一、什么是函数式接口
1、只包含一个抽象方法的接口,称为函数式接口。
2、你可以通过Lambda表达式来创建该接口的对象。(若Lambda表达式抛出一个受检异常,那么该异常需要在目标接口的抽象方法上进行声明)。
3、我们可以在任意函数式接口上使用@FunctionalInterface注解,这样做可以检查它是否是一个函数式接口,同时javadoc也会包含一条声明,说明这个接口是一个函数式接口。
例如:
@FunctionalInterface public interface MyFucntion2<T,R> { public R getValue(T t1,T t2); }
以下对这个函数式接口进行测试:
@Test public void test2(){ Long op = op(200L, 300L, (x, y) -> x + y); System.out.println(op); } public Long op(Long l1,Long l2,MyFucntion2<Long,Long> myFucntion2){ return myFucntion2.getValue(l1,l2); }
二、Java内置四大核心函数式接口
在学习lambda表达式的时候,我们知道,要使用lambda表达式,我们就要创建一个函数式接口,那每次用lambda表达式的时候岂不是很麻烦,这时候,java给我们内置了四大核心函数式接口:
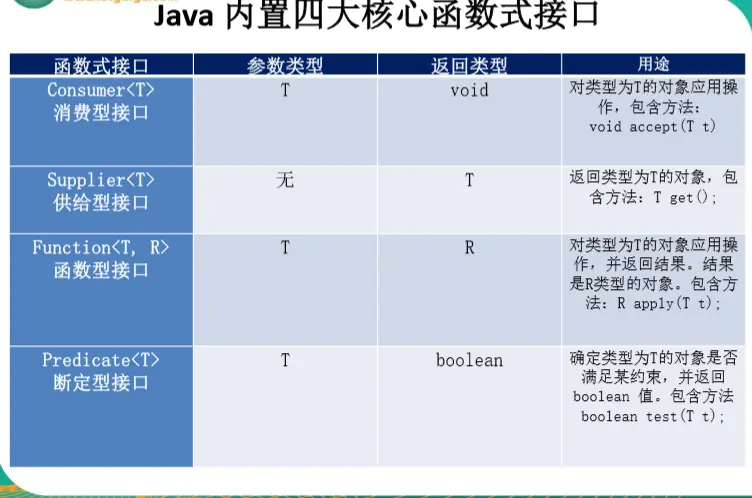
1、 Consumer<T> : 消费型接口,void accept(T t);
代码示例:
@Test public void test3(){ consumenMoney(2312,(m)-> { if (m>1000){ System.out.println("买衣服花了 1000,还剩"+(m-1000)); m-=1000; } if (m>1000){ System.out.println("买鞋花了 1000,还剩"+(m-1000)); m-=1000; } System.out.println("最后还剩"+m); }); } public void consumenMoney(double money, Consumer<Double> comsumer){ //可以实现 Consumer接口怎么花钱 comsumer.accept(money); }
2、 Supplier<T> : 供给型接口,T get();
代码示例:
@Test public void test4(){ int id=0; List<Apple> list = getAppleList(5,()->{ Apple apple1 = new Apple(id,"苹果1",new BigDecimal("3"),10); return apple1; }); list.forEach(System.out::println); } //产生指定数量的苹果 public List<Apple> getAppleList(int num ,Supplier<Apple> supplier){ List<Apple> list = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i <num ; i++) { Apple apple = supplier.get(); list.add(apple); } return list; }
3、Function<T, R> : 函数型接口,R apply(T t);
代码示例:
@Test public void test5() { String trimStr=strHandler(" 你好,world! ",(String::trim);
System.out.println(trimStr); String sumString=strHandler("Helloworld!",(str)->str.substring(2, 4)); System.out.println(sumString); } //需求:用于处理字符串 public String strHandler(String str,Function<String,String> fun) { return fun.apply(str); }
4、 Predicate<T> : 断言型接口,boolean test(T t);
代码示例:
@Test public void test5() { List<String> list=Arrays.asList("Hello","world","hi","o","123"); List<String> filterStr = filterStr(list, (str)->str.length()>1); filterStr.forEach(System.out::println); } //需求:将满足条件的字符串,放入集合中 public List<String> filterStr(List<String> list, Predicate<String> pre){ List<String> list2=new ArrayList<>(); list.forEach((str)->{ if(pre.test(str)){ list2.add(str); } }); return list2; }
三、其他接口
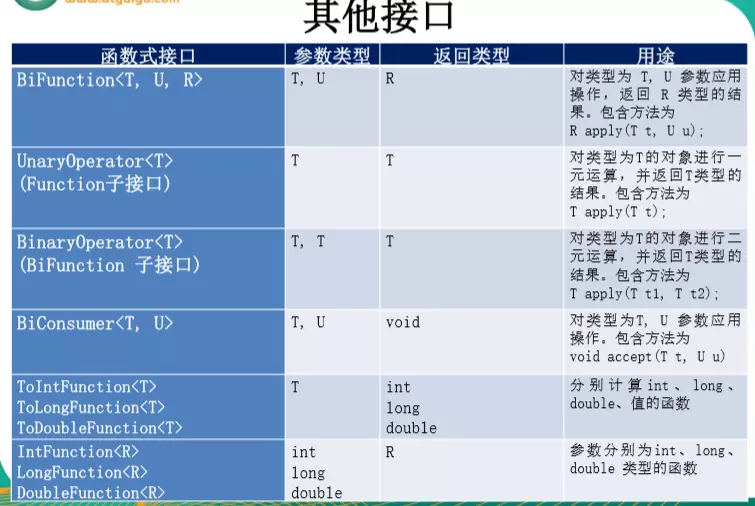
我们熟悉的:
public interface Runnable { void run(); } public interface Callable<V> { V call() throws Exception; } public interface ActionListener { void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e); } public interface Comparator<T> { int compare(T o1, T o2); boolean equals(Object obj); }