关于继承,我之前知道的事es6的继承,写法更偏向于java。但是es6的继承是一种语法糖,他的内部原理还是es5的原型链继承。
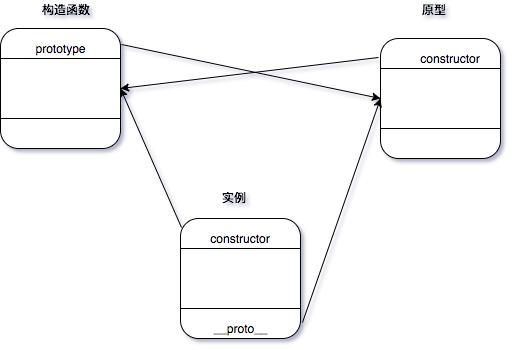
首先要了解构造函数、原型、实例的关系。
图片来自网络
构造函数的prototype指向原型
原型的constructor指向构造函数
实例的constructor指向构造函数
实例的_proto_指向原型
我们先来看下es6的继承方式
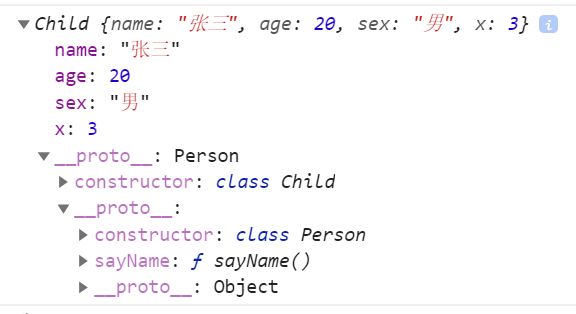
//父类 class Person{ constructor(name,age){ this.name=name this.age=age } sayName(){ console.log(this.name) } static A(){ console.log("父类静态函数") } } //子类 class Child extends Person{ constructor(sex,name,age){ super(name,age) this.sex=sex this.x=2 super.x=3//super指向子类this console.log(this.x)//3 改了x console.log(super.x)//undefined super代表父类 但父类没有x方法 } static A(){ console.log("子类静态函数") super.A() } } let c=new Child("男","张三",20) console.log(c) c.sayName()//子实例调用父类函数 Child.A()//调用静态函数
使用class声明,Child继承自Person,使用extends。
super()要在子类的constructor中使用,代表父类的构造函数,返回this对象,指向子类。子类里必须写super(),用于将父类的属性方法传给子类。
super既可以是函数也可以是对象,但是不能直接打印。
super在子类中代表this,可以改变属性
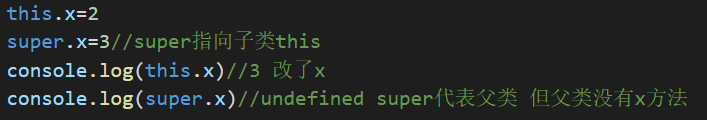
constructor是类的构造函数。
继承后子类就可以调用父类的方法了,本身没有的,js会向对象的原型上面找。
es5方式如何继承?
原型链实现继承:
子构造函数的原型对象=父构造函数的实例
//父类构造 const Person=function(name,age){ this.name=name this.age=age } Person.prototype.sayName=function(){ console.log(this.name) } //子类构造 const Child=function(sex,name,age){ this.sex=sex this.name=name this.age=age } Child.prototype=new Person() let c=new Child("男","张三",20) console.log(c) c.sayName()
上方代码可知,原本父类Person和子类Child的是并没有什么关系的,但是通过原型指向后,就形成了父子继承关系。
构造函数call改变指向形成继承:
//父类构造 const Person=function(name,age){ this.name=name this.age=age } Person.prototype.sayName=function(){ console.log(this.name) } //子类构造 const Child=function(sex,name,age){ this.sex=sex Person.call(this,name,age) } let c=new Child("男","张三",20) console.log(c)
call可以改变实例的指向,指向this就是指向子类
这种方式有个缺点:就是无法继承父类上原型链的函数,只能继承内部属性和内部方法。
所以,一般使用混合继承方式:
const Person=function(name,age){ this.name=name this.age=age } Person.prototype.sayName=function(){ console.log(this.name) } const Child=function(sex,name,age){ this.sex=sex Person.call(this,name,age) } // Child.prototype=new Person() Child.prototype=Object.create(Person.prototype) Child.prototype.constructor=Child let c1=new Child("男","张三",20) console.log(c1) c1.sayName()
让子类的原型构造器指向自己,形成原型链。