1、提纲
- 什么是iOS的事件分发机制 ?
- 一个事件UIEvent又是如何响应的?
- 手势对于响应链有何影响?
2、事件分发机制
2.1、来源
以直接触摸事件为例:
- 当用户一个手指触摸屏幕是会生成一个UITouch对象,多个手指就是多个对象,手指移动系统会更新对象的相应信息。
- 系统会将UITouch对象封装生成一个事件UIEvent对象,将这个事件交给最佳具有响应能力的视图处理。
- 系统有个UIResponder类,只有继承UIResponder的类才具有响应事件能力,所以UIKit系统控件大多是继承此类。
如何找到处理这个事件的视图的过程——事件分发机制
2.2、具体步骤
2.2.1、事件Event的产生
点击一下iOS设备的屏幕,UIKit就会生成一个事件对象UIEvent,然后会把这个Event分发给当前活动的app;
当前活动的app得知有事件,UIApplication 单例就会从事件队列中去取最新的事件,然后分发给能够处理该事件的对象(具体视图)。
2.2.2、运用到的两个UIView中的方法
- (nullable UIView *)hitTest:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event; //找到并返回最合适的视图来 - (BOOL)pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event; //判断点是否在视图内
当一个视图View收到hitTest消息时,会调用自己的poinInside方法;
如果返回YES,View会遍历自己的子视图(遍历顺序先addSubView先遍历),子视图就会调用自己的hitTest方法;
如果返回NO,View就不会遍历自己子视图(很节约);
直到找到最小的能够处理事件的view,如果整了一圈没找到能够处理的view,则返回自身。
2.2.3、举例说明
白色:ViewController , 绿色:一个View视图 , 蓝色:一个Button按钮
现象:点击绿色视图内的按钮区域,正常;点击绿色视图外的按钮区域,按钮的selector方法不会调用?

重新绿色view的hitTest方法:
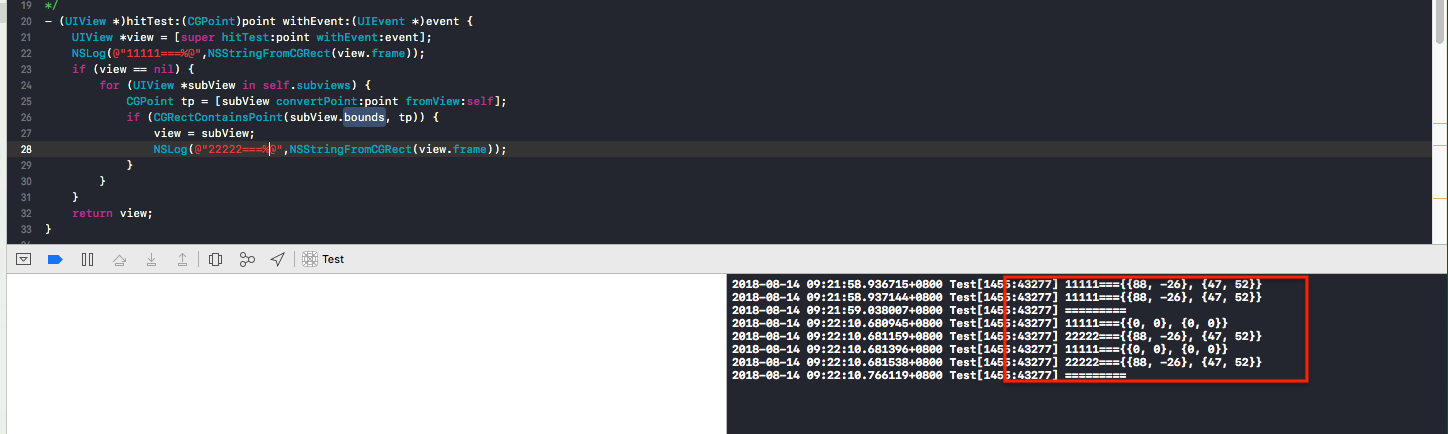
点击有效区域时:返回视图坐标{{88, -26}, {47, 52}},此坐标是相对父视图的;
点击区域外的部分时:返回视图坐标{{0, 0}, {0, 0}},所以按钮不会响应;
重新hitTest方法,修改返回view,当点击区域外按钮部分时也返回有效视图{{88, -26}, {47, 52}},如图所示;
另外一种解决方案:更暴力
- (BOOL)pointInside:(CGPoint)point withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{ return YES; }
号外:
如果触摸点不在 view 中,直接返回 nil (例子就是此现象)。
3、响应链
1. UIView 的 nextResponder 是直接管理它的 UIViewController (也就是 VC.view.nextResponder = VC ),如果当前 View 不是 ViewController 直接管理的 View,则 nextResponder 是它的 superView( view.nextResponder = view.superView )。 2. UIViewController 的 nextResponder 是它直接管理的 View 的 superView( VC.nextResponder = VC.view.superView )。 如果viewcontroller的view是window的根view,那么下一个响应者是window; 如果viewcontroller是另一个viewcontroller模态推出的,那么下一个响应者是另一个viewcontroller; 如果viewcontroller的view被add到另一个viewcontroller的根view上,那么下一个响应者是另一个viewcontroller的根view 3. UIWindow 的 nextResponder 是 UIApplication 。 4. UIApplication 的 nextResponder 是 AppDelegate。
一般来说,某个 UIResponder 的子类想要自己处理一些事件,就需要重写它的这些方法(触摸为例):
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event; - (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event; - (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event; - (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event; - (void)touchesEstimatedPropertiesUpdated:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches NS_AVAILABLE_IOS(9_1);
如果想自己处理后,继续让事件响应下去:
- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [super touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event]; } - (void)touchesMoved:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [super touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event]; } - (void)touchesEnded:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [super touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event]; } - (void)touchesCancelled:(NSSet<UITouch *> *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event { [super touchesBegan:touches withEvent:event]; }
4、手势对响应链有何影响
手势识别器并不是响应者链中的一员,但是手势识别器会观察touch事件,并延迟事件向所绑定的视图传递;
在上例中给Button和view添加点击手势:
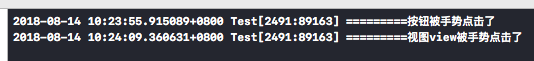
按钮会优先响应手势,而不是自身的selector;
- (BOOL)gestureRecognizer:(UIGestureRecognizer *)gestureRecognizer shouldReceiveTouch:(UITouch *)touch{ if ([touch.view isKindOfClass:[UIButton class]]) { return NO; }else{ return YES; } }

添加手势又屏蔽:有毛病?
在其他UICollectionView和UIScrollView、UITableView等,如果需要在视图上添加手势,cell上也会响应手势,此方法可以解决手势和自身方法的冲突!