一、算数操作符类别
- 基本的有:
+ - * / % |
- 自增 自减:
++ -- |
二、基本算数操作符
+ - * / |
基本的加 减 乘 除
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 10; int j = 5; int a = i+j; int b = i - j; int c = i*j; int d = i /j; } } |
三、练习--求和
题目:
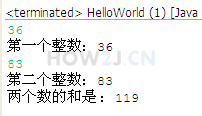
使用Scanner从控制台获取两个数字,然后计算这两个数字的和,达到下图中的效果。
如果不会使用Scanner,请参考 如何使用Scanner读取整数
官方答案:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int a = s.nextInt(); System.out.println("第一个整数:"+a); int b = s.nextInt(); System.out.println("第二个整数:"+b); int c = a+b; System.out.println("两个数的和是 :" + c); } } |
个人整理答案:
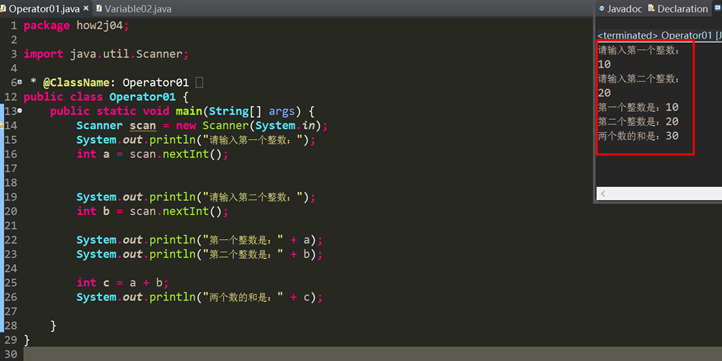
四、任意运算单元的长度超过int
如果有任何运算单元的长度超过int,那么运算结果就按照最长的长度计算
比如:
int a = 5;
long b = 6;
a+b -> 结果类型是long
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 5; long b = 6; int c = (int) (a+b); //a+b的运算结果是long型,所以要进行强制转换 long d = a+b; } } |
五、任意运算单元的长度小于int
如果任何运算单元的长度都不超过int,那么运算结果就按照int来计算
比如:
byte a = 1;
byte b= 2;
a+b -> int 类型
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { byte a = 1; byte b= 2; byte c = (byte) (a+b); //虽然a b都是byte类型,但是运算结果是int类型,需要进行强制转换 int d = a+b; } } |
六、%取模
% 取余数,又叫取模
比如:5除以2,余1
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 5; int j = 2; System.out.println(i%j); //输出为1 } } |
七、自增 、自减
++
--
在原来的基础上增加1或者减少1
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 5; i++; System.out.println(i);//输出为6 } } |
八、自增、自减操作符置前以及置后的区别
以++为例
int i = 5;
i++; 先取值,再运算
++i; 先运算,再取值
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 5; System.out.println(i++); //输出5 System.out.println(i); //输出6 int j = 5; System.out.println(++j); //输出6 System.out.println(j); //输出6 } } |
九、练习--自增
题目:
int i = 1;
int j = ++i + i++ + ++i + ++i + i++;
问 j的结果是多少?
注: 先不要放在eclipse中,根据++置前 置后的理解自己先算一遍,然后再看答案
官方答案:
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { int i = 1; int j = ++i + i++ + ++i + ++i + i++; //i值 2 3 4 5 6 //取值 2 2 4 5 5 System.out.println(j); } } |
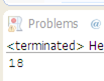
个人整理答案:
心算给出答案18
十、练习--BMI
题目:
使用Scanner收集你的身高体重,并计算出你的BMI值是多少
BMI的计算公式是:体重(kg) / (身高*身高)
比如邱阳波的体重是72kg, 身高是1.69,那么这位同学的BMI就是
72 / (1.69*1.69) = ?
要求的实现效果:
可以根据BMI指数表增加判断肥胖及健康情况的功能

官方答案:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class HelloWorld { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入身高(m):"); float height = s.nextFloat(); System.out.println("请输入体重(kg):"); float weight = s.nextFloat(); float BMI = weight/ (height*height); System.out.println("当前的BMI是: " + BMI); } } |
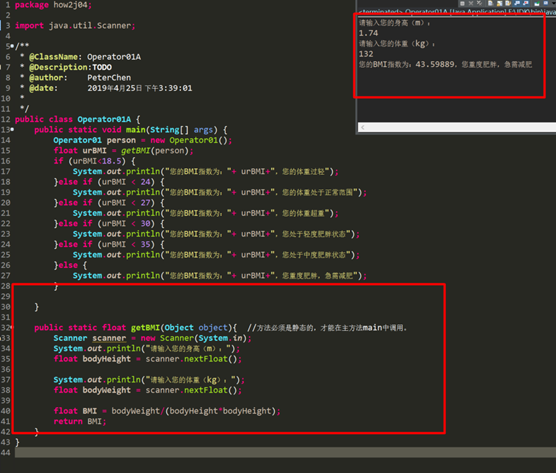
个人整理答案:
public class Operator01A { public static void main(String[] args) { Operator01 person = new Operator01(); float urBMI = getBMI(person); if (urBMI<18.5) { System.out.println("您的BMI指数为:"+ urBMI+",您的体重过轻"); }else if (urBMI < 24) { System.out.println("您的BMI指数为:"+ urBMI+",您的体重处于正常范围"); }else if (urBMI < 27) { System.out.println("您的BMI指数为:"+ urBMI+",您的体重超重"); }else if (urBMI < 30) { System.out.println("您的BMI指数为:"+ urBMI+",您处于轻度肥胖状态"); }else if (urBMI < 35) { System.out.println("您的BMI指数为:"+ urBMI+",您处于中度肥胖状态"); }else { System.out.println("您的BMI指数为:"+ urBMI+",您重度肥胖,急需减肥"); } }
public static float getBMI(Object object){//方法必须是静态的,才能在主方法main中调用。 Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.println("请输入您的身高(m):"); float bodyHeight = scanner.nextFloat();
System.out.println("请输入您的体重(kg):"); float bodyWeight = scanner.nextFloat();
float BMI = bodyWeight/(bodyHeight*bodyHeight); return BMI; } } |