envoy英文指南:https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/intro/what_is_envoy
一、什么是envoy?
Envoy 是一个 L7 代理和通信总线,专为大型现代面向服务的架构而设计。该项目的诞生源于以下信念:
网络应该对应用程序透明。当确实发生网络和应用程序问题时,应该很容易确定问题的根源。
二、envoy的核心功能
1)Out of process architecture: Envoy is a self contained process that is designed to run alongside every application server. All of the Envoys form a transparent communication mesh in which each application sends and receives messages to and from localhost and is unaware of the network topology. The out of process architecture has two substantial benefits over the traditional library approach to service to service communication:
2)Envoy works with any application language. A single Envoy deployment can form a mesh between Java, C++, Go, PHP, Python, etc. It is becoming increasingly common for service oriented architectures to use multiple application frameworks and languages. Envoy transparently bridges the gap.
3)As anyone that has worked with a large service oriented architecture knows, deploying library upgrades can be incredibly painful. Envoy can be deployed and upgraded quickly across an entire infrastructure transparently.
4)L3/L4 filter architecture: At its core, Envoy is an L3/L4 network proxy. A pluggable filter chain mechanism allows filters to be written to perform different TCP/UDP proxy tasks and inserted into the main server. Filters have already been written to support various tasks such as raw TCP proxy, UDP proxy, HTTP proxy, TLS client certificate authentication, Redis, MongoDB, Postgres, etc.
5)HTTP L7 filter architecture: HTTP is such a critical component of modern application architectures that Envoy supports an additional HTTP L7 filter layer. HTTP filters can be plugged into the HTTP connection management subsystem that perform different tasks such as buffering, rate limiting, routing/forwarding, sniffing Amazon’s DynamoDB, etc.
6)First class HTTP/2 support: When operating in HTTP mode, Envoy supports both HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2. Envoy can operate as a transparent HTTP/1.1 to HTTP/2 proxy in both directions. This means that any combination of HTTP/1.1 and HTTP/2 clients and target servers can be bridged. The recommended service to service configuration uses HTTP/2 between all Envoys to create a mesh of persistent connections that requests and responses can be multiplexed over.
7)HTTP/3 support (currently in alpha): As of 1.19.0, Envoy now supports HTTP/3 upstream and downstream, and translating between any combination of HTTP/1.1, HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 in either direction.
8)HTTP L7 routing: When operating in HTTP mode, Envoy supports a routing subsystem that is capable of routing and redirecting requests based on path, authority, content type, runtime values, etc. This functionality is most useful when using Envoy as a front/edge proxy but is also leveraged when building a service to service mesh.
9)gRPC support: gRPC is an RPC framework from Google that uses HTTP/2 or above as the underlying multiplexed transport. Envoy supports all of the HTTP/2 features required to be used as the routing and load balancing substrate for gRPC requests and responses. The two systems are very complementary.
10)Service discovery and dynamic configuration: Envoy optionally consumes a layered set of dynamic configuration APIs for centralized management. The layers provide an Envoy with dynamic updates about: hosts within a backend cluster, the backend clusters themselves, HTTP routing, listening sockets, and cryptographic material. For a simpler deployment, backend host discovery can be done through DNS resolution (or even skipped entirely), with the further layers replaced by static config files.
11)Health checking: The recommended way of building an Envoy mesh is to treat service discovery as an eventually consistent process. Envoy includes a health checking subsystem which can optionally perform active health checking of upstream service clusters. Envoy then uses the union of service discovery and health checking information to determine healthy load balancing targets. Envoy also supports passive health checking via an outlier detection subsystem.
12)Advanced load balancing: Load balancing among different components in a distributed system is a complex problem. Because Envoy is a self contained proxy instead of a library, it is able to implement advanced load balancing techniques in a single place and have them be accessible to any application. Currently Envoy includes support for automatic retries, circuit breaking, global rate limiting via an external rate limiting service, request shadowing, and outlier detection. Future support is planned for request racing.
13)Front/edge proxy support: There is substantial benefit in using the same software at the edge (observability, management, identical service discovery and load balancing algorithms, etc.). Envoy has a feature set that makes it well suited as an edge proxy for most modern web application use cases. This includes TLS termination, HTTP/1.1 HTTP/2 and HTTP/3 support, as well as HTTP L7 routing.
14)Best in class observability: As stated above, the primary goal of Envoy is to make the network transparent. However, problems occur both at the network level and at the application level. Envoy includes robust statistics support for all subsystems. statsd (and compatible providers) is the currently supported statistics sink, though plugging in a different one would not be difficult. Statistics are also viewable via the administration port. Envoy also supports distributed tracing via thirdparty providers.
非侵入的架构(Out of process architecture) : Envoy 是一个独立进程,设计为伴随每个应用程序服务运行。所有的 Envoy
非侵入的架构有两个实质性的好处:
Envoy 适用于任何应用程序语言。单个 Envoy 部署可以在 Java、C++、Go、PHP、Python 等之间形成网格。面向服务的架构使用多种应用程序框架和语言变得越来越普遍。Envoy 透明地弥合了差距。
Envoy 可以透明地跨整个基础设施快速部署和升级。
L3/L4 过滤器架构: Envoy 的核心是一个 L3/L4 网络代理。可插入的
HTTP L7 过滤器架构: HTTP 是现代应用程序架构的关键组件,Envoy
一流的 HTTP/2 支持:在 HTTP 模式下运行时,Envoy
HTTP/3 支持(目前处于 alpha 阶段):从 1.19.0 开始,Envoy 现在支持 HTTP/3 上游和下游,并在任意方向的 HTTP/1.1、HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 之间进行转换。
HTTP L7 路由:在 HTTP 模式下运行时,Envoy 支持一个
gRPC 支持:
服务发现和动态配置: Envoy 可选择使用一组分层的
健康检查: 构建 Envoy 网格的
高级负载均衡: 分布式系统中不同组件之间的
前端/边缘代理支持:在边缘使用相同的软件(可观察性、管理、相同的服务发现和负载平衡算法等)有很大的好处。Envoy 的功能集使其非常适合作为大多数现代 Web 应用程序用例的边缘代理。这包括
一流的可观察性:如上所述,Envoy 的主要目标是使网络透明。然而,问题出现在网络层和应用层。Envoy 包括对所有子系统的强大
envoy的显著特性
1)性能、可扩展及动态配置 性能:除了大量功外, Envoy EnvoyEnvoyEnvoy还提供极高的 吞吐量和低尾延迟差异,同时消耗相对较少CPUCPUCPU和 RAMRAMRAM; 可扩展性: Envoy EnvoyEnvoyEnvoy在L4 和L7 上提供丰富的可插拔过滤器功能,允许用户轻松添加新; API可配置性: Envoy提供了一组可由控制平面服务实现的管理 API,也称为 xDS API 若控制平面实现了这所有的 API ,则可以使用通引导配置在整个基础架构中运行 EnvoyEnvoy Envoy 所有进一步的配置更改都可通过管理服务器无缝地行动态传递,使得 Envoy永远不需要重新启动 于是,这使得 EnvoyEnvoy Envoy 成为一个通用数据平面,当与足够复杂的控制相结合时可大降低整体操作性 2)Envoy xDS API 存在 v1 、v2 和v3 三个版本 v1 API 仅使用 JSON/RESTJSON,本质上是轮询 v2 API 是 v1 的演进,而不是 革命它v1 功能的 超集,新API模式使用 proto3指定,并同时以 gRPC和 REST + JSON/YAML 端点实现 2021 年第 1季度结束支持 v3 API:当前支持 的版本,start_tls、拒绝传入的 tcp 连接、 4096位的 tls 密钥、 SkyWalking和WASM等 3) Envoy 业已 成为现代服务网格和边缘关的 “ 通用数据平面 API ” ,Istio 、Ambassador和 Gloo 等项目均是为此数据平面代理提供 的控制平面 ;
1、envoy的结构
envoy data path
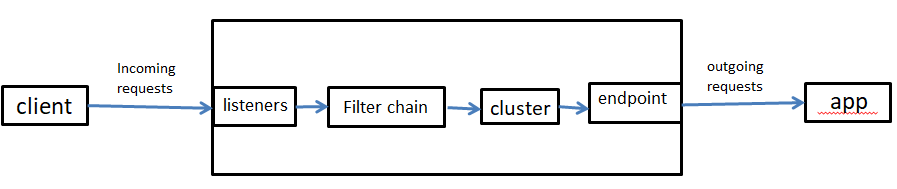
envoy的架构
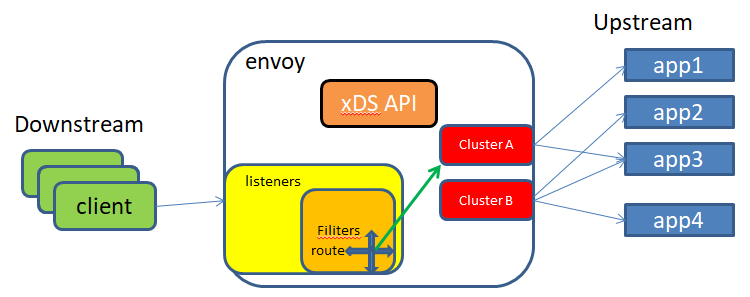
envoy的基础组件
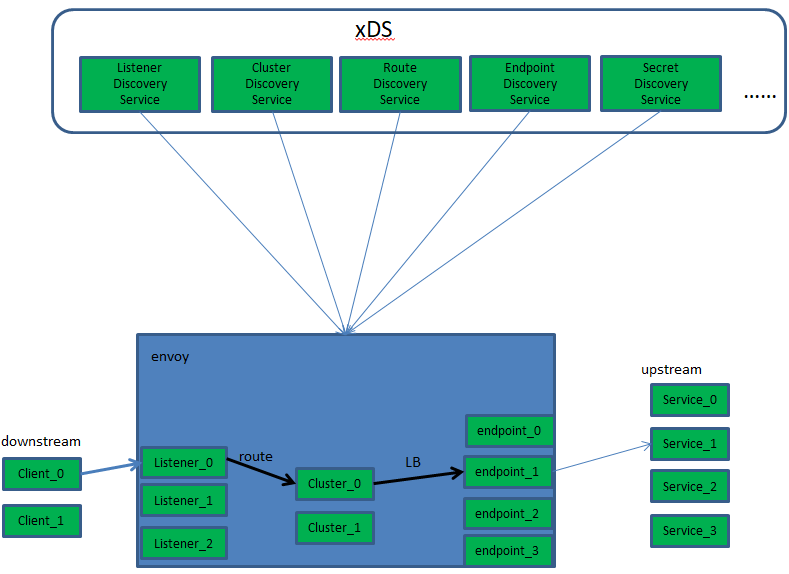
主机( HostHost ):一个具有网络通信能力的端点,例如服务器、移动智设备等(能够进行网络通信的实体(手机、服务器等上的应用程序)。在envoy中,主机是逻辑网络应用程序。一个物理硬件可能有多个主机在其上运行,只要每个主机都可以独立寻址。)
集群( Cluster ):集群是 Envoy Envoy 连接到的一组逻辑上相似端点;在 v2 中, RDSRDSRDS通过路由指向集群, CDS CDS提供集群 配置,而 Envoy 通过 EDS EDS发现集群成员,即端点;
下游( DownstreamDownstream DownstreamDownstream DownstreamDownstream):下游主机连接到 Envoy ,发送请求并接收响应它们是 Envoy 的客户端;
上游( Upstream UpstreamUpstream UpstreamUpstream):上游主机接收来自 Envoy Envoy 的连接和请求并返回响应,它们是 Envoy Envoy 代理的后端服务器;
端点( Endpoint Endpoint ):端点即上游主机,是一个或多集群的成员可通过 EDS EDS发现;
侦听器( ListenerListenerListener Listener):侦听器是能够由下游客户端连接的命名网络位置,例如口或 unix 域套接字等;
位置( LocalityLocality LocalityLocalityLocalityLocalityLocality):上游端点运行的区域拓扑,包括地、和子等;
管理服务器( Management Server Management Server Management ServerManagement ServerManagement ServerManagement ServerManagement Server Management ServerManagement Server Management Server):实现 v2 API v2 APIv2 API 的服务器,它支持复制和分片并且能够在不同物理机上实 现针对不同 xDS API xDS API xDS API xDS API的API API服务;
地域( Region Region ):区域所属地理位置;
区域( Zone ): AWS AWS中的可用区( AZ )或 GCPGCP 中的区域等;
子区域: Envoy 实例或端点运行的区域内位置,用于支持多个负载均衡目标;
xDS xDS:CDS CDS 、EDS EDS、HDS HDS HDS 、LDSLDSLDS、RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit) RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)RLS(Rate Limit)、 RDS RDS RDS 、 SDS SDS、VHDS VHDSVHDS和RTDSRTDSRTDSRTDS等API 的统称;
Mesh Mesh和Envoy MeshEnvoy Mesh Envoy MeshEnvoy Mesh Envoy(一组主机,它们协调以提供一致的网络拓扑。在本文档中,“Envoy 网格”是一组 Envoy 代理,它们为由许多不同服务和应用程序平台组成的分布式系统形成消息传递基础。)
运行时配置:与 Envoy 一起部署的带外实时配置系统。可以更改配置设置以影响操作,而无需重新启动 Envoy 或更改主要配置。
3、envoy的部署类型
Envoy is usable in a variety of different scenarios, however it’s most useful when deployed as a mesh across all hosts in an infrastructure.
Envoy可用于各种不同的场景,但是当它作为一个跨基础设施中所有主机的网格部署时,它是最有用的。
常见的部署方式如下图
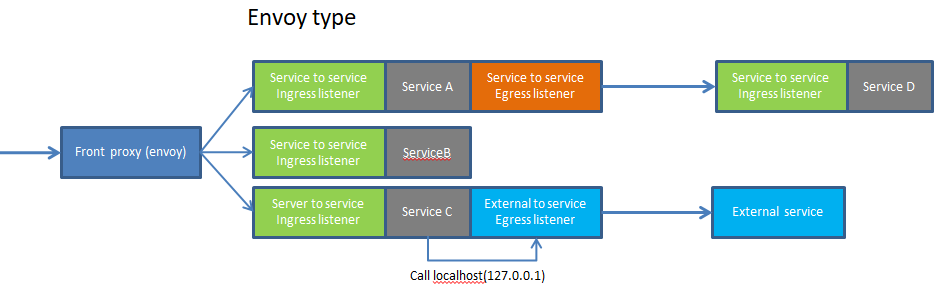
仅服务到服务
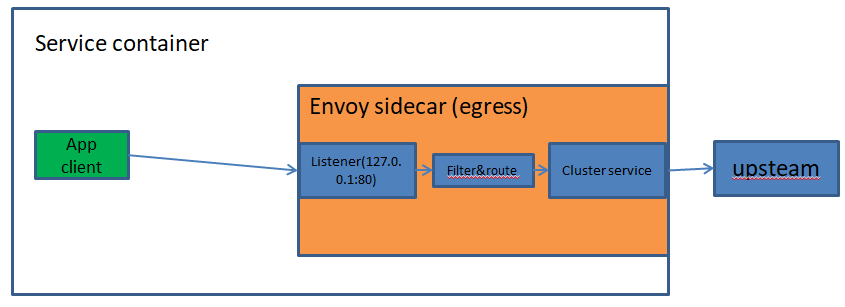
(1)service to service egress listener
This is the port used by applications to talk to other services in the infrastructure. HTTP and gRPC requests use the HTTP/1.1 host header or the HTTP/2 :authority header to indicate which remote cluster the request is destined for. Envoy handles service discovery , load balancing , rate limiting , etc. depending on the details in the configuration. Services only need to know about the local Envoy and do not need to concern themselves with network topology, whether they are running in development or production, etc.
1、这是应用程序用来与基础设施中的其他服务进行通信的端口。
3、Envoy根据配置中的细节处理服务发现、负载平衡、速率限制等。
4、 服务只需要了解本地Envoy,不需要关心网络拓扑、它们是在开发中运行还是在生产中运行等等。
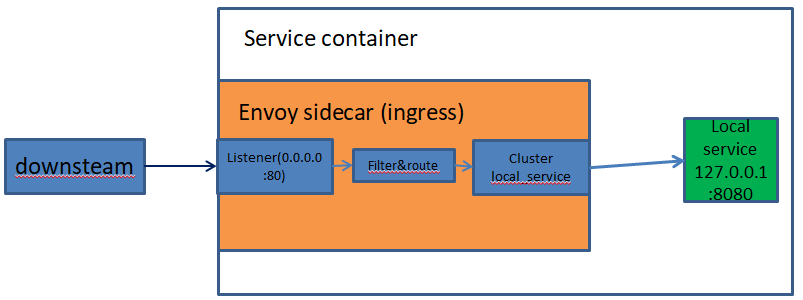
(2)service to service ingress listener
This is the port used by remote Envoys when they want to talk to the local service. ◆Incoming requests are routed to the local service on the configured port(s). ◆Multiple application ports may be involved depending on application or load balancing needs (for example if the service needs both an HTTP port and a gRPC port). The local Envoy performs buffering, circuit breaking, etc. as needed.
1、通过远程访问envoy的ip+port来访问envoy后端的服务
根据应用或负载均衡的需要,可能涉及多个应用端口(例如,如果服务同时需要一个HTTP端口和一个gRPC端口)。
2、本地envoy根据需要执行缓冲、断路等。
(3)Optional external service egress listener
本地服务通过envoy的egress listener访问外部的服务。
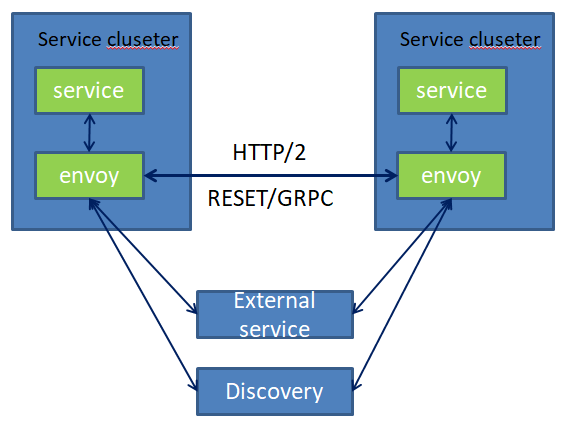
2) Service to service Plus front proxy
服务到服务+前端代理
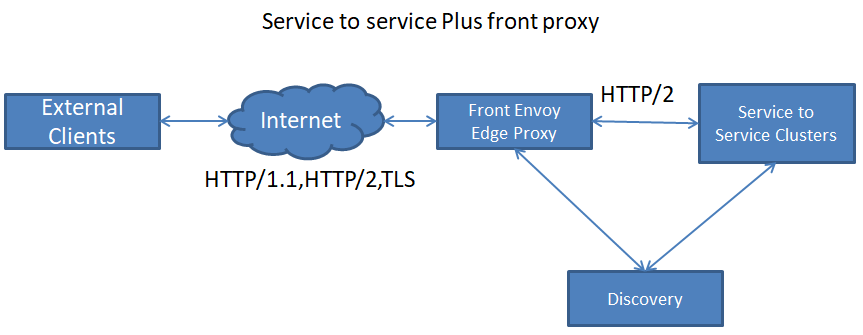
The above diagram shows the service to service configuration sitting behind an Envoy cluster used as an HTTP L7 edge reverse proxy. 终止TLS连接; 支持HTTP/1.1和HTTP/2; HTTP L7路由; 通过Front-Envoy的Ingress接入请求,并结合发现服务与Service-to-Service的Envoy网格进行通信; The front Envoy hosts work identically to any other Envoy host, other than the fact that they do not run collocated with another service.
上图显示了用作HTTP L7边缘反向代理的Envoy集群背后的服务到服务配置。
支持HTTP / 1.1和HTTP / 2;
HTTP L7路由;
通过Front-Envoy的入口接入请求,并结合发现服务与service - to - service的特使网格进行通信;
envoy主机的工作与任何其他envoy主机相同,除了它们不与另一个服务并列运行之外。
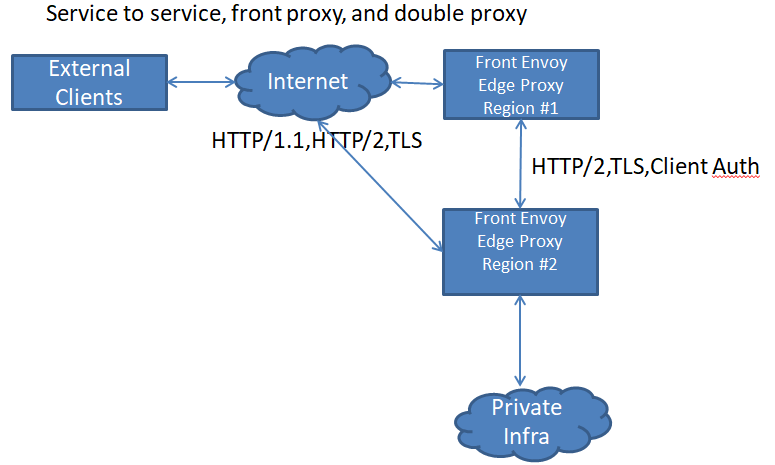
3) Service to service, front proxy, and double proxy
服务到服务、前端代理和双代理
双代理的目标是尽可能接近用户地终止 TLS 和客户端连接会更高效