一、算法原理
随机样本一致性(Random Sample Consensus RANSAC) 是一种迭代方法,用于从包含异常值的观察数据中估计出数学模型参数,因此也可以理解为一种异常值检测方法。RANSAC的一个基本假设是,数据由内点("inliers")和外点("outliers")组成,其中内点是在一定误差范围内可以通过一些模型参数来解释的数据,外点是不符合模型的数据。RANSAC的另一个假设是,随机选取的样本数据都是内点,存在一个可以估计模型参数的过程,该模型可以最佳地解释或拟合该数据。
二、算法步骤
- step1 从原始数据集\(S\)中随机选择子集\(s\),\(s\)为假设的内点(子集\(s\)一般为最小子集,如:直线选取两个点,圆选择三个点)
- step2 依据子集\(s\)估计模型参数
- step3 遍历数据集\(S\)中除子集\(s\)外的所有数据,如果数据点在给定误差\(e\)以内,则标记为内点,否则标记为外点
- step4 所有内点组成一致集,如果一致集中点的个数满足给定阈值\(T\),则用一致集中所有内点重新估计模型参数,然后结束算法
- step5 如果一致集中内点个数少于阈值\(T\),则重新选择新的子集\(s\),并重复step1-4
- step6 经过\(K\)次迭代,选择一个内点数量最多的一致集,用一致集中所有内点重新估计模型参数,然后结束算法
三、代码
3.1 伪代码
-
输入:
\(S\): 观测数据集
Model: 待求模型(如:直线,圆)
\(N\): 估计模型参数最小数据个数
\(K\): 最大迭代次数
\(e\):允许的误差阈值
\(T\):内点个数阈值 -
输出:
最满足数据的模型参数
iterations = 0
bestFit = null
bestInliers = null
bestErr = 无穷大
while iterations < \(K\) do
MaybeInliers := 从数据集\(S\)中随机选择\(N\)个样本
maybeModel := 通过MaybeInliers中拟合的模型参数
alsoInliers := 空集
for 数据集中除MaybeInliers外的所有点pt do
if 点pt和现有模型的误差值小于 \(e\)
将点pt添加至alsoInliers
end if
end for
if 内点个数大小于\(T\) then
// 内点已经足够多, 依据内点重新估计模型参数
betterModel := 通过alsoInliers和MaybeInliers估计模型参数
thisErr := 模型估计后与数据集的误差
if thisErr < bestErr then
bestFit := betterModel
bestErr := thisErr
return bestFit
end if
else
if alsoInliers的内点数量 大于 bestInliers的内点数量 then
bestInliers := alsoInliers + maybeInliers
end if
end if
iterations增加1
end while
bestFit := 通过bestInliers估计模型参数
return bestFit
3.2 C++ 代码
点击展开
#include <limits>
#include <cmath>
inline void GetCircle(const core::Point2& p1, const core::Point2& p2, const core::Point2& p3, core::Point2& center, double & radius2)
{
double r12 = p1.x * p1.x + p1.y * p1.y;
double r22 = p2.x * p2.x + p2.y * p2.y;
double r32 = p3.x * p3.x + p3.y * p3.y;
double A = p1.x * (p2.y - p3.y) - p1.y * (p2.x - p3.x) + p2.x * p3.y - p3.x * p2.y;
double B = r12 * (p2.y - p3.y) + r22 * (p3.y - p1.y) + r32 * (p1.y - p2.y);
double C = r12 * (p2.y - p3.y) + r22 * (p3.y - p1.y) + r32 * (p1.y - p2.y);
center.x = B / (2 * A);
center.y = C / (2 * A);
radius2 = (center.x - p1.x) * (center.x - p1.x) + (center.y - p1.y) * (center.y - p1.y);
}
inline void GetNRand(const int maxV, const int N, std::set<int>& idxs)
{
if (N > maxV) {
return;
}
while(idxs.size() < N) {
idxs.insert(rand() % maxV);
}
}
double Fitter::FitCircleByRANSAC(const std::vector<core::Point2>& pointArray, core::Point2& center, double& radius, const int iterNum, const double e, const float ratio)
{
const int N = pointArray.size();
const int targetN = N * ratio;
int iter = 0;
std::vector<core::Point2> bestInliers;
while (iter < iterNum) {
std::set<int> seedIds;
GetNRand(N, 3, seedIds); // circle need 3 point
if (seedIds.size() < 3) {
break;
}
std::vector<core::Point2> seedPts;
for (const int idx : seedIds) {
seedPts.push_back(pointArray[idx]);
}
core::Point2 seedCenter;
double seedR2 = 0.0;
GetCircle(seedPts[0], seedPts[1], seedPts[2], seedCenter, seedR2);
std::vector<core::Point2> maybeInliers;
for (const core::Point2 pt : pointArray) {
if (std::abs((pt.x - seedCenter.x) * (pt.x - seedCenter.x) + (pt.y - seedCenter.y) * (pt.y - seedCenter.y) - seedR2) < e) {
maybeInliers.push_back(pt);
}
}
if (maybeInliers.size() > targetN) {
// it show the inliers is enough
return FitCircleByLeastSquare(maybeInliers, center, radius);
}
else {
if (maybeInliers.size() > bestInliers.size()) {
bestInliers.swap(maybeInliers);
for (const core::Point2 pt : seedPts) {
bestInliers.push_back(pt);
}
}
}
++iter;
}
return FitCircleByLeastSquare(bestInliers, center, radius);
}
- test.cpp
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
std::vector<core::Point2> pts;
pts.push_back(core::Point2(50.0, 60.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(60.0, 50.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(50.0, 40.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(40.0, 50.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(39.0, 50.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(38.0, 50.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(38.5, 49.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(30.5, 49.0));
pts.push_back(core::Point2(35.5, 49.0));
core::Point2 center1, center2;
double r1, r2;
double err1 = core::Fitter().FitCircleByLeastSquare(pts, center1, r1);
double err2 = core::Fitter().FitCircleByRANSAC(pts, center2, r2);
cv::Mat img = cv::Mat::zeros(cv::Size(100, 100), CV_8UC3);
img.setTo(255);
for (core::Point2 pt : pts) {
cv::circle(img, cv::Point(pt.x, pt.y), 1, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0), -1); // draw pt
}
cv::circle(img, cv::Point(center1.x, center1.y), r1, cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
cv::circle(img, cv::Point(center2.x, center2.y), r2, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 255), 1);
cv::namedWindow("img", cv::WINDOW_NORMAL);
cv::imshow("img", img);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::destroyAllWindows();
return 0;
}
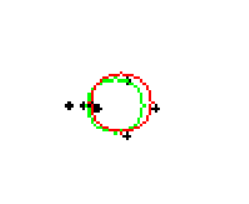
在这个例子中RANSAC拟合(红色圆)比最小二乘拟合(绿色圆)的误差相对小一些