查询
子查询
即嵌套在其他查询中的查询
-
表结构说明:每个订单包含订单编号,客户ID,订单日期,在Orders表中。各订单的物品存储在相关的OrderItems表中,Orders表中不存储客户信息,只存储客户ID。客户实际信息存储在Customers表中。
-
问题1:检索出订购物品RGAN01的所有顾客
-
解:
- 步骤一:检索出包含物品RGAN01的订单
select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'RGAN01';可以得到,

- 步骤二:检索出和订单号20007,20008相关的顾客
select cust_id from Orders where order_num in (20007,20008);可以得到,

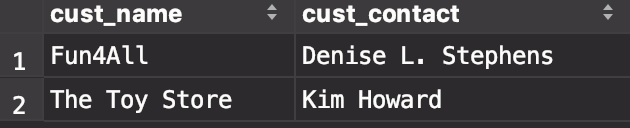
- 步骤三:检索出这些客户ID的顾客信息
select cust_name,cust_contact from Customers where cust_id in ('1000000004','1000000005');可以得到,
-
总结:
select cust_name,cust_contact from Customers where cust_id in (select cust_id from Orders where order_num in (select order_num from OrderItems where prod_id = 'RGAN01'));
需要注意的地方:1. 作为子查询的SELECT语句只能查询单个列,企图检索多个列将返回错误;2. 对于能嵌套的子查询的数目没有限制,不过在实际使用的时候由于性能的限制,不能嵌套太多的子查询。
-
问题2:显示Custormers表中每个顾客的订单总数
-
解:
- 步骤一:检索出Custormers表中的顾客列表
select cust_name,cust_state,cust_id from Customers order by cust_name;- 步骤二:对于检索出的顾客,检索其在Orders表中的订单数目
select count(*) from Orders where cust_id = '1000000003'; -
总结:
select cust_name, cust_state , (select count(*) from Orders where Orders.cust_id = Customers.cust_id) from Customers order by cust_name;
其中,where Orders.cust_id = Customers.cust_id表示比较从Orders表中的cust_id和当前正从Customers表中检索出的cust_id。
另外,虽然样例可以完成需求,但并不是解决这种数据检索的最有效方法,后面讲到JOIN方法时我们会重新做这道题。
组合查询
可用
UNION操作符来组合数条SQL查询
仍然是从题目入手,
-
题目:需要Illinois,Indiana,Michigan等美国几个州的所有顾客的报表,还想包括不管位于哪个州的所有的Fun4All。
-
解1:利用
WHERE
select cust_name,cust_contact,cust_email,cust_state from Customers where cust_state in ('IL','IN','MI') or cust_name = 'Fun4All';
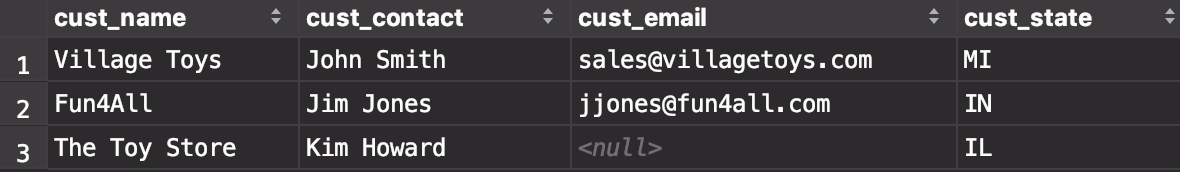
- 解2:利用
UNION
select cust_name,cust_contact,cust_email,cust_state from Customers where cust_state in ('IL','IN','MI');
select cust_name,cust_contact,cust_email from Customers where cust_name = 'Fun4All';

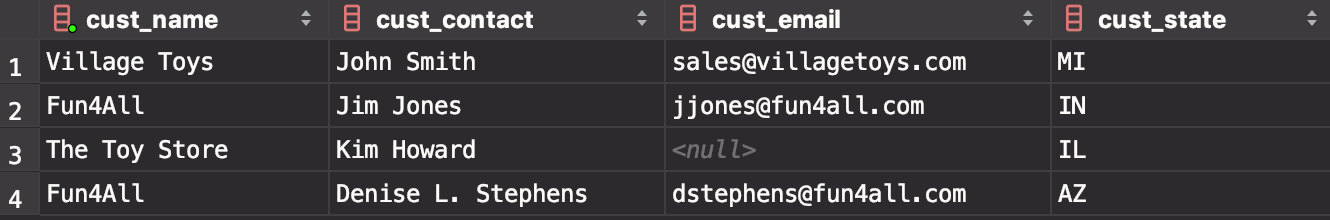
组合起来,
select cust_name,cust_contact,cust_email from Customers where cust_state in ('IL','IN','MI') UNION select cust_name,cust_contact,cust_email from Customers where cust_name = 'Fun4All';
注意,UNION中每个查询必须包含相同的列,表达式或者聚集函数,不过各个列不需要以相同的次序列出。另外,UNION从查询结果集中自动去除了重复的行,如果想返回所有的匹配行,可以使用UNION ALL。最后还需要说明的是,在用UNION组合查询时,只能使用一条ORDER BY子句,它必须位于最后一条SELECT语句之后。
联结表
如果数据存储在多个表中,怎样用一句
SELECT语句就检索出数据呢?答案是,使用联结。
笛卡尔积:由没有联结条件的表关系返回的结果为笛卡尔积,检索出的行的数目将是第一个表中的行数乘以第二个表中的行数。有时,返回笛卡尔积的联结也被称为叉联结。
select prod_name,prod_price,vend_name from Products,Vendors;
等值联结,基于两个表之间的相等测试,这种联结也被称为内联结。
select vend_name,prod_name,prod_price from Vendors inner join Products on Vendors.vend_id = Products.vend_id;
再来看一个问题,
-
显示订单20007中的物品
-
解:
订单物品存储在Orderitems表中,每个产品按照产品ID存储,它引用Products表中的产品。这些产品通过供应商ID联结到Vendors表中相应的供应商,供应商ID存储在每个产品的记录中。
select prod_name,vend_name,prod_price,quantity from OrderItems,Products,Vendors where Products.vend_id = Vendors.vend_id and OrderItems.prod_id = Products.prod_id and order_num = '20007';
注意,联结的表越多,性能下降就越厉害。
创建高级联结
使用表别名
select cust_name,cust_contact from Customers as C ,Orders as O,OrderItems as OI where C.cust_id=O.cust_id and OI.order_num = O.order_num and prod_id = 'RGAN01';
自联结
-
问题:要给与Jim Jones同一公司的所有顾客发送一封邮件
-
解:
首先找出Jim Jones的公司,然后找出在该公司工作的所有顾客
- 子查询
select cust_id,cust_name,cust_contact from Customers where cust_name = (select cust_name from Customers where cust_contact = 'Jim Jones');- 自联结
select C1.cust_id,C1.cust_name,C1.cust_contact from Customers as C1,Customers as C2 where C1.cust_name = C2.cust_name and C2.cust_contact = 'Jim Jones';
虽然以上两种方式结果相同,但是许多DBMS处理联结的性能远比处理子查询快得多。
自然联结
迄今为止,建立的所有联结都是自然联结,很可能永远都不会用到不是自然联结的内联结。
外联结
联结包含了那些在相关表中没有关联行的行,这种联结被称为外联结。
-
例1:检索所有的顾客和订单
select Customers.cust_id,Orders.order_num from Customers inner join Orders on Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id;

-
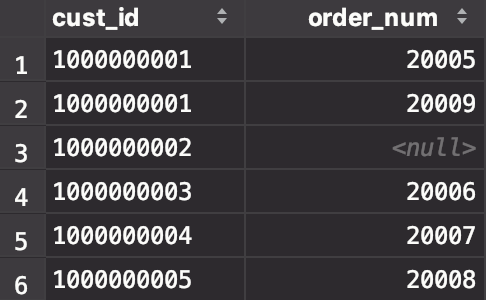
题:检索包括没有订单顾客在内的所有顾客
-
解:
select Customers.cust_id,Orders.order_num from Customers left outer join Orders on Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id;
在使用outer join时必须使用RIGHT或者LEFT关键字指定包括其所有行的表,left outer join指的是从From子句中左边的表Customers中选择所有的行。
使用带聚集函数的联结
- 题:检索有所的顾客及每个顾客所下的订单数量
- 解:
select Customers.cust_id,count(Orders.order_num) as num_ord from Customers inner join Orders on Customers.cust_id = Orders.cust_id group by Customers.cust_id;