在看HashMap的源码时候看到了TreeNode。因此需要对其进行一个了解。是一个红黑树。可以百度一下红黑树的数据结构。分析了下源码,还是比较枯燥的
红黑树的性质:本身是一个二叉查找树(所有左节点的值都比右节点的小)。另:
- 节点是红色或者黑色
- 根节点是黑色
- 每个叶节点(Nil节点,空节点)是黑色的
- 每个红节点对应的两个子节点都是黑色的(不可能有两个相连的红节点)。
- 从任意节点出发,到每个叶子节点都有相同的黑色节点。
这保证了红黑数是平衡的,从根到叶子的最长的可能路径不多于最短的可能路径的两倍长,因此插入、删除查找的最坏情况是有所保证的,与树的高度成正比。原因有两点:
- 最短的可能路径都是黑色节点。
- 最长的路径是红黑节点交替的路径。
因为从同一节点出发,到每一个叶子有相同的黑色节点,所以保证了最长路径是最短路径的两倍长。
一、成员变量与构造函数
1 static final class TreeNode<K,V> extends LinkedHashMap.Entry<K,V> { 2 //父节点 3 HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> parent; // red-black tree links 4 //左节点 5 HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> left; 6 //右节点 7 HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> right; 8 //用来删除下一个节点用的,因此prev也就是上一个节点 9 HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> prev; // needed to unlink next upon deletion 10 //节点是否为红色 11 boolean red; 12 TreeNode(int hash, K key, V val, HashMap.Node<K,V> next) { 13 super(hash, key, val, next); 14 } 15 }
二、Function root
1 /** 2 * 返回包含此节点的树的根节点 3 */ 4 final HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> root() { 5 //定义两个TreeNode,一个是父节点指针,指向当前节点的parent,所以功能很明显了。就是遍历直到头节点 6 for (HashMap.TreeNode<K,V> r = this, p;;) { 7 if ((p = r.parent) == null) 8 return r; 9 r = p; 10 } 11 }
三、Function checkInvariants
1 /** 2 * 不变性检查,保证红黑树的结构不改变。 3 */ 4 static <K, V> boolean checkInvariants(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> t) { 5 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> tp = t.parent, tl = t.left, tr = t.right, 6 tb = t.prev, tn = (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) t.next; 7 if (tb != null && tb.next != t) 8 return false; 9 if (tn != null && tn.prev != t) 10 return false; 11 if (tp != null && t != tp.left && t != tp.right) 12 return false; 13 if (tl != null && (tl.parent != t || tl.hash > t.hash)) 14 return false; 15 if (tr != null && (tr.parent != t || tr.hash < t.hash)) 16 return false; 17 if (t.red && tl != null && tl.red && tr != null && tr.red) 18 return false; 19 if (tl != null && !checkInvariants(tl)) 20 return false; 21 if (tr != null && !checkInvariants(tr)) 22 return false; 23 return true; 24 } 25 }
四、Function moveRootToFront
1 /** 2 * 确保所给的root是第一个节点。也就是把所给的root移到第一个节点。确保桶的红黑树的跟节点是root 3 */ 4 static <K, V> void moveRootToFront(HashMap.Node<K, V>[] tab, HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root) { 5 int n; 6 if (root != null && tab != null && (n = tab.length) > 0) { 7 //根节点的位置 8 int index = (n - 1) & root.hash; 9 10 //链表的操作,把root移到第一个节点。root的next指向原先的头节点,原先的头节点的prev指向root; 11 //root的next的prev指向root的prev,root的prev指向root的next,即把root在prev和next中去掉 12 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> first = (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) tab[index]; 13 if (root != first) { 14 HashMap.Node<K, V> rn; 15 tab[index] = root; 16 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> rp = root.prev; 17 if ((rn = root.next) != null) 18 ((HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) rn).prev = rp; 19 if (rp != null) 20 rp.next = rn; 21 if (first != null) 22 first.prev = root; 23 root.next = first; 24 root.prev = null; 25 } 26 //红黑树的一致性检查 27 assert checkInvariants(root); 28 } 29 }
五、Function find
1 /** 2 * Finds the node starting at root p with the given hash and key. 3 * The kc argument caches comparableClassFor(key) upon first use 4 * comparing keys. 5 */ 6 final HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> find(int h, Object k, Class<?> kc) { 7 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p = this; 8 do { 9 int ph, dir; 10 K pk; 11 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> pl = p.left, pr = p.right, q; 12 13 //p的hash > 目标hash, 则查找左子树,否则右子树 14 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 15 p = pl; 16 else if (ph < h) 17 p = pr; 18 //找到则返回 19 else if ((pk = p.key) == k || (k != null && k.equals(pk))) 20 return p; 21 //如果左节点是Null则找右子树,右节点是Null则找左子树 22 else if (pl == null) 23 p = pr; 24 else if (pr == null) 25 p = pl; 26 //如果不按照hash比较,则按照比较器比较,查找左子树还是右子树 27 else if ((kc != null || 28 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) != null) && 29 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) != 0) 30 p = (dir < 0) ? pl : pr; 31 //如果在右子树找到则直接返回 32 else if ((q = pr.find(h, k, kc)) != null) 33 return q; 34 //否则在左子树查找 35 else 36 p = pl; 37 } while (p != null); 38 //否则返回Null 39 return null; 40 }
六、Function tieBreakOrder
1 /** 2 * 在像红黑树插入即节点的时候,为了确定相同hashCode的节点插入的顺序, 3 * 设定了插入顺序的规则,结果一定是不想等的。非左即右。 4 */ 5 static int tieBreakOrder(Object a, Object b) { 6 int d; 7 8 //会对两个类名相等的类进行比较 9 if (a == null || b == null || 10 (d = a.getClass().getName(). 11 compareTo(b.getClass().getName())) == 0) 12 //返回两个类内存地址的hashCode比较结果,小的或者相都是-1,否则1,并非是类的hashCode的比较 13 d = (System.identityHashCode(a) <= System.identityHashCode(b) ? 14 -1 : 1); 15 return d; 16 }
七、Function rotateLeft, 左旋
图片来源(https://blog.csdn.net/sun_tttt/article/details/65445754)

1 static <K, V> HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> rotateLeft(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root, 2 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p) { 3 //三个节点,右节点,parent的parent节点,右的左节点 4 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> r, pp, rl; 5 //该节点不为null并且右节点不为null 6 if (p != null && (r = p.right) != null) { 7 //因为是左旋,所以如果右节点的左节点如果不为null,则rl的根节点设为p 8 if ((rl = p.right = r.left) != null) 9 rl.parent = p; 10 //如果左旋后的头节点为根节点,则根据红黑树的性质,颜色为黑色 11 if ((pp = r.parent = p.parent) == null) 12 (root = r).red = false; 13 //因为是左旋,所以p的位置由pr取代,所以p的parent节点的p位置设为现在pr的位置。 14 else if (pp.left == p) 15 pp.left = r; 16 else 17 pp.right = r; 18 //然后r的left是p,p的父节点是r 19 r.left = p; 20 p.parent = r; 21 } 22 return root; 23 }
八、Function rightRotate, 右旋
图片来源(https://blog.csdn.net/sun_tttt/article/details/65445754)
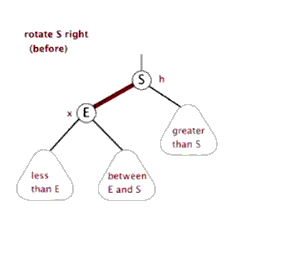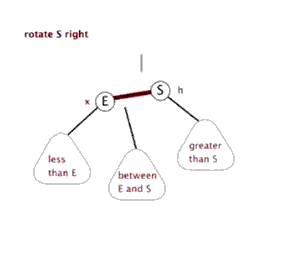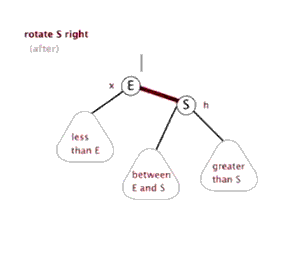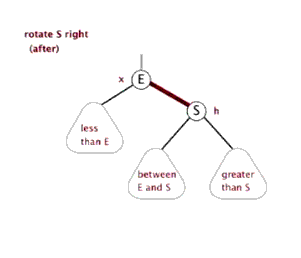
1 static <K, V> HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> rotateRight(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root, 2 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p) { 3 //定义3个节点,左节点,头节点的头节点,左节点的右节点 4 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> l, pp, lr; 5 //要旋转的节点和左节点不为空时 6 if (p != null && (l = p.left) != null) { 7 //根据右旋,(原)头节点的左节点为原先左节点的右节点,并且把其父节点设为原头节点,即p 8 if ((lr = p.left = l.right) != null) 9 lr.parent = p; 10 //同样,如果现在的头节点为根节点的话,标记节点的颜色为黑色 11 if ((pp = l.parent = p.parent) == null) 12 (root = l).red = false; 13 //头节点的头节点设定其自节点 14 else if (pp.right == p) 15 pp.right = l; 16 else 17 pp.left = l; 18 //同样,根据右旋,指定现在的头节点的右节点为原先的头节点,原先的头节点的父节点为现在的头节点 19 l.right = p; 20 p.parent = l; 21 } 22 return root; 23 }
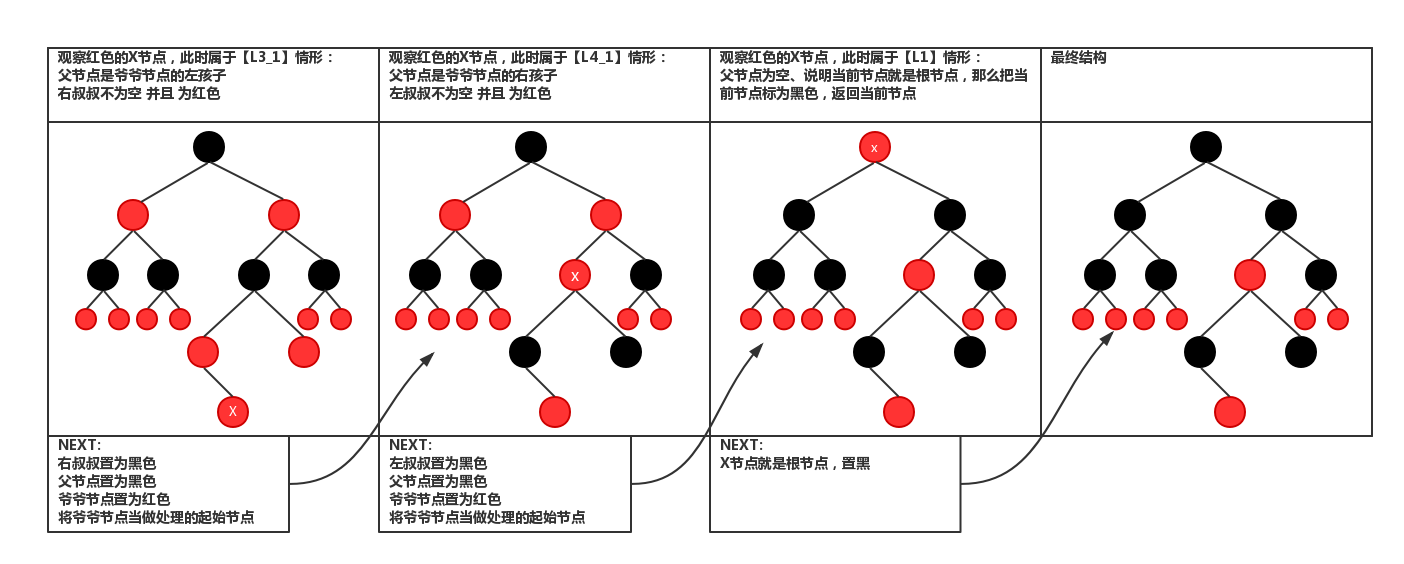
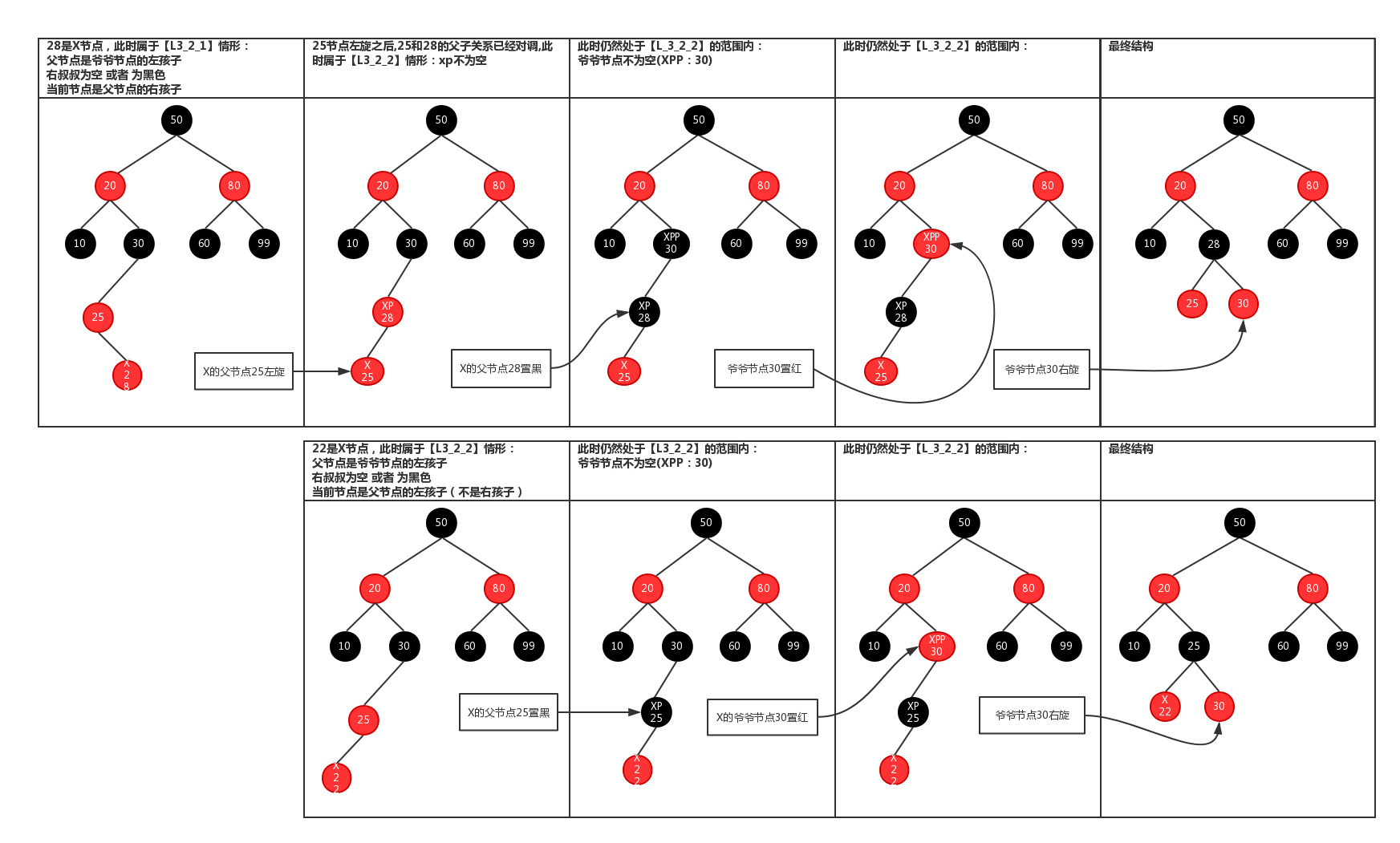
九、Function balanceInsertion 代码和图结合看很好理解过程,至于为什么会平衡还要分析。
图片来源https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42340670/article/details/80550932
1.无旋转
2.旋转情况1
3.旋转情况2

1 /* 2 保证插入节点后,红黑树仍然是平衡的,代码很长,结合图看更好理解点,这样看太抽象了。但是虽然逻辑复杂,但是足以 3 见证红黑树的高效性,因为更新树的话只是旋转操作,即改变下指针的位置,并且设置一下节点的位置就可以了 4 */ 5 static <K, V> HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> balanceInsertion(HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root, 6 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> x) { 7 //先把节点设为红色 8 x.red = true; 9 //定义四个节点 10 for (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> xp, xpp, xppl, xppr; ; ) { 11 //如果x是根节点,则把它设为黑色,并返回根节点 12 if ((xp = x.parent) == null) { 13 x.red = false; 14 return x; 15 } 16 //如果x的父节点即xp是黑色,并且xp为根节点,则返回,什么也不做。 17 else if (!xp.red || (xpp = xp.parent) == null) 18 return root; 19 //如果xp为xp父节点的左节点 20 if (xp == (xppl = xpp.left)) { 21 //如果xpp的右节点非空并且是红色的,那么把其设为黑色,xpp的左节点也设为黑色,xpp设为红色,并且x等于xpp 22 if ((xppr = xpp.right) != null && xppr.red) { 23 xppr.red = false; 24 xp.red = false; 25 xpp.red = true; 26 x = xpp; 27 } 28 //如果xpp的右节点是空或者为黑色的话 29 else { 30 //如果x是xp的右节点,那么左旋xp节点,并且重新更新xp和xpp 31 if (x == xp.right) { 32 root = rotateLeft(root, x = xp); 33 xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent; 34 } 35 //如果x的父节点不为空,先把它设为黑色 36 if (xp != null) { 37 xp.red = false; 38 //如果xp的父节点不为空,则先把xpp设为红色,然后再右旋 39 if (xpp != null) { 40 xpp.red = true; 41 root = rotateRight(root, xpp); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 } 46 //如果xp为xp父节点的右右节点 47 else { 48 //如果xpp的左节点非空并且是红色的话,把xppl设为黑色,xp设为黑色,xp的父节点设为红色 49 if (xppl != null && xppl.red) { 50 xppl.red = false; 51 xp.red = false; 52 xpp.red = true; 53 x = xpp; 54 } 55 //如果xpp的左节点是空或者是黑色的话 56 else { 57 //如果x为父节点的左节点,则右旋xp节点,并重新设置xp,xpp 58 if (x == xp.left) { 59 root = rotateRight(root, x = xp); 60 xpp = (xp = x.parent) == null ? null : xp.parent; 61 } 62 //如果x的父节点为空, 63 if (xp != null) { 64 //先把其设为黑色 65 xp.red = false; 66 //如果xp的父节点不为空,则xpp设为红色,并左旋xpp节点 67 if (xpp != null) { 68 xpp.red = true; 69 root = rotateLeft(root, xpp); 70 } 71 } 72 } 73 } 74 } 75 }
十、Function treeify
1 /** 2 * 把链表生成红黑树,返回头节点 3 */ 4 final void treeify(HashMap.Node<K, V>[] tab) { 5 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> root = null; 6 7 //两个指针,一个是链表的表头,一个是下一个指针 8 for (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> x = this, next; x != null; x = next) { 9 next = (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V>) x.next; 10 x.left = x.right = null; 11 12 //先设定 root为头节点,parent为null,根节点为黑色, 13 if (root == null) { 14 x.parent = null; 15 x.red = false; 16 root = x; 17 } else { 18 K k = x.key; 19 int h = x.hash; 20 Class<?> kc = null; 21 22 //遍历红黑树 23 for (HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> p = root; ; ) { 24 int dir, ph; 25 K pk = p.key; 26 //如果当前树节点的hash > 链表节点的hash则dir值为-1 27 if ((ph = p.hash) > h) 28 dir = -1; 29 //否则为1 30 else if (ph < h) 31 dir = 1; 32 //如果不按照hash值比较的话,并且比较器不存在或者比较器比较的值是0的话,则把死结打开 33 else if ((kc == null && 34 (kc = comparableClassFor(k)) == null) || 35 (dir = compareComparables(kc, k, pk)) == 0) 36 dir = tieBreakOrder(k, pk); 37 //设置一个红黑树的节点 38 HashMap.TreeNode<K, V> xp = p; 39 //设置节点的走向,如果dir <= 0则p为做节点,否则为右,也就是找到链表节点应该插入的位置 40 if ((p = (dir <= 0) ? p.left : p.right) == null) { 41 //设置链表节点的父节点 42 x.parent = xp; 43 if (dir <= 0) 44 xp.left = x; 45 else 46 xp.right = x; 47 //插入节点,并且不破坏红黑树的性质 48 root = balanceInsertion(root, x); 49 break; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 } 54 //设置头节点 55 moveRootToFront(tab, root); 56 }
十一、Function split
1 /** 2 * 树减枝, 3 * 只有在resize的时候才调用该方法 4 * @param map the map 5 * @param tab 新的table 6 * @param index 老的table的index 7 * @param bit oldCap 8 */ 9 final void split(HashMap<K,V> map, Node<K,V>[] tab, int index, int bit) { 10 TreeNode<K,V> b = this; 11 // Relink into lo and hi lists, preserving order 12 TreeNode<K,V> loHead = null, loTail = null; 13 TreeNode<K,V> hiHead = null, hiTail = null; 14 // 如果size很小的话则把树变成链表,用lc和hc来计数 15 int lc = 0, hc = 0; 16 // 遍历红黑树 17 for (TreeNode<K,V> e = b, next; e != null; e = next) { 18 next = (TreeNode<K,V>)e.next; 19 e.next = null; 20 // 判断将树的节点归为哪一部分 21 if ((e.hash & bit) == 0) { 22 if ((e.prev = loTail) == null) 23 loHead = e; 24 else 25 loTail.next = e; 26 loTail = e; 27 ++lc; 28 } 29 else { 30 if ((e.prev = hiTail) == null) 31 hiHead = e; 32 else 33 hiTail.next = e; 34 hiTail = e; 35 ++hc; 36 } 37 } 38 39 //lo这部分树放入的位置,index即原先的位置 40 if (loHead != null) { 41 if (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) 42 tab[index] = loHead.untreeify(map); 43 else { 44 tab[index] = loHead; 45 if (hiHead != null) // (else is already treeified) 46 loHead.treeify(tab); 47 } 48 } 49 //index+bit这部分改变了 50 if (hiHead != null) { 51 if (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) 52 tab[index + bit] = hiHead.untreeify(map); 53 else { 54 tab[index + bit] = hiHead; 55 if (loHead != null) 56 hiHead.treeify(tab); 57 } 58 } 59 }