8、文 件 处 理
写文件
import time path = r"G:谢义lunwenjisuanjigongchengpython_test文件读写练习.txt" f = open(path,"w") #写文件 #1、将信息写入缓冲区 f.write("sunck is a good man 1 ") f.write("xieyi is a good man ") # 2、刷新缓冲区 #直接把内部缓冲区的数据立刻写入文件 #而不是被动的等待自动刷新缓冲区写入 f.flush() while 1: f.write("sunck is a good man 1 ") f.flush()#刷新文件 f.write("xieyi is a good man ") time.sleep(0.01) f.close() with open(path, "a") as f2: f2.write("sunck is a bade man ")
读文件
读文件: 过程: 1、打开文件 2、读取文件内容 3、关闭文件 1、打开文件 open(path, flag[, encoding][, errors]) path:要打开文件的路径 flag:打开方式 r 以只读方式打开,文件的描述符放在文件的开头 rb 以二进制格式打开一个文件用于只读,文件的描述符放在文件的开头 r+ 打开一个文件用于读写,文件描述符放在文件开头 w 打开一个文件只用于写入,如果该文件已经存在会覆盖,如果不存在 则创建新文件 wb 打开一个文件只用于写入二进制,如果该文件已经存在会覆盖,如果不存在 则创建新文件 w+ 打开一个文件用于读写 a 打开一个文件用于追加,如果文件存在,文件描述符将会被放在 文件末尾 a+ encoding:编码方式 error:错误处理 path = r"G:谢义lunwenjisuanjigongchengpython_test文件读写练习.txt " # f = open(path,"r",encoding="utf-8",errors= "ignore") f = open(path,"r") 2、读文件内容 #1、读取文件全部内容 #str = f.read() #print(str) #2、读取指定字符数 #str2 = f.read(10) #print("*" + str2 + "*") #3、读取整行,包括“ ”字符 str4 = f.readline() print(str4) str5 = f.readline() print(str5) #4、读取指定字符数 str6 = f.readline(10) print(str6) #5、读取所有行并返回列表 list7 = f.readlines() print(list7) #6、若给定的数字大于0,返回实际size的行数 list8 = f.readlines(25) print(list8) #修改描述符的位置 f.seek(0) str9 = f.read() #一个完整的过程 try: f1 = open(path, "r",encoding="utf-8") print(f1.read()) finally: if f1: fl.close()#关闭文件 # 效果与上一个等效,最常用 with open(path, "r",encoding= "utf-8") as f2: print(f2.read)
8.1 文件打开/关闭
# 文件打开 file = open('test.txt') # 必须保证文件是存在的 # 文件模式 # 文件关闭 file = open('test.txt', 'w') # 以写为目的打开或创建一个文件 file.close()
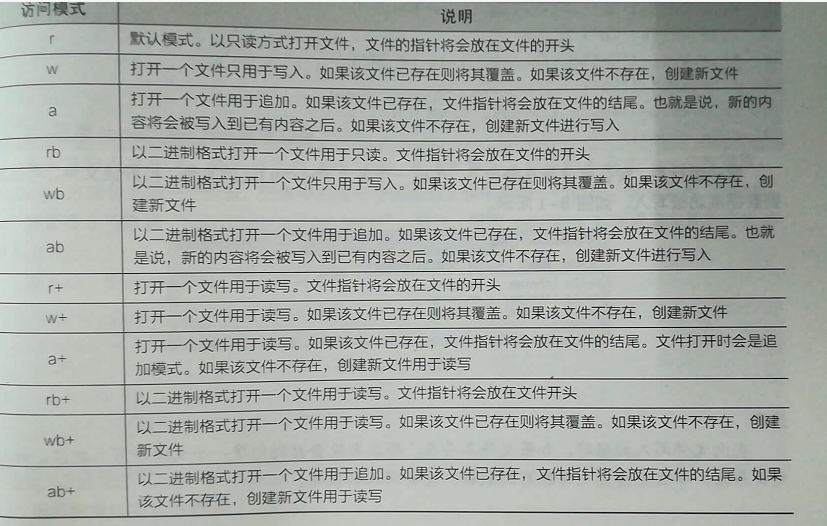
8.2 文件写、读
file = open('test.txt','w') file.write('hello itheima , i am here !') # 每次写入的内容会添加到文档内容最后 file.write(' ') file.write('hahahhah') file.close()
file = open('test.txt','r') content = file.read(12) # 读取12个字节的内容,如果没有参数时则读取文档全部内容 print(content) print('-'*30) content = file.read() # 读取全部元素 print(content) file.close()
file = open('test.txt','r') content = file.readlines() # 以行读取,一行为一个元素返回列表 i= 1 for temp in content: print("%d:%s" %(i, temp)) i += 1 file.close()
# 用readline()一行行的读取文本内容 file = open('test.txt','r') content = file.readline() print("1:%s"%(content)) content = file.readline() print("2:%s"%(content)) file.close()
文件读写应用:制作文件备份
# 制作文件的备份 old_file_name = input("请输入要拷贝的文件名字:") old_file = open(old_file_name, 'r') # 如果打开文件 if old_file: location_flag = old_file_name.rfind('.') if location_flag > 0: file_flag = old_file_name[location_flag:] # 组织新的文件名 new_file_name = old_file_name[:location_flag] + '[复件]' + file_flag # 创建新文件 new_file = open(new_file_name, 'w') # 把旧文件的数据一行行的写入新文件内 for line_content in old_file.readlines(): new_file.write(line_content) # 关闭文件 old_file.close() new_file.close()
文件定位读写
# 文件定位读写 # tell()定位当前位置 file = open('test.txt', 'r') words = file.read(4) print("读取的数据为:",words) position = file.tell() # 查找当前位置 print("当前位置是:", position) file.close() # seek()定位读写位置 # 定位到指定位置 file = open('test.txt','r') words = file.read(15) print("读取当前的数据是:",words) # 查找当前位置 position = file.tell() print("当前位置是:", position) # 重新设置位置 file.seek(4) # 查找当前位置 position = file.tell() print("当前位置是:", position) file.close()
8.3 文件重命名 + 删除
# 文件重命名 import os os.rename("test.txt", "test01.txt") # 文件删除 import os os.remove("test[复件].txt") # 添加path
8.4 文件夹操作
# 创建文件夹 import os os.mkdir("毛聪") # 获取当前目录 import os r = os.getcwd() print(r) # 改变默认目录 import os r = os.chdir ("../") # 获取目录列表 import os r = os.listdir ("./") # 获取当前目录列表 print(r) # 删除文件夹 import os os.rmdir("毛聪")
8.5 文件操作应用
文件和异常
读取整个文件 + 文件路径
f_path = r"C:UsersYiDesktopyouxi毛聪02 est01.txt" # 文件路径 with open(f_path) as f_object: # 读取全部文件内容 contents = f_object.read() print(contents) # 末尾的空行直接输出 print(contents.rstrip()) # 去掉末尾的空行
逐行读取
f_path = r"C:UsersYiDesktopyouxi毛聪02 est01.txt" # 文件路径 with open(f_path) as f_object: # 读取全部文件内容 for line in f_object: # 逐行读取 print(contents) # 末尾的空行直接输出 print(contents.rstrip()) # 去掉末尾的空行
f_path = r"C:UsersYiDesktopyouxi毛聪02 est01.txt" # 文件路径 with open(f_path) as f_object: # 读取全部文件内容 for line in f_object: # 逐行读取 print(line) # 读取出来的内容含有更多空白行
f_path = r"C:UsersYiDesktopyouxi毛聪02 est01.txt" with open(f_path) as f_object: for line in f_object: print(line.rstrip()) # 输出全部内容,删除空行