一、得到图片中的数据
1、现有一副png图片,提取其中某个区域的内容,保存成另外的图片。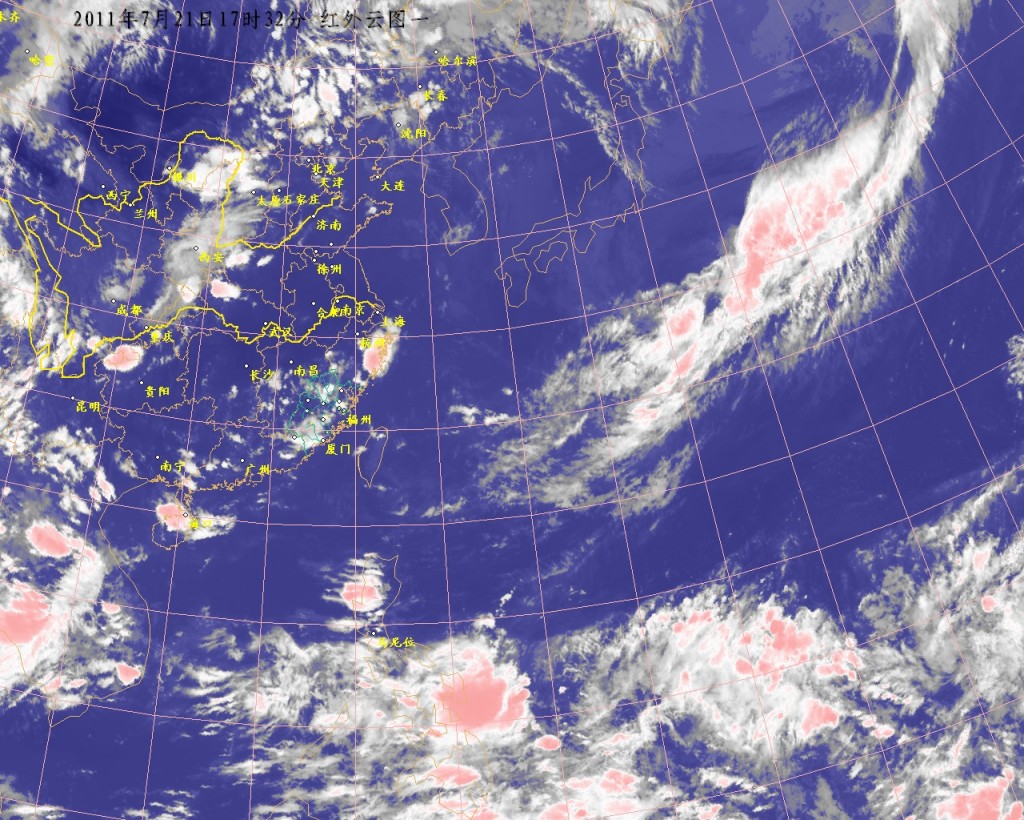
处理后云图如下,黑色的表示云。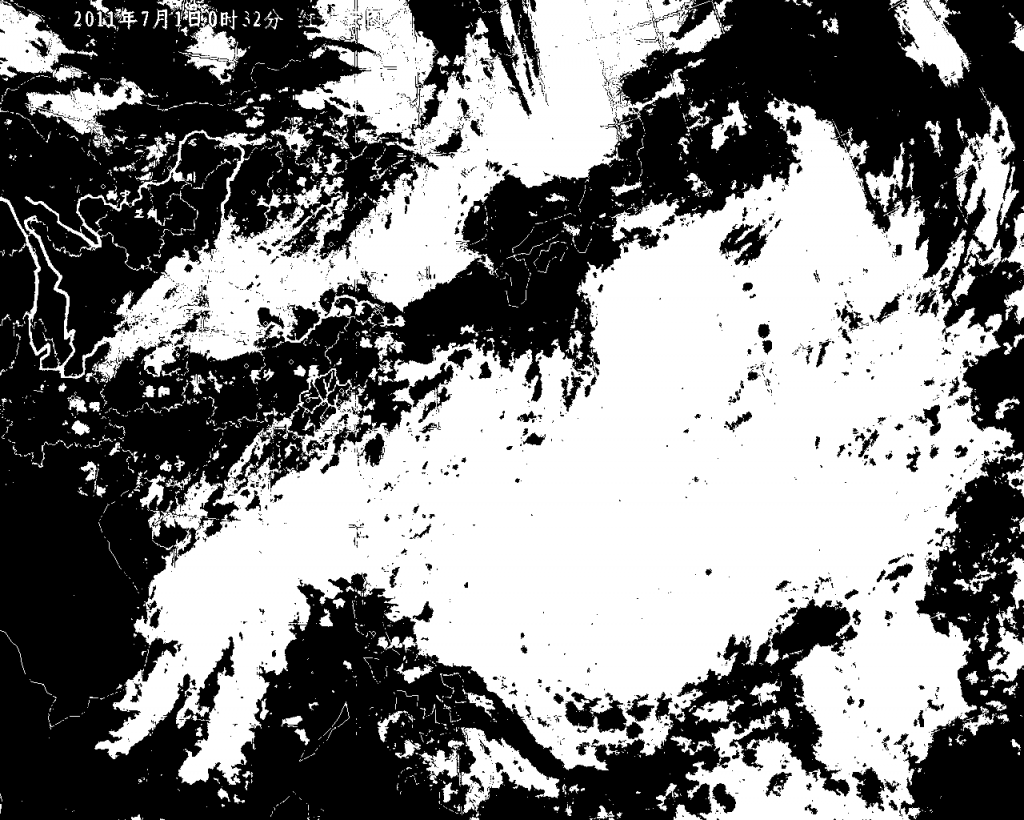
现在要得到河南省的的,比如区域的范围是(270,270)到(390,390)的区域。
import java.awt.BasicStroke;
import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.Graphics;
import java.awt.Graphics2D;
import java.awt.GraphicsConfiguration;
import java.awt.GraphicsDevice;
import java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment;
import java.awt.HeadlessException;
import java.awt.Image;
import java.awt.Transparency;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.awt.image.ColorModel;
import java.awt.image.PixelGrabber;
import java.io.File;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import javax.swing.ImageIcon;
public class LoadOneImage {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String myreadline = "";
// 定义一个String类型的变量,用来每次读取一行
try {
myreadline = "mask_cloud.png";// 读取一行
BufferedImage image = toBufferedImage(new ImageIcon("data/Image/"
+ myreadline).getImage());
int height = image.getHeight();
int width = image.getWidth();
System.out.println("图片的高度为------>" + height);
System.out.println("图片的宽度为------>" + width);
// 创建BufferedImage对象
BufferedImage targetimage = new BufferedImage(1280, 1024,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// 获取Graphics2D
Graphics2D g2d = targetimage.createGraphics();
// ---------- 增加下面的代码使得背景透明 -----------------
targetimage = g2d.getDeviceConfiguration().createCompatibleImage(
1280, 1024, Transparency.TRANSLUCENT);
// 释放对象
g2d.dispose();
g2d = targetimage.createGraphics();
// ---------- 背景透明代码结束 -----------------
for (int y = 270; y < 390; y++) {
for (int x = 270; x < 390; x++) {
Color color = new Color(image.getRGB(x, y));
if (color.equals(Color.BLACK))
g2d.setColor(Color.RED);
else
g2d.setColor(Color.BLUE);
g2d.setStroke(new BasicStroke(1));
g2d.drawLine(x, y, x, y);
}
}
// 释放对象
g2d.dispose();
ImageIO.write(targetimage, "png", new File("test.png"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
// This method returns a buffered image with the contents of an image
public static BufferedImage toBufferedImage(Image image) {
if (image instanceof BufferedImage) {
return (BufferedImage) image;
}
// Determine if the image has transparent pixels; for this method's
// implementation, see e661 Determining If an Image Has Transparent
// Pixels
boolean hasAlpha = hasAlpha(image);
// Create a buffered image with a format that's compatible with the
// screen
BufferedImage bimage = null;
GraphicsEnvironment ge = GraphicsEnvironment
.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
try {
// Determine the type of transparency of the new buffered image
int transparency = Transparency.OPAQUE;
if (hasAlpha) {
transparency = Transparency.BITMASK;
}
// Create the buffered image
GraphicsDevice gs = ge.getDefaultScreenDevice();
GraphicsConfiguration gc = gs.getDefaultConfiguration();
bimage = gc.createCompatibleImage(image.getWidth(null), image
.getHeight(null), transparency);
} catch (HeadlessException e) {
// The system does not have a screen
}
if (bimage == null) {
// Create a buffered image using the default color model
int type = BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB;
if (hasAlpha) {
type = BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_ARGB;
}
bimage = new BufferedImage(image.getWidth(null), image
.getHeight(null), type);
}
// Copy image to buffered image
Graphics g = bimage.createGraphics();
// Paint the image onto the buffered image
g.drawImage(image, 0, 0, null);
g.dispose();
return bimage;
}
// This method returns true if the specified image has transparent pixels
public static boolean hasAlpha(Image image) {
// If buffered image, the color model is readily available
if (image instanceof BufferedImage) {
BufferedImage bimage = (BufferedImage) image;
return bimage.getColorModel().hasAlpha();
}
// Use a pixel grabber to retrieve the image's color model;
// grabbing a single pixel is usually sufficient
PixelGrabber pg = new PixelGrabber(image, 0, 0, 1, 1, false);
try {
pg.grabPixels();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
// Get the image's color model
ColorModel cm = pg.getColorModel();
return cm.hasAlpha();
}
}
结果如下:
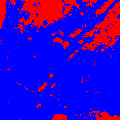
其中黑色的用红色填充了,白色的用蓝色填充了。