分享一个关于java算法的问题:怎么合并两个有序链表
这里提供两种解决方法:1.递归实现 ; 2.非递归实现
任何一种方式,都要先创建节点类,没有什么重点,直接写代码:

package com.dataClass; /** * @author 新生代菜鸟 */ public class Node { // 数据存储变量 public int data; // 节点信息存放(指针信息) public Node next; // 构造函数,用来给data传值 ---这里先不考虑批量插入的问题 public Node(int data) { this.data = data; } }
递归实现:
传入的两个链表是list1和list2,考虑它们是否为空会有三种情况:
- 两个都是null , 怎么合并都会是一个空链表,直接返回null即可
- 两个中有一个是null , 找到非空的那一个直接返回即可
- 两个都不是null,此时就是重点了
我们分析第三种情况:
假如:list1为: 1 --> 3 --> 5 -- null ; list2为:2 --> 4 --> 6 --> 8 -- > null;
我们指定head用来存放data小的那个对象,刚开始时list与list实际是指向了两个链表的表头,即list1.data = 1 , list2.data = 2 ,此时我们发现1 <= 2 ,我们将head指向list1 ,那么新问题就是:head的next指向哪?递归算法的魅力就在这,我们不用考虑别的,反正一定是在两个链表剩下的元素中,那么我们将list1.next和list2作为递归方法的参数,继续调用递归方法即可 。
我们发现当list1指向null时,list并没有指向null,就是说本例中list2中还有元素没有被合并,那么在实际中可能是list1也可能是list2会有元素没有合并,但其中一个已经已经是null了,此时只需判断哪个非null,将其合并在后面即可。下面看代码:

public Node mergeByRecursion(Node list1, Node list2) { //将1,2合并 if (list1== null || list2 == null) { return list1 == null ? list2 : list1; } Node head = null; if (list1.data <=list2.data) { head = list1; head.next = mergeByRecursion(list1.next, list2); } else { head = list2; head.next = mergeByRecursion(list1, list2.next); } return head; }
非递归实现:
递归算法实现简单,代码也容易理解,但是它的弊端也很明显时间空间开销都很大,效率低,现在考虑一种比较容易理解的非递归算法:
传入的两个链表是node1和node2 , 开头和递归算法一样,也是那三种情况,前两种情况处理也一样,关键在第三种情况,此时我们这么考虑,node1是一个在node1链表上的指针,node2是node2链表上的一个指针,我们有一个新的指针head,在两个指针所指都不是null时,我们让head指向data更小的那个,同样:
假如list1为: 1 --> 3 --> 5 -- null ; list2为:2 --> 4 --> 6 --> 8 -- > null;
刚开始1 < 2 , 让head = list1 , 然后list1 = list.next, 使用另一个指针Node point = head 来记注这个合并后链表的表头,
现在再看那么list1.data = 3 , list2.data = 2 , 2 < 3 ,那么head.next = list2 , list2 = list2.next , 在让head指针也向着后移动,即head = head.next ,
...
其实就是使用四个指针,一个记录node1上的当前位置,一个记录node2上的当前位置,一个记录合并链表的表头,另外一个不断的指向当前位置下data更小的那一个。看一下代码:

/** * 非递归算法---简化 * * @param node1测试链表1 * @param node2测试链表2 * @return 返回合并后的链表 */ public Node mergeNoRecursion2(Node node1, Node node2) { // 合并1,2 if (node1 == null || node2 == null) { return node1 == null ? node2 : node1; } // head记录合并后链表的表头(理解有边的代码) Node head = node1.data <= node2.data ? node1 : node2; // list1,list2用来记录两链表当前位置 Node list1 = head == node1 ? node1 : node2; Node list2 = head == node1 ? node2 : node1; // point用来指向合并链表的下一个节点 Node point = head; list1 = list1.next;// 开始时已经指向了list1的表头,后面的比较list1要从第二个开始 // 使用循环遍历两个链表,根据list1.data和list2.data的比较结果,决定point下一节点 while (list1 != null && list2 != null) { if (list1.data <= list2.data) { // list1.data <= list2.data 首先更新point的下一节点list1,然后更新list1的位置 point.next = list1; list1 = list1.next; } else { // list1.data > list2.data 首先更新point的下一节点list2,然后更新list2的位置 point.next = list2; list2 = list2.next; } // 更新point的位置为它的下一节点 point = point.next; } /* * 至少有一个为空了,list1是否已经便利完 如果list1遍历完,则将point.next直接指向list2 * 否则及list2遍历完,那么point.next直接指向list1 **/ point.next = list1 == null ? list2 : list1; return head; } }
两种实现已经写完了,下面就是比较期待又紧张的测试阶段了,天灵灵,地灵灵,保佑测试一定过...

public class Test { //输出函数 public static void syso(Node head) { while (head != null) { System.out.print(head.data + "-->"); head = head.next; } System.out.println("null"); } public static void main(String[] args) { MyNodeList list = new MyNodeList(); //测试递归算法 // 测试链表1.1 Node node1 = new Node(1); Node node3 = new Node(3); node1.next = node3; Node node5 = new Node(5); node3.next = node5; // 测试链表1.2 Node node2 = new Node(2); Node node4 = new Node(4); node2.next = node4; Node node6 = new Node(6); node4.next = node6; // 递归方法测试 Node test1 = list.mergeByRecursion(node1, node2); System.out.print("递归合并结果:"); syso(test1); //测试非递归算法 // 测试链表2.1 Node node21 = new Node(1); Node node23 = new Node(3); node21.next = node23; Node node25 = new Node(5); node23.next = node25; // 测试链表2.2 Node node22 = new Node(2); Node node24 = new Node(4); node22.next = node24; Node node26 = new Node(6); node24.next = node26; Node node28 = new Node(8); node26.next = node28; Node test2 = list.mergeNoRecursion2(node21, node22); System.out.print("非递归合并结果:"); syso(test2); } }
测试结果为:
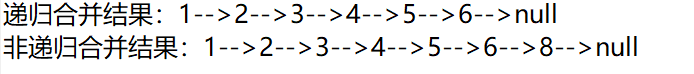 |
