React是facebook推出的js框架,React 本身只涉及UI层,如果搭建大型应用,必须搭配一个前端框架。也就是说,你至少要学两样东西,才能基本满足需要:React + 前端框架。
Facebook官方使用的是 Flux 框架。本文就介绍如何在 React 的基础上,使用 Flux 组织代码和安排内部逻辑。
首先,Flux将一个应用分成四个部分:
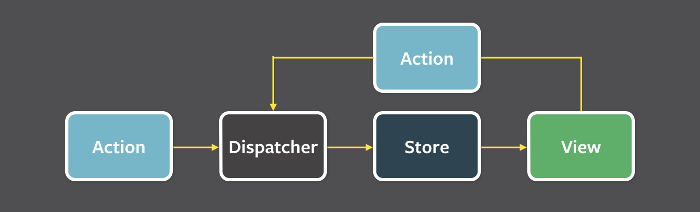
Flux 的最大特点,就是数据的"单向流动"。
- 用户访问 View
- View 发出用户的 Action
- Dispatcher 收到 Action,要求 Store 进行相应的更新
- Store 更新后,发出一个"change"事件
- View 收到"change"事件后,更新页面.
1 // index.jsx 2 var React = require('react'); 3 var ReactDOM = require('react-dom'); 4 var MyButtonController = require('./components/MyButtonController'); 5 6 ReactDOM.render( 7 <MyButtonController/>, 8 document.querySelector('#example') //渲染组件到id=example的元素中 9 );
1 // components/MyButtonController.jsx 2 var React = require('react'); 3 var ButtonActions = require('../actions/ButtonActions'); 4 var MyButton = require('./MyButton'); 5 6 var MyButtonController = React.createClass({ 7 createNewItem: function (event) { 8 ButtonActions.addNewItem('new item'); //这里是什么? buttonActions 9 }, 10 11 render: function() { 12 return <MyButton 13 onClick={this.createNewItem} //看到这里下面肯定还会有个button组件 会调用此处的onclick事件 14 />; 15 } 16 }); 17 18 module.exports = MyButtonController;
1 // components/MyButton.jsx 2 var React = require('react'); 3 4 var MyButton = function(props) { 5 return <div> 6 <button onClick={props.onClick}>New Item</button> //果然没错吧 通过prop调用在上面定义好的促发函数 7 </div>; 8 }; 9 10 module.exports = MyButton;
每个Action都是一个对象,包含一个
actionType属性(说明动作的类型)和一些其他属性(用来传递数据)。 -
1 // actions/ButtonActions.js 2 var AppDispatcher = require('../dispatcher/AppDispatcher'); 3 4 var ButtonActions = { 5 addNewItem: function (text) { //现在知道上面的调用是怎么来的了 就是此处 6 AppDispatcher.dispatch({ 7 actionType: 'ADD_NEW_ITEM', 8 text: text 9 }); 10 }, 11 };
1 // dispatcher/AppDispatcher.js 2 var ListStore = require('../stores/ListStore'); 3 4 AppDispatcher.register(function (action) { //register和dispatch是相对的 一个是注册事件 一个是派发事件和数据 5 switch(action.actionType) { //这里的action是.dispatch方法里的参数 6 case 'ADD_NEW_ITEM': 7 ListStore.addNewItemHandler(action.text); //当传过来的actionType = ‘add——new——item’ 会发生这个事件 往下看 8 ListStore.emitChange(); //这里添加玩内容后,自动触发下面的emitchangge事件 往下看 9 break; 10 default: 11 // no op 12 } 13 })
Dispatcher 的作用是将 Action 派发到 Store、。你可以把它看作一个路由器,负责在 View 和 Store 之间,建立 Action 的正确传递路线。注意,Dispatcher 只能有一个,而且是全局的。
1 // stores/ListStore.js 2 var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter; 3 var assign = require('object-assign'); 4 5 var ListStore = assign({}, EventEmitter.prototype, { //es6浅克隆方法 6 items: [], 7 8 getAll: function () { 9 return this.items; 10 }, 11 12 addNewItemHandler: function (text) { //就是这里 上面调用了这个函数 就是添加内容的实现 13 this.items.push(text); 14 }, 15 16 emitChange: function () { 17 this.emit('change'); 18 }, 19 20 addChangeListener: function(callback) { 21 this.on('change', callback); //监听change事件 然后进行回调 22 }, 23 24 removeChangeListener: function(callback) { 25 this.removeListener('change', callback); 26 } 27 });
Store 保存整个应用的状态。它的角色有点像 MVC 架构之中的Model 。上面代码中,
ListStore继承了EventEmitter.prototype,因此就能使用ListStore.on()和ListStore.emit(),来监听和触发事件了。1 // components/MyButtonController.jsx 修改后完整的view代码 2 var React = require('react'); 3 var ListStore = require('../stores/ListStore'); 4 var ButtonActions = require('../actions/ButtonActions'); 5 var MyButton = require('./MyButton'); 6 7 var MyButtonController = React.createClass({ 8 getInitialState: function () { 9 return { 10 items: ListStore.getAll() //初始化state是根据listStore里面取出来的 11 }; 12 }, 13 14 componentDidMount: function() { 15 ListStore.addChangeListener(this._onChange); //当listStore促发change事件会导致 该组件调用_onChange() 16 }, 17 18 componentWillUnmount: function() { 19 ListStore.removeChangeListener(this._onChange); 20 }, 21 22 _onChange: function () { 23 this.setState({ 24 items: ListStore.getAll() //重新填充数据 25 }); 26 }, 27 28 createNewItem: function (event) { 29 ButtonActions.addNewItem('new item'); 30 }, 31 32 render: function() { 33 return <MyButton 34 items={this.state.items} 35 onClick={this.createNewItem} 36 />; 37 } 38 });
上面代码中,你可以看到当
MyButtonController发现 Store 发出change事件,就会调用this._onChange更新组件状态,从而触发重新渲染。1 // components/MyButton.jsx 最终的mybutton 2 var React = require('react'); 3 4 var MyButton = function(props) { 5 var items = props.items; //prop调用上级组件的参数 6 var itemHtml = items.map(function (listItem, i) { 7 return <li key={i}>{listItem}</li>; 8 }); 9 10 return <div> 11 <ul>{itemHtml}</ul> 12 <button onClick={props.onClick}>New Item</button> 13 </div>; 14 }; 15 16 module.exports = MyButton;
关于redux:如果你的UI层非常简单,没有很多互动,Redux 就是不必要的,用了反而增加复杂性,下面描述了需要redux的情景
- 用户的使用方式复杂
- 不同身份的用户有不同的使用方式(比如普通用户和管理员)
- 多个用户之间可以协作
- 与服务器大量交互,或者使用了WebSocket
- View要从多个来源获取数据
1 //Store 就是保存数据的地方,你可以把它看成一个容器。整个应用只能有一个 Store。 2 import { createStore } from 'redux'; 3 const store = createStore(fn); 4 当前时刻的 State,可以通过store.getState()拿到。 5 const state = store.getState(); 6 Redux 规定, 一个 State 对应一个 View。只要 State 相同,View 就相同。 7 8 State 的变化,会导致 View 的变化。但是,用户接触不到 State,只能接触到 View。所以,State 的变化必须是 View 导致的。Action 就是 View 发出的通知,表示 State 应该要发生变化了。 9 10 const action = { 11 type: 'ADD_TODO', 12 payload: 'Learn Redux' 13 };//上面代码中,Action 的名称是ADD_TODO,它携带的信息是字符串Learn Redux。 14 15 const ADD_TODO = '添加 TODO'; 16 17 function addTodo(text) { 18 return { 19 type: ADD_TODO, 20 text 21 } 22 } 23 24 const action = addTodo('Learn Redux'); 25 //上面代码中,addTodo函数就是一个 Action Creator。 26 27 store.dispatch({ 28 type: 'ADD_TODO', 29 payload: 'Learn Redux' 30 }); //store.dispatch接受一个 Action 对象作为参数,将它发送出去。 31 32 Store 收到 Action 以后,必须给出一个新的 State,这样 View 才会发生变化。这种 State 的计算过程就叫做 Reducer。 33 34 const defaultState = 0; 35 const reducer = (state = defaultState, action) => { 36 switch (action.type) { 37 case 'ADD': 38 return state + action.payload; 39 default: 40 return state; 41 } 42 }; 43 44 import { createStore } from 'redux'; 45 const store = createStore(reducer); //fn就是这里的reducer 46 47 //上面代码中,createStore接受 Reducer 作为参数,生成一个新的 Store。以后每当store.dispatch发送过来一个新的 Action,就会自动调用 Reducer,得到新的 State。 48 49 //Store 允许使用store.subscribe方法设置监听函数,一旦 State 发生变化,就自动执行这个函数。 50 const store = createStore(reducer); 51 store.subscribe(listener); 52 53 显然,只要把 View 的更新函数(对于 React 项目,就是组件的render方法或setState方法)放入listen,就会实现 View 的自动渲染。 54 55 let unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => 56 console.log(store.getState()) 57 ); 58 unsubscribe(); //store.subscribe方法返回一个函数,调用这个函数就可以解除监听。
下面是
createStore方法的一个简单实现,可以了解一下 Store 是怎么生成的。1 import { createStore } from 'redux'; 2 let { subscribe, dispatch, getState } = createStore(reducer); 3 4 const createStore = (reducer) => { 5 let state; 6 let listeners = []; 7 8 const getState = () => state; 9 10 const dispatch = (action) => { 11 state = reducer(state, action); //派发action执行state变更 12 listeners.forEach(listener => listener()); //调用所有监听函数 13 }; 14 15 const subscribe = (listener) => { //添加监听的事件 16 listeners.push(listener); 17 return () => { 18 listeners = listeners.filter(l => l !== listener); 19 } 20 }; 21 22 dispatch({}); 23 24 return { getState, dispatch, subscribe }; //返回的就是这3个const 25 };
Reducer 函数负责生成 State。由于整个应用只有一个 State 对象,包含所有数据,对于大型应用来说,这个 State 必然十分庞大,导致 Reducer 函数也十分庞大。
1 const chatReducer = (state = defaultState, action = {}) => { 2 const { type, payload } = action; 3 switch (type) { 4 case ADD_CHAT: 5 return Object.assign({}, state, { 6 chatLog: state.chatLog.concat(payload) 7 }); 8 case CHANGE_STATUS: 9 return Object.assign({}, state, { 10 statusMessage: payload 11 }); 12 case CHANGE_USERNAME: 13 return Object.assign({}, state, { 14 userName: payload 15 }); 16 default: return state; 17 } 18 };//上面代码中,三种 Action 分别改变 State 的三个属性。
Redux 提供了一个
combineReducers方法,用于 Reducer 的拆分。你只要定义各个子 Reducer 函数,然后用这个方法,将它们合成一个大的 Reducer。import { combineReducers } from 'redux'; const chatReducer = combineReducers({ chatLog, statusMessage, userName }) export default todoApp; //下面是combineReducer的简单实现。 const combineReducers = reducers => { return (state = {}, action) => { return Object.keys(reducers).reduce( (nextState, key) => { nextState[key] = reducers[key](state[key], action); return nextState; }, {} ); }; }; //你可以把所有子 Reducer 放在一个文件里面,然后统一引入。 import { combineReducers } from 'redux' import * as reducers from './reducers' const reducer = combineReducers(reducers)1 //listener可以通过store.getState()得到当前状态。如果使用的是 React,这时可以触发重新渲染 View。 2 // 设置监听函数 3 store.subscribe(listener); 4 function listerner() { 5 let newState = store.getState(); 6 component.setState(newState); 7 }
来一个实例练练手
1 //redux/index.js 2 export default (state = 0, action) => { //每次有dispatch过来 根据action.type促发相应事件 返回一个新的state 3 switch (action.type) { 4 case 'INCREMENT': 5 return state + 1 6 case 'DECREMENT': 7 return state - 1 8 default: 9 return state 10 } 11 }
1 import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react' 2 3 class Counter extends Component { 4 static propTypes = { //这里对数据类型做了规范 5 value: PropTypes.number.isRequired, 6 onIncrement: PropTypes.func.isRequired, 7 onDecrement: PropTypes.func.isRequired 8 } 9 10 incrementIfOdd = () => { 11 if (this.props.value % 2 !== 0) { 12 this.props.onIncrement() 13 } 14 } 15 16 incrementAsync = () => { //异步调用 等待1s执行prop上的 onIncrement 17 setTimeout(this.props.onIncrement, 1000) 18 } 19 20 render() { 21 const { value, onIncrement, onDecrement } = this.props //注意这里的用法 等下看下调用该组件的是哪一个 22 return ( 23 <p> 24 Clicked: {value} times 25 {' '} 26 <button onClick={onIncrement}> 27 + 28 </button> 29 {' '} 30 <button onClick={onDecrement}> 31 - 32 </button> 33 {' '} 34 <button onClick={this.incrementIfOdd}> 35 Increment if odd 36 </button> 37 {' '} 38 <button onClick={this.incrementAsync}> 39 Increment async 40 </button> 41 </p> 42 ) 43 } 44 } 45 46 export default Counter
1 import React from 'react' 2 import ReactDOM from 'react-dom' 3 import { createStore } from 'redux' 4 import Counter from './components/Counter' 5 import counter from './reducers' 6 7 const store = createStore(counter) 8 const rootEl = document.getElementById('root') 9 10 const render = () => ReactDOM.render( 11 <Counter //这里的prop浮出水面 往上面看属性是否对应 12 value={store.getState()} 13 onIncrement={() => store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' })} 14 onDecrement={() => store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' })} 15 />, 16 rootEl 17 ) 18 19 render() 20 store.subscribe(render) //每回state变化 就会从新render()
希望对大家有帮助,今天就一直在研究这2个东西,有点搞人呀。。。本文参考了许多很好的文章和博客