问题概述
最近在处理一些TCP客户端的项目,服务端是C语言开发的socket. 实际项目开始的时候使用默认的阻塞模式并未发现异常。代码如下

1 public class SocketService 2 { 3 public delegate void TcpEventHandler1(byte[] receivebody, int length); 4 public event TcpEventHandler1 OnGetCS; 5 Socket client = null; 6 IPEndPoint endPoint = null; 7 public SocketService(string ip, int port) 8 { 9 client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); 10 //client.Blocking = false;默认是阻塞模式 11 endPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip), port); 12 IsRcv = true; 13 } 14 15 Thread rthr = null;//异步线程用于接收数据 16 17 /// <summary> 18 /// 表示是否继续接收数据 19 /// </summary> 20 public bool IsRcv { get; set; } 21 /// <summary> 22 /// 打开连接 23 /// </summary> 24 /// <returns></returns> 25 public bool Open() 26 { 27 if (client != null && endPoint != null) 28 { 29 try 30 { 31 client.Connect(endPoint); 32 Console.WriteLine("连接成功"); 33 34 //启动异步监听 35 rthr = new Thread(ReceiveMsg); 36 rthr.IsBackground = true; 37 rthr.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA); 38 rthr.Start(); 39 return true; 40 } 41 catch 42 { 43 AbortThread(); 44 Console.WriteLine("连接失败!"); 45 } 46 } 47 return false; 48 } 49 50 /// <summary> 51 /// 关闭接收数据线程 52 /// </summary> 53 private void AbortThread() 54 { 55 if (rthr != null) 56 { 57 rthr.Abort(); 58 } 59 } 60 61 /// <summary> 62 /// 关闭连接 63 /// </summary> 64 public void Close() 65 { 66 if (client.Connected) 67 { 68 client.Close(); 69 } 70 } 71 72 /// <summary> 73 /// 接收数据 74 /// </summary> 75 private void ReceiveMsg() 76 { 77 byte[] arrMsg = new byte[1024 * 1024]; 78 try 79 { 80 while (IsRcv) 81 { 82 int length = client.Receive(arrMsg);//阻塞模式,此次线程会停止继续执行,直到socket内核有数据 83 byte type; 84 if (length > 0) 85 OnGetCS(arrMsg, length); //出发数据接收事件 86 } 87 } 88 catch (Exception ex) 89 { 90 rthr.Abort(); 91 client.Close(); 92 client = null; 93 Console.WriteLine("服务器断开连接"); 94 } 95 } 96 }
当客户运行久后就发现 从服务器端发过来的数据到处理完成整个环节消耗的时间比较多(比同行慢)。
使用TCP 监听助手,和客户端程序在OnGetCS处打印出时间比较分析,发现TCP助手显示收到的时间会比客户端程序显示的快500-800MS左右。
.也就是说服务器已经吧数据发送到客户端TCP缓冲区了,只是客户端 int length = client.Receive(arrMsg); 并么有及时获得相应。
查了很多资料都没有查到有类似的问题。最后我用C#模拟做了一个TCP服务端与自己的TCP客户端之间通信,则完全没有延迟。
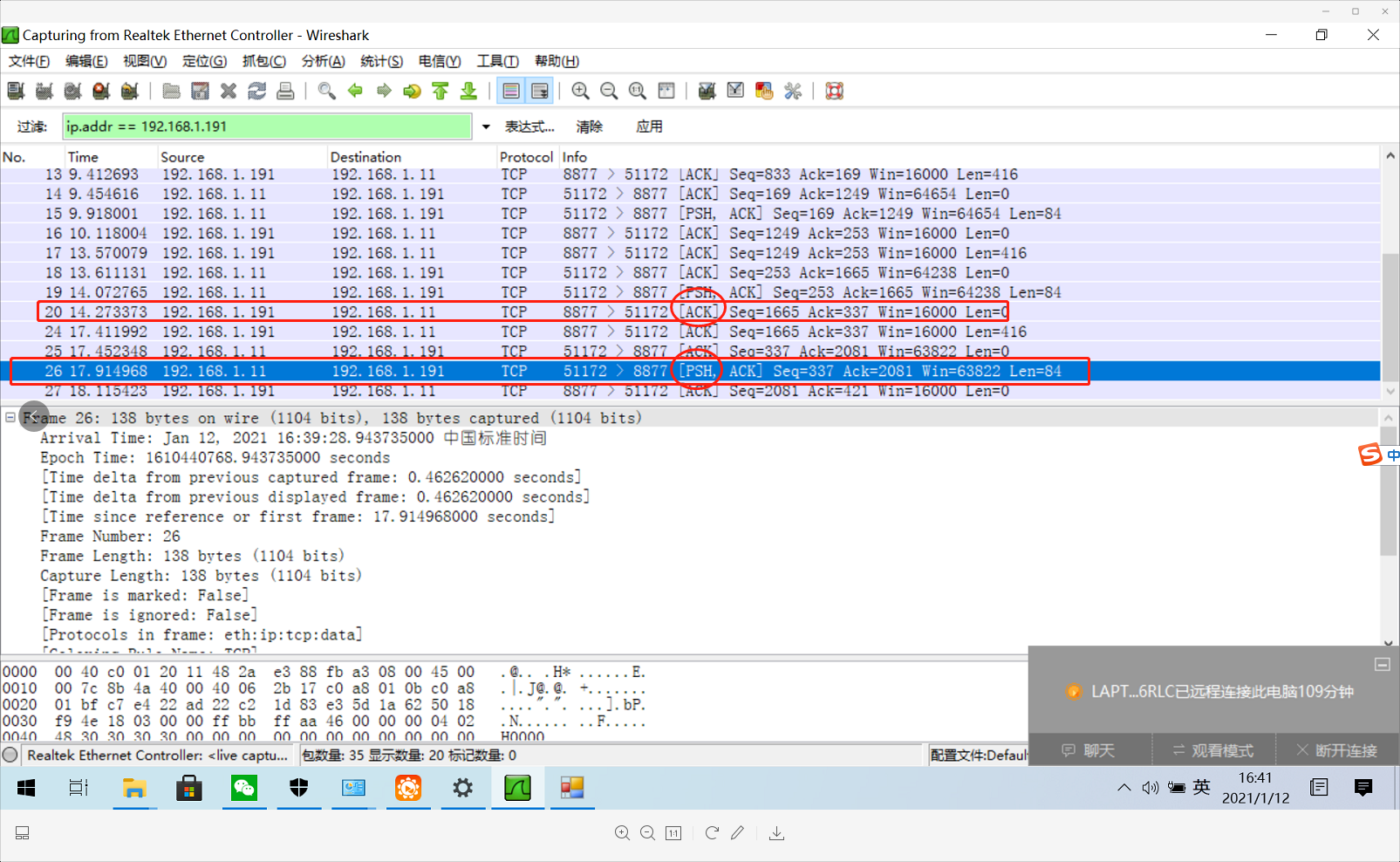
因此只能考虑语言特性的差别了。C#毕竟封装了很多信息。这个时候再查看TCP监听助手对比服务器是C的和C#的发现 C服务器在指令标记位没有PSH标记位,而C#的则有这个标记位,如下图(此处C#作为服务器的有兴趣的可以自己去试)
查询网络上的一段解释如下
PSH 的作用
TCP 模块什么时候将数据发送出去(从发送缓冲区中取数据),以及 read 函数什么时候将数据从接收缓冲区读取都是未知的。
如果使用 PSH 标志,上面这件事就确认下来了:
- 发送端
对于发送方来说,由 TCP 模块自行决定,何时将接收缓冲区中的数据打包成 TCP 报文,并加上 PSH 标志(在图 1 中,为了演示,我们假设人为的干涉了 PSH 标志位)。一般来说,每一次 write,都会将这一次的数据打包成一个或多个 TCP 报文段(如果数据量大于 MSS 的话,就会被打包成多个 TCP 段),并将最后一个 TCP 报文段标记为 PSH。
当然上面说的只是一般的情况,如果发送缓冲区满了,TCP 同样会将发送缓冲区中的所有数据打包发送。
- 接收端
如果接收方接收到了某个 TCP 报文段包含了 PSH 标志,则立即将缓冲区中的所有数据推送给应用进程(read 函数返回)。
当然有时候接收缓冲区满了,也会推送。
通过这个解释瞬间总算是明白了,早期C开发的很多TCP通信,都是不带PSH标记位的,后来的产品很多都遵守这个模式了,然后我们的C#默认就是使用PSH标记位。 因此就导致了数据接收延迟500-800MS(根据PSH的解释这个延迟具体多久是未知的)。
解决方案
最简单的是服务器端增加这个标记位发送过来。一番讨论后,人家写这个服务器的人都已经离职了,没人会处理。那么客户是上帝,只能我们这边来处理了。这里就要用到非阻止模式的socket了。
首先我在网上查到很多人说异步就是非阻止模式。这个完全是错误的。异步同步与阻止模式是没有关系的两个概念。 当阻塞模式下有一个线程不断在等待缓冲区把数据交给它处理,异步的话就是触发回调方法,同步的话就继续执行同步的业务代码。
而非阻塞模式的逻辑是,客户端的连接,读取数据线程都不会被阻塞,也就是会立即返回。比如连接的逻辑是客户端发起connect连接,因为TCP连接有几次握手的情况,需要一定的时间,然而非阻塞要求立即返回,这个时候系统会抛一个异常(Win32Excetion)。
我们则只需要在异常里处理这个TCP连接需要一定时间的问题。可以循环读取TCP连接状态来确认是否连接成功。client.Poll 方法来查询当前连接状态。同理读取的时候也是在该异常里循环读取。

1 public class SocketService 2 { 3 public delegate void TcpEventHandler1(byte[] receivebody, int length); 4 public event TcpEventHandler1 OnGetCS; 5 Socket client = null; 6 IPEndPoint endPoint = null; 7 public SocketService(string ip, int port) 8 { 9 client = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp); 10 client.Blocking = false;//非阻塞模式,定时循环读取缓冲区的数据把它拼接到缓冲区数据队列 arrMsg 11 endPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip), port); 12 } 13 14 Thread rthr = null; 15 /// <summary> 16 /// 表示是否继续接收数据 17 /// </summary> 18 public bool IsRcv { get; set; } 19 /// <summary> 20 /// 非阻塞模式 21 /// </summary> 22 /// <param name="timeout"></param> 23 /// <returns></returns> 24 public bool Open(int timeout = 1000) 25 { 26 bool connected = false; 27 if (client != null && endPoint != null) 28 { 29 try 30 { 31 client.Connect(endPoint);//此处不会阻塞,如果是正在连接服务器的话,则会跑出win32Excetion异常(这里如果是netcore在linux上的话,怎么也会抛出异常,具体异常自行查阅) 32 Console.WriteLine("连接成功"); 33 //启动异步监听 34 connected = true; 35 } 36 catch (Win32Exception ex) 37 { 38 if (ex.ErrorCode == 10035) // WSAEWOULDBLOCK is expected, means connect is in progress 39 { 40 var dt = DateTime.Now; 41 while (true)//循环读取当前连接的状态,如果timeout时间内还没连接成功,则反馈连接失败。 42 { 43 if (dt.AddMilliseconds(timeout) < DateTime.Now) 44 { 45 break; 46 } 47 connected = client.Poll(1000000, SelectMode.SelectWrite);//不会阻塞 48 if (connected) 49 { 50 connected = true; 51 break; 52 } 53 } 54 } 55 } 56 catch (Exception ex) 57 { 58 AbortThread(); 59 Console.WriteLine("连接失败"); 60 } 61 } 62 if (connected) 63 { 64 StartReceive();//连接成功则启动数据读取线程 65 } 66 return connected; 67 } 68 69 private void StartReceive() 70 { 71 rthr = new Thread(ReceiveMsgNonBlock); 72 rthr.IsBackground = true; 73 rthr.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA); //设置通信线程通信线程同步设置,才能在打开接受文件时 打开 文件选择框 74 rthr.Start(); 75 } 76 77 private void AbortThread() 78 { 79 if (rthr != null) 80 { 81 rthr.Abort(); 82 } 83 } 84 85 public void Close() 86 { 87 if (client.Connected) 88 { 89 client.Close(); 90 } 91 } 92 93 /// <summary> 94 /// app端缓冲池 95 /// </summary> 96 byte[] arrMsg = new byte[1024 * 1024]; 97 /// <summary> 98 /// 当前缓冲池的长度 99 /// </summary> 100 int currentlength = 0; 101 102 /// <summary> 103 /// 读取TCP缓冲数据 104 /// </summary> 105 private void ReceiveMsgNonBlock() 106 { 107 while (true) 108 { 109 try 110 { 111 byte[] tempBytes = new byte[1024 * 1024]; 112 113 int length = client.Receive(tempBytes);//此处不会阻塞,如果有数据则继续,如果没有数据则抛出Win32Exception异常(linux 下netcore自行查找异常类型 ) 114 115 DealMsg(tempBytes, length); 116 } 117 catch (Win32Exception ex) 118 { 119 120 if (ex.ErrorCode == 10035) // WSAEWOULDBLOCK is expected, means connect is in progress 121 { 122 Thread.Sleep(50); 123 } 124 125 } 126 catch (Exception ex) 127 { 128 rthr.Abort(); 129 client.Close(); 130 client = null; 131 Console.WriteLine("服务器断开连接"); 132 break; 133 } 134 } 135 } 136 137 /// <summary> 138 /// 把当前读取到的数据添加到app,并且根据自己的TCP约定的规则分析包头包尾长度校验等等信息,来确认在arrMsg中获取自己想要的数据包最后交给OnGetCS事件 139 /// </summary> 140 /// <param name="bytes"></param> 141 /// <param name="length"></param> 142 public void DealMsg(byte[] bytes, int length) 143 { 144 //先把数据拷贝到 全局数组arrMsg 145 if (bytes.Length + this.currentlength > 1024 * 1024) 146 { 147 byte[] arrMsg = new byte[1024 * 1024]; 148 } 149 150 Array.Copy(bytes, 0, arrMsg, this.currentlength, length); 151 this.currentlength += length; 152 153 154 ///根据自己的包头包尾的规则来截取TCP数据包,因为实际运行当中要考虑到服务端发送特别大的数据包,以及服务器太忙的时候分段发送数据包的情况。因此不能盲目的以为读取的缓冲区的数据就是一个完成的数据包。 155 ///最终生成tmpMsg。 156 var tmpMsg = new byte[1000]; 157 OnGetCS(tmpMsg, tmpMsg.Length); 158 } 159 }
经过测试,通过循环主动去读取缓冲带完美的解决了客户端缓慢的问题,实际运行的时候读取缓冲区的时间间隔可以根据需求自行更改,本例中用了50ms。
