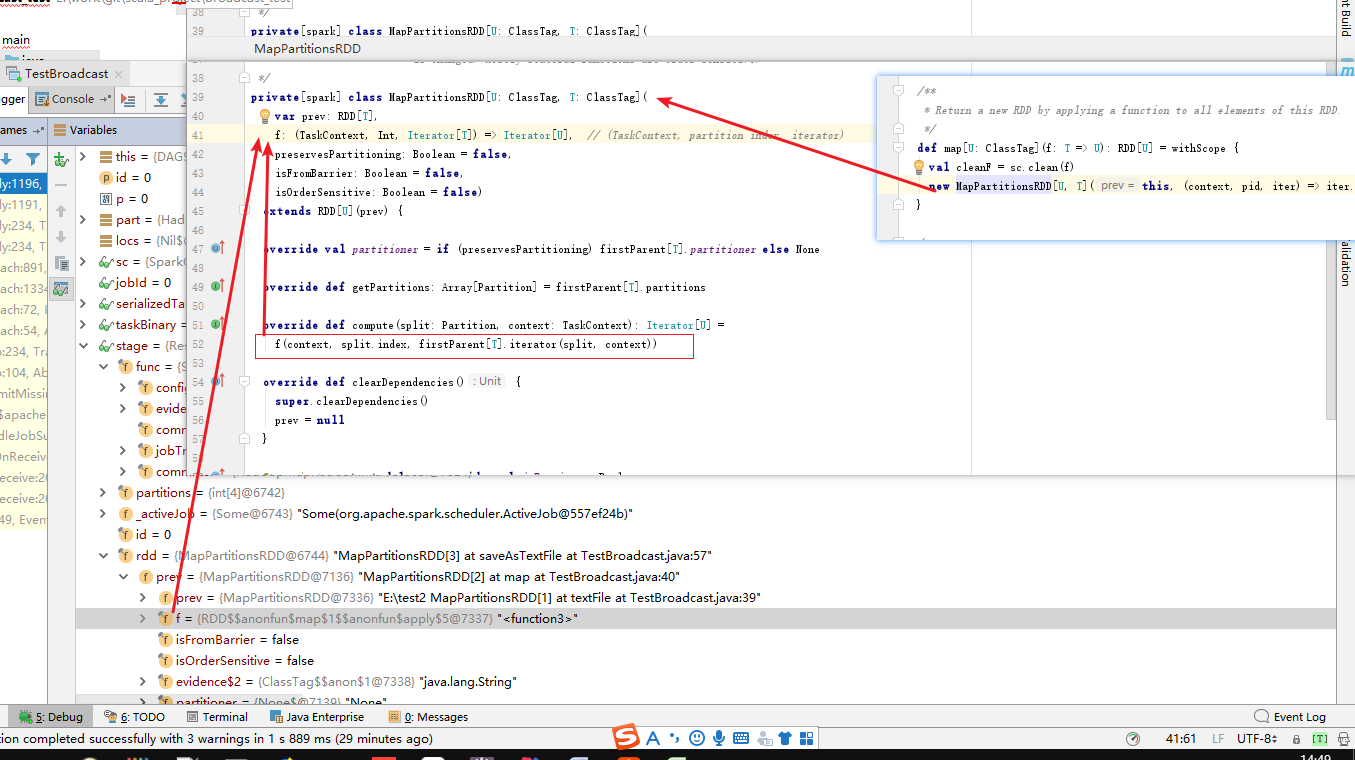
当stage转化为Task后,Task内部包含的操作数据实际上就是RDD的某一个分区,该RDD依然携带了RDD#f 函数属性,因此当task被序列化为Task时,这些实现函数也被序列化。等到达了Executor后会被反序列化加载到TaskRunner中去执行。
TaskRunner执行时,会加载driver传递给container的application.jar等jar,如果Task的反序列化的RDD的f依赖jar包的会从加载jar包中读取依赖函数等。
ResultTask的func从哪里来?
以上边例子来说
dataset.saveAsTextFile("E:\test3");
的调用信息为:
CallSite( runJob at SparkHadoopWriter.scala:78,org.apache.spark.SparkContext.runJob(SparkContext.scala:2114) org.apache.spark.internal.io.SparkHadoopWriter$.write(SparkHadoopWriter.scala:78) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopDataset$1.apply$mcV$sp(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1096) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopDataset$1.apply(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1094) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopDataset$1.apply(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1094) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDDOperationScope$.withScope(RDDOperationScope.scala:151) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDDOperationScope$.withScope(RDDOperationScope.scala:112) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD.withScope(RDD.scala:363) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions.saveAsHadoopDataset(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1094) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopFile$4.apply$mcV$sp(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1067) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopFile$4.apply(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1032) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopFile$4.apply(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1032) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDDOperationScope$.withScope(RDDOperationScope.scala:151) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDDOperationScope$.withScope(RDDOperationScope.scala:112) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD.withScope(RDD.scala:363) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions.saveAsHadoopFile(PairRDDFunctions.scala:1032) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopFile$1.apply$mcV$sp(PairRDDFunctions.scala:958) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopFile$1.apply(PairRDDFunctions.scala:958) org.apache.spark.rdd.PairRDDFunctions$$anonfun$saveAsHadoopFile$1.apply(PairRDDFunctions.scala:958) org.apache.spark.rdd.RDDOperationScope$.withScope(RDDOperationScope.scala:151))
Dataset#saveAsTextFile(。。。)内部实现是调用SparkContext.runJob(...)来提交任务:
org.apache.spark.internal.io.SparkHadoopWriter
def write[K, V: ClassTag]( rdd: RDD[(K, V)], config: HadoopWriteConfigUtil[K, V]): Unit = { // Extract context and configuration from RDD. val sparkContext = rdd.context val commitJobId = rdd.id // Set up a job. val jobTrackerId = createJobTrackerID(new Date()) val jobContext = config.createJobContext(jobTrackerId, commitJobId) config.initOutputFormat(jobContext) // Assert the output format/key/value class is set in JobConf. config.assertConf(jobContext, rdd.conf) val committer = config.createCommitter(commitJobId) committer.setupJob(jobContext) // Try to write all RDD partitions as a Hadoop OutputFormat. try { val ret = sparkContext.runJob(rdd, (context: TaskContext, iter: Iterator[(K, V)]) => { // SPARK-24552: Generate a unique "attempt ID" based on the stage and task attempt numbers. // Assumes that there won't be more than Short.MaxValue attempts, at least not concurrently. val attemptId = (context.stageAttemptNumber << 16) | context.attemptNumber executeTask( context = context, config = config, jobTrackerId = jobTrackerId, commitJobId = commitJobId, sparkPartitionId = context.partitionId, sparkAttemptNumber = attemptId, committer = committer, iterator = iter) }) committer.commitJob(jobContext, ret) logInfo(s"Job ${jobContext.getJobID} committed.") } catch { case cause: Throwable => logError(s"Aborting job ${jobContext.getJobID}.", cause) committer.abortJob(jobContext) throw new SparkException("Job aborted.", cause) } }
其中SparkContext#runJob(...)传递的第二个参数就是func。SparkContext#runJob(...)内部调用DAGScheduler#runJob(...)
def runJob[T, U: ClassTag]( rdd: RDD[T], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U, partitions: Seq[Int], resultHandler: (Int, U) => Unit): Unit = { if (stopped.get()) { throw new IllegalStateException("SparkContext has been shutdown") } val callSite = getCallSite val cleanedFunc = clean(func) logInfo("Starting job: " + callSite.shortForm) if (conf.getBoolean("spark.logLineage", false)) { logInfo("RDD's recursive dependencies: " + rdd.toDebugString) } dagScheduler.runJob(rdd, cleanedFunc, partitions, callSite, resultHandler, localProperties.get) progressBar.foreach(_.finishAll()) rdd.doCheckpoint() }
在DAGScheduler内部会将func作为ResultStage的属性,
/** * Create a ResultStage associated with the provided jobId. */ private def createResultStage( rdd: RDD[_], func: (TaskContext, Iterator[_]) => _, partitions: Array[Int], jobId: Int, callSite: CallSite): ResultStage = { checkBarrierStageWithDynamicAllocation(rdd) checkBarrierStageWithNumSlots(rdd) checkBarrierStageWithRDDChainPattern(rdd, partitions.toSet.size) val parents = getOrCreateParentStages(rdd, jobId) val id = nextStageId.getAndIncrement() val stage = new ResultStage(id, rdd, func, partitions, parents, jobId, callSite) stageIdToStage(id) = stage updateJobIdStageIdMaps(jobId, stage) stage }
在DAGScheduler#submitMissingTasks(...)中生成序列化的taskBinary时,如果stage为ResultStage时,将stage#func也和stage#rdd一起序列化,最终跟随Task一起被发送到executor上。
var taskBinaryBytes: Array[Byte] = null // taskBinaryBytes and partitions are both effected by the checkpoint status. We need // this synchronization in case another concurrent job is checkpointing this RDD, so we get a // consistent view of both variables. RDDCheckpointData.synchronized { taskBinaryBytes = stage match { case stage: ShuffleMapStage => JavaUtils.bufferToArray( closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.shuffleDep): AnyRef)) case stage: ResultStage => JavaUtils.bufferToArray(closureSerializer.serialize((stage.rdd, stage.func): AnyRef)) } partitions = stage.rdd.partitions } taskBinary = sc.broadcast(taskBinaryBytes)
在Executor中启动Task是会调用org.apache.spark.executor.Executor#launchTask()加载task进行反序列化,在org.apache.spark.executor.Executor.TaskRunner中对Task执行,如果Task是ResultTask时,会调用ResultTask#runTask()。
在ResultTask#runTask()中会反序列化taskBinary,反序列化出func和rdd,之后调动func函数,函数内部进行RDD迭代执行。
override def runTask(context: TaskContext): U = { // Deserialize the RDD and the func using the broadcast variables. val threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean val deserializeStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis() val deserializeStartCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime } else 0L val ser = SparkEnv.get.closureSerializer.newInstance() val (rdd, func) = ser.deserialize[(RDD[T], (TaskContext, Iterator[T]) => U)]( ByteBuffer.wrap(taskBinary.value), Thread.currentThread.getContextClassLoader) _executorDeserializeTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - deserializeStartTime _executorDeserializeCpuTime = if (threadMXBean.isCurrentThreadCpuTimeSupported) { threadMXBean.getCurrentThreadCpuTime - deserializeStartCpuTime } else 0L func(context, rdd.iterator(partition, context)) }
到这里,应该可以清楚的知道ResultTask中从taskBinary中反序列化的func就是SparkContext#runJob(...)的第二个参数。在ResutlTask中rdd#compute()在func内部迭代被调用,这也是真正算子触发的地方。
参考:
