解析excel我们常用的应该就是poi了,这个比较坑,之前项目用过一下,这次我们使用一下阿里的easyexcel吧!easyexcel的使用很简单,比较类似于最开始解析xml使用的SAX,就是每读取文件一行,就直接进行处理,完全不需要文件都加载到内存中!!!
easyexcel的官方文档
1. 随意新建一个springboot项目,导入常见的依赖(基于springboot+mybatis+mybatisplus+lombok+swagger),然后再导入easyexcel:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>easyexcel</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
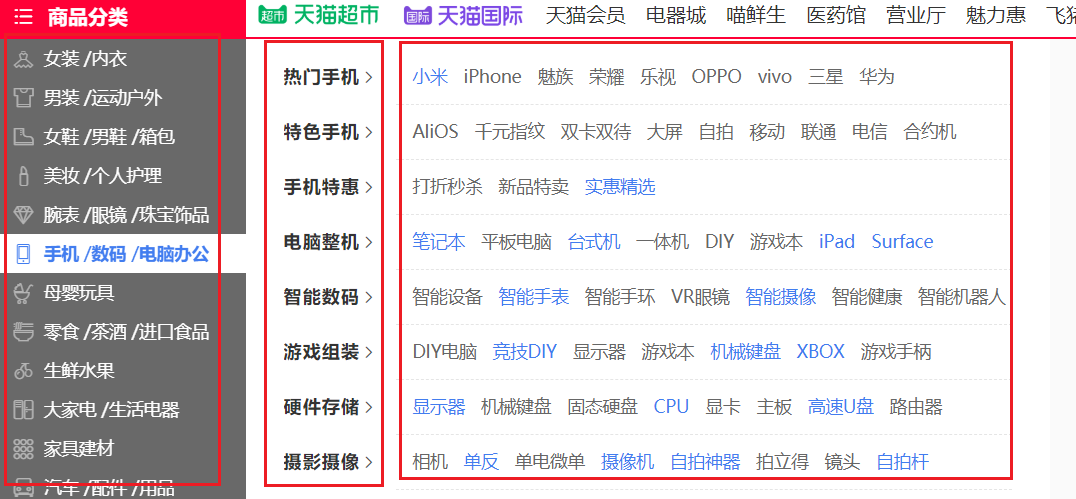
2. excel文件中的内容,比如淘宝商品的分类,肯定是分为一级,二级,三级分类等等,下图所示,一个一级分类对应多个二级分类,一个二级对应多个三级,等等
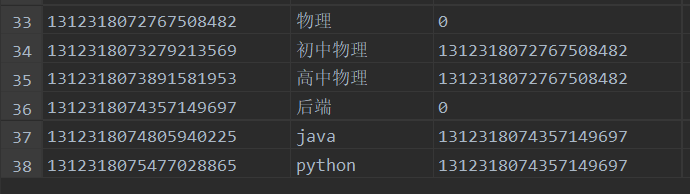
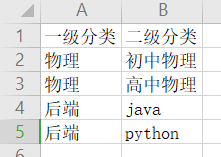
我们就不弄那么麻烦了,以一个课程的分类为例,有一级分类二级分类,下图的excel文件所示,我们需要将这个excel文件上传,然后通过easyexcel解析出来,丢到数据库中,类似图中数据库表中的数据
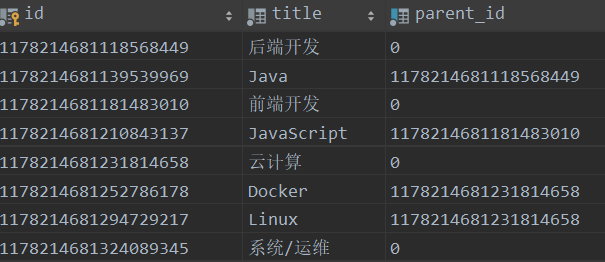
sql脚本如下::
create table subject ( id char(19) not null comment '课程类别ID' primary key, title varchar(10) not null comment '类别名称', parent_id char(19) default '0' not null comment '父ID' )comment '课程科目'; create index idx_parent_id on subject (parent_id);
3. controller代码:
package com.protagonist.edu.controller; import com.protagonist.edu.service.SubjectService; import com.protagonist.responseVO.Result; import com.protagonist.responseVO.StatusCode; import io.swagger.annotations.Api; import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile; import javax.annotation.Resource; /** * <p> * 课程科目 前端控制器 * </p> * * @author protagonist * @since 2020-10-01 */ @Api("课程分类的api") @RestController @RequestMapping("/edu/subject") @Slf4j public class SubjectController { @Resource private SubjectService subjectServiceImpl; //添加课程分类,上传excel然后进行读取,解析成对象 @PostMapping("/addSubject") @ApiOperation(value = "上传excel文件中的一级分类和二级分类") public Result addSubject(MultipartFile file) { subjectServiceImpl.saveSubject(file); return new Result<>(true, StatusCode.OK, "添加课程分类成功"); } }
4.service和serviceImpl:
public interface SubjectService extends IService<Subject> { /** * 添加课程分类 * @param file */ void saveSubject(MultipartFile file); } @Service @Slf4j public class SubjectServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<SubjectMapper, Subject> implements SubjectService { @Override public void saveSubject(MultipartFile file) { try{ InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream(); //读取excel EasyExcel.read(inputStream, ExcelSubjectData.class,new SubjectExcelListener(this)).sheet().doRead(); }catch (Exception e){ log.error("读取excel文件异常",e); throw new ProtagonistException(StatusCode.READ_FILE_ERROR,"读取excel文件异常"); } } }
5.entity
@Data @EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false) @Accessors(chain = true) @TableName("subject") @ApiModel(value="Subject对象", description="课程科目") public class Subject implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; @ApiModelProperty(value = "课程类别ID") @TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.ID_WORKER_STR) private String id; @ApiModelProperty(value = "类别名称") private String title; @ApiModelProperty(value = "父ID") private String parentId; }
6.我们还需要一个类,这个类的每一个实例都对应excel中每一行数据,我们将每一行数据都转成一个对象之后,然后进行处理就方便了;
package com.protagonist.edu.excel; import com.alibaba.excel.annotation.ExcelProperty; import lombok.Data; @Data public class ExcelSubjectData { /** * 一级分类 */ @ExcelProperty(index = 0) private String oneSubjectName; /** * 二级分类 */ @ExcelProperty(index = 1) private String twoSubjectName; }
7.listener,之前说过easyexcel是每读一行数据都会处理一下, 所以这里需要来一个监听器:
package com.protagonist.edu.entity.listener; import com.alibaba.excel.context.AnalysisContext; import com.alibaba.excel.event.AnalysisEventListener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON; import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.conditions.query.QueryWrapper; import com.protagonist.edu.entity.Subject; import com.protagonist.edu.excel.ExcelSubjectData; import com.protagonist.edu.service.SubjectService; import com.protagonist.responseVO.StatusCode; import com.protagonist.servicebase.exception.ProtagonistException; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import java.util.Objects; @Slf4j public class SubjectExcelListener extends AnalysisEventListener<ExcelSubjectData> { //这里必须来个构造器,将service传过来,然后再监听器中每处理一行就可以直接进行入库操作; //其实可以使用mybatis的批量入库的 private SubjectService subjectService; public SubjectExcelListener(SubjectService subjectService){ this.subjectService = subjectService; } //这个方法读取excel内容,一行一行读取,每一行都会触发这个方法,而excelSubjectData表示的就是excel中的一行数据 //注意这里的第一行不会读,默认是表头 @Override public void invoke(ExcelSubjectData excelSubjectData, AnalysisContext analysisContext) { log.info("每一行处理excel数据============================="); if (Objects.isNull(excelSubjectData)){ throw new ProtagonistException(StatusCode.ERROR,"文件内容为空"); } //获取每一行中的第一个数据和第二个数据,然后判断数据库中是否有该分类信息,没有的话才会插入数据库 String oneSubjectName = excelSubjectData.getOneSubjectName(); String twoSubjectName = excelSubjectData.getTwoSubjectName(); //判断数据库中有没有一级分类,没有的话就插入一级分类 Subject oneSubject = getOneOrTwoSubject(subjectService, oneSubjectName, "0"); if (Objects.isNull(oneSubject)){ oneSubject = new Subject(); oneSubject.setTitle(oneSubjectName); oneSubject.setParentId("0"); subjectService.save(oneSubject); } log.info("数据入库之后:{}", JSON.toJSONString(oneSubject)); //判断数据库中有没有二级分类,要判断这个二级分类的话必须先获取此时的父id,这里有个很神奇的地方,mybatisplus在执行save(T obj)方法完成之后, // 就会将生成的主键赋值给obj中 //oneSubject.getId()可以获取当前二级分类对应的一级分类的id Subject twoSubject = getOneOrTwoSubject(subjectService, twoSubjectName, oneSubject.getId()); if (Objects.isNull(twoSubject)){ twoSubject = new Subject(); twoSubject.setParentId(oneSubject.getId()); twoSubject.setTitle(twoSubjectName); subjectService.save(twoSubject); } } /** * 根据课程名称和父id查询课程分类表中的数据 * @param subjectService * @param name * @param pid * @return */ private Subject getOneOrTwoSubject(SubjectService subjectService,String name,String pid){ QueryWrapper<Subject> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); queryWrapper.eq("title",name); queryWrapper.eq("parent_id",pid); return subjectService.getOne(queryWrapper); } @Override public void doAfterAllAnalysed(AnalysisContext analysisContext) { } }
8.测试成功