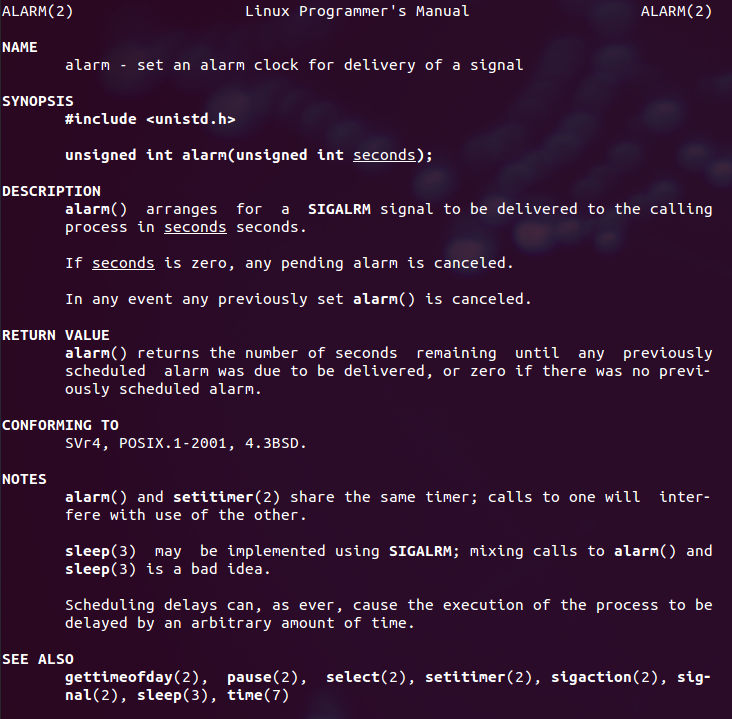
alarm()函数说明
1.引用头文件:#include <unistd.h>;
2.函数标准式:unsigned int alarm(unsigned int seconds);
3.功能与作用:alarm()函数的主要功能是设置信号传送闹钟,即用来设置信号SIGALRM在经过参数seconds秒数后发送给目前的进程。如果未设置信号SIGALARM的处理函数,那么alarm()默认处理终止进程。
4.函数返回值:如果在seconds秒内再次调用了alarm函数设置了新的闹钟,则后面定时器的设置将覆盖前面的设置,即之前设置的秒数被新的闹钟时间取代;当参数seconds为0时,之前设置的定时器闹钟将被取消,并将剩下的时间返回。
alarm()测试1.1
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
void sig_handler(int num)
{
printf("receive the signal %d.
", num);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGALRM, sig_handler); //SIGALRM是在定时器终止时发送给进程的信号
alarm(2);
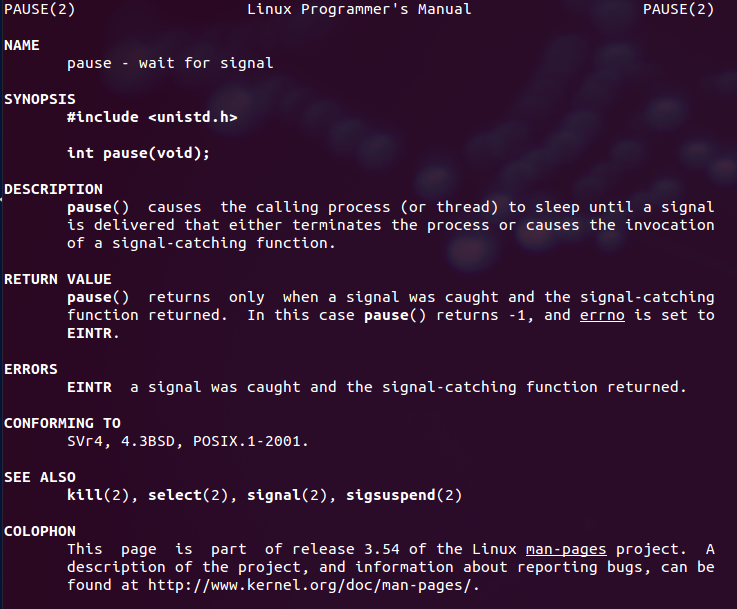
pause();//pause()函数使该进程暂停让出CPU
exit(0);
}
运行结果:两秒钟后输出

如果我们想程序每2秒都定时一下,这样实现也很简单,我们在处理定时信号的函数中再次定时2秒;实例如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
void sig_handler(int num)
{
printf("receive the signal %d.
", num);
alarm(2);
}
int main()
{
signal(SIGALRM, sig_handler);
alarm(2);
while(1)//做一个死循环,防止主线程提早退出,相等于线程中的join
{
pause();
}
//pause();//如果没有做一个死循环则只会让出一次cpu然后就还给主线程,主线程一旦运行结束就会退出程序
exit(0);
}
运行结果:每隔2秒钟就会输出一次。
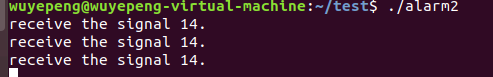
可以看出程序每隔2秒就会收到信号14,也就是SIGALRM信号;并且当处理完该信号之后,直接执行pause()函数下面的语句;说明pause()是可被中断的暂停;
备注:这样就可以使用alarm函数来实现server和client之间的定时通信,比如说我想在一个小时后发送xxx给xxx