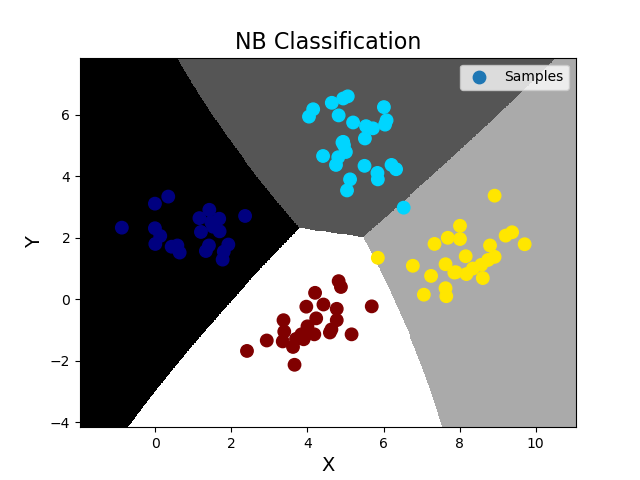
''' 分类之交叉验证: 由于数据集的划分有不确定性,若随机划分的样本正好处于某类特殊样本,则得到的训练模型所预测的结果的可信度将受到质疑。 所以需要进行多次交叉验证,把样本空间中的所有样本均分成n份,使用不同的训练集训练模型,对不同的测试集进行测试时输出指标得分。 sklearn提供了交叉验证相关API: import sklearn.model_selection as ms ms.cross_val_score(模型, 输入集, 输出集, cv=折叠数, scoring=指标名)->指标值数组 交叉验证指标: 1.精确度(accuracy):分类正确的样本数/总样本数 2.查准率(precision_weighted):针对每一个类别,预测正确的样本数比上预测出来的样本数 3.召回率(recall_weighted):针对每一个类别,预测正确的样本数比上实际存在的样本数 4.f1得分(f1_weighted):2x查准率x召回率/(查准率+召回率) 在交叉验证过程中,针对每一次交叉验证,计算所有类别的查准率、召回率或者f1得分,然后取各类别相应指标值的平均数, 作为这一次交叉验证的评估指标,然后再将所有交叉验证的评估指标以数组的形式返回调用者。 ''' import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as mp import sklearn.naive_bayes as nb import sklearn.model_selection as ms data = np.loadtxt('./ml_data/multiple1.txt', delimiter=',', unpack=False, dtype='f8') print(data.shape) x = np.array(data[:, :-1]) y = np.array(data[:, -1]) # 训练集和测试集的划分 使用训练集训练 再使用测试集测试,并绘制测试集样本图像 train_x, test_x, train_y, test_y = ms.train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.25, random_state=7) # 针对训练集,做5次交叉验证,若得分还不错再训练模型 model = nb.GaussianNB() # 精确度 score = ms.cross_val_score(model, train_x, train_y, cv=5, scoring='accuracy') print('accuracy score=', score) print('accuracy mean=', score.mean()) # 查准率 score = ms.cross_val_score(model, train_x, train_y, cv=5, scoring='precision_weighted') print('precision_weighted score=', score) print('precision_weighted mean=', score.mean()) # 召回率 score = ms.cross_val_score(model, train_x, train_y, cv=5, scoring='recall_weighted') print('recall_weighted score=', score) print('recall_weighted mean=', score.mean()) # f1得分 score = ms.cross_val_score(model, train_x, train_y, cv=5, scoring='f1_weighted') print('f1_weighted score=', score) print('f1_weighted mean=', score.mean()) # 训练NB模型,完成分类业务 model.fit(train_x, train_y) pred_test_y = model.predict(test_x) # 得到预测输出,可以与真实输出作比较,计算预测的精准度(预测正确的样本数/总测试样本数) ac = (test_y == pred_test_y).sum() / test_y.size print('预测精准度 ac=', ac) # 绘制分类边界线 l, r = x[:, 0].min() - 1, x[:, 0].max() + 1 b, t = x[:, 1].min() - 1, x[:, 1].max() + 1 n = 500 grid_x, grid_y = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(l, r, n), np.linspace(b, t, n)) bg_x = np.column_stack((grid_x.ravel(), grid_y.ravel())) bg_y = model.predict(bg_x) grid_z = bg_y.reshape(grid_x.shape) # 画图 mp.figure('NB Classification', facecolor='lightgray') mp.title('NB Classification', fontsize=16) mp.xlabel('X', fontsize=14) mp.ylabel('Y', fontsize=14) mp.tick_params(labelsize=10) mp.pcolormesh(grid_x, grid_y, grid_z, cmap='gray') mp.scatter(test_x[:, 0], test_x[:, 1], s=80, c=test_y, cmap='jet', label='Samples') mp.legend() mp.show() 输出结果: (400, 3) accuracy score= [1. 1. 1. 1. 0.98305085] accuracy mean= 0.9966101694915255 precision_weighted score= [1. 1. 1. 1. 0.98411017] precision_weighted mean= 0.996822033898305 recall_weighted score= [1. 1. 1. 1. 0.98305085] recall_weighted mean= 0.9966101694915255 f1_weighted score= [1. 1. 1. 1. 0.98303199] f1_weighted mean= 0.9966063988235516 预测精准度 ac= 0.99