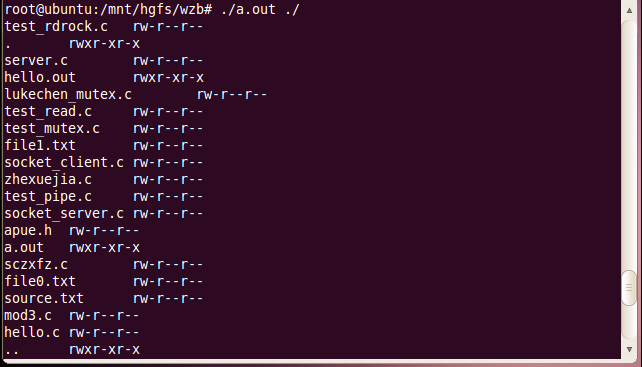
就是遍历一个目录下面的所有文件,显示信息
Linux下面有点绕
要通过 opendir打开目录,返回一个DIR结构
用readdir来读DIR结构,返回目录下面的第一项,是个dirent结构体,再次调用readdir回读到第二项,以此类推
dirent结构体里面有该文件的文件名,通过stat可以获得该文件的详细信息。
注意stat结构要malloc一下,不然后segment fail??好像是这个单词。可能是没有分配的话指针会乱指。
读写执行权限在mode_t里面,没有直接输出的函数,要自己写一个,判断有没有该权限,用与运算,不是判等。
其它信息都在stat里面,这里只输出了st_mode。
#include<dirent.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> void show(mode_t mode){ if(mode&S_IRUSR) printf("r"); else printf("-"); if(mode&S_IWUSR) printf("w"); else printf("-"); if(mode&S_IXUSR) printf("x"); else printf("-"); /*********Group********/ if(mode&S_IRGRP) printf("r"); else printf("-"); if(mode&S_IWGRP) printf("w"); else printf("-"); if(mode&S_IXGRP) printf("x"); else printf("-"); /**********Else***************/ if(mode&S_IROTH) printf("r"); else printf("-"); if(mode&S_IWOTH) printf("w"); else printf("-"); if(mode&S_IXOTH) printf("x"); else printf("-"); printf(" "); } int main(int argc,char * argv[]){ DIR *dp; struct dirent* dir; struct stat * buf = (struct stat *)malloc(sizeof(struct stat)); int fd; dp = opendir(argv[1]); while((dir = readdir(dp))!=NULL){ printf("%s ",dir->d_name); //fd = open(dir->d_name,O_RDWR); //fstat(fd,buf); stat(dir->d_name,buf); show(buf->st_mode); } printf("Done!!!! "); }