2017.03.03 中度霾
循环结构:
一、Demo01(循环输出10000次语句)
1、老师写的代码:
public class While02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* while(循环条件){
* 循环体(循环操作)
* }
* 循环条件 必须是一个boolean类型的值!
*
* 当满足了循环条件,会执行循环体,直到不满足循环条件是退出!
*/
System.out.println("大家辛苦了1");
System.out.println("大家辛苦了2");
System.out.println("大家辛苦了3");
System.out.println("大家辛苦了4");
System.out.println("大家辛苦了5");
System.out.println("**************************************");
// 定义一个变量 用来保存 循环的次数
int num = 0;
while (num <= 10000) {
System.out.println("大家辛苦了" + num);
// 自身+1
num++;
}
System.out.println(num);
}
}
2、自己写的代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>While01
*<P>Description<P>while循环练习(连续输出同样的10^4句话)
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3上午10:01:14
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
public class While01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 0;
while (i <= 10000) {
System.out.println("老师辛苦了!" + i);
i++;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
}
二、WhileDemo02(循环打印50份试卷)
1、老师写的代码:
public class WhileDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 循环打印50份试卷
* 分析:
* 循环条件:count<=50 小于等于50次
* 循环体: 打印试卷
*/
int count = 1;
while (count <= 50) {
System.out.println("正在打印第" + count + "份试卷");
// 迭代变量
count++;
}
}
}
2、我写的代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>While02
*<P>Description<P>打印50份试卷
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3上午10:22:25
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
public class While02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 50) {
System.out.println("打印第" + i + "份试卷");
i++;
}
}
}
三、WhileDemo3(检查是否完成学习任务)
1、老师写的代码:
public class WhileDemo04 {
/**
* 老师每天检查张浩的学习任务是否合格。
* 如果不合格,则继续进行。
老师给张浩安排的每天的学习任务为:
上午阅读教材,学习理论部分,
下午上机编程,掌握代码部分
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入是否合格?(y/n)");
String answer = scanner.next();
// 循环条件 -==》是否合格? 如果不合格 一直学习!
while (answer.equalsIgnoreCase("n")) {
System.out.println("阅读教材,学习理论部分");
System.out.println("上机编程,掌握代码部分");
System.out.println("再次输入是否合格?(y/n)");
answer = scanner.next();
}
System.out.println("完成了 学习任务!");
}
}
2、自己写的代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>While03
*<P>Description<P>
* 老师每天检查张浩的学习任务是否合格。
* 如果不合格,则继续进行。
老师给张浩安排的每天的学习任务为:
上午阅读教材,学习理论部分,
下午上机编程,掌握代码部分
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3上午10:23:21
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class While03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 提示用户输入是否完成学习任务
System.out.println("你是否完成学习任务(y/n)?");
String answer = input.next();
// 循环条件:是否完成学习任务;循环操作:如果未完成,循环上下午学习!
while (answer.equalsIgnoreCase("n")) {
System.out.println("上午阅读教材,学习理论部分!");
System.out.println("下午上机编程,掌握代码部分!");
System.out.println("你是否完成学习任务(y/n)?");// 循环判断是否完成任务
answer = input.next();
}
System.out.println("已经完成学习任务,回家看完视频好好休息!");
}
}
四、WhileDemo04(到哪一年培训学员人数将达到100万人)
1、老师写的代码:
public class WhileDemo05 {
/**
* 2012年培养学员25万人,每年增长25%。
* 请问按此增长速度
* 到哪一年培训学员人数将达到100万人?
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int year = 2012;
double person = 25;
while (person <= 100) {
person *= (1 + 0.25); // person*=(1+0.25);
year++;
}
System.out.println(year + "培训学员人数将达到100万人");
}
}
2、自己写的代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>While04
*<P>Description<P>
* 2012年培养学员25万人,
* 每年增长25%。
* 请问按此增长速度,
* 到哪一年培训学员人数将达到100万人?
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3上午10:42:06
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
public class While04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 分别声明学生人数和所处年份
double stuNum = 25;
int year = 2012;
// 循环条件为学生人数未达到100万人
while (stuNum < 100) {
stuNum *= (1 + 0.25);// 等价于stuNum=stuNum*(1+0.25);
year++;
}
// 输出到哪一年培训学员人数将达到100万人
System.out.println("到" + year + "年培训学员人数将达到100万人");
}
}
五、WhileDemo05(100以内偶数和)
1、老师写的代码:
public class WhileDemo06 {
/**
* 编程实现:计算100以内(包括100)的偶数之和
设置断点并调试程序,观察每一次循环中变量值的变化
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 0;
int sum = 0;// 记录所有的偶数和
while (num <= 100) {
if (num % 2 == 0) { // 偶数
sum += num; // sum=sum+num
}
num++;
}
System.out.println("所有的偶数和:" + sum);
}
}
2、自己写的代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>While05
*<P>Description<P>100以内偶数和
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3上午11:04:27
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
public class While05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;// 声明偶数之和
int i = 0;// 数字编号
while (i <= 100) {
if (i % 2 == 0) {
sum += i;
}
i++;// 放在if结构外,while结构内!
}
System.out.println("100以内的偶数之和为:" + sum);
}
}
六、WhileDemo(MyShopping管理系统->购物结算)
需求图:
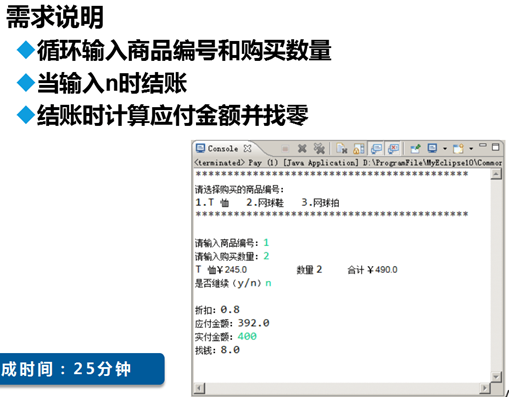
附加说明:提供打印购物清单服务
1、老师写的代码:
public class WhileDemo07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("欢迎进入MyShopping管理系统");
System.out.println("***************************");
System.out.println("1.帽子 2.网球鞋 3.球拍");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请您输入购买物品的编号");
int choose = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户的选择
System.out.println("请您输入购买的数量");
int count = scanner.nextInt();// 获取用户购买的数量
// 定义一个总消费
double money = 0;
switch (choose) {
case 1:
System.out.println("您购买的是 1.帽子 ¥50 总金额:" + (count * 50));
money += (count * 50);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("您购买的是 2.网球鞋 ¥30 总金额:" + (count * 30));
money += (count * 30);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("您购买的是 3.球拍 ¥5 总金额:" + (count * 5));
money += (count * 5);
break;
}
System.out.println("是否继续购物?(y/n)");
String answer = scanner.next();
while (answer.equalsIgnoreCase("y")) { // 循环购物操作
System.out.println("***************************");
System.out.println("1.帽子 2.网球鞋 3.球拍");
System.out.println("请您输入购买物品的编号");
choose = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户的选择
System.out.println("请您输入购买的数量");
count = scanner.nextInt();// 获取用户购买的数量
switch (choose) {
case 1:
System.out.println("您购买的是 1.帽子 ¥50 总金额:" + (count * 50));
money += (count * 50);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("您购买的是 2.网球鞋 ¥30 总金额:" + (count * 30));
money += (count * 30);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("您购买的是 3.球拍 ¥5 总金额:" + (count * 5));
money += (count * 5);
break;
}
System.out.println("是否继续购物?(y/n)");
answer = scanner.next();
}
System.out.println("您本次消费是:" + money);
System.out.println("请您输入支付金额:");
double pay = scanner.nextDouble();
while (pay < money) { // 说明金额不正确
System.out.println("金额不正确!请重新支付!");
pay = scanner.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println("找零:" + (pay - money));
}
}
2、自己写的代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>While06--》MyShopping管理系统-》购物结算
*循环输入商品编号和购买数量
*当输入n时结账
*结账时计算应付金额并找零
*如果顾客需要,打印购物小票
*<P>Description<P>
*
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3上午11:14:24
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class While06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 数组输入每个商品的价格
double price[] = { 0.0, 245.0, 1088.0, 2088.0 };
// 定义商品总金额
double total = 0.0;
// 定义折扣
double discount = 0.8;
// 定义输出小票信息:
String printBill = "";
System.out.println("MyShopping管理系统>购物结算");
System.out.println("***************************************");
System.out.println("请选择购买的商品编号:");
System.out.println("1、T恤 2、网球鞋 3、网球拍");
System.out.println("***************************************");
// 提示用户输入商品编号
System.out.println("请输入商品编号:");
int index = input.nextInt();
// 提示用户输入购买数量
System.out.println("请输入购买数量:");
int num = input.nextInt();
// 计算单次购物的金额=购买商品单价*数量
double money = price[index] * num;
switch (index) {
case 1:
String x1 = "T恤¥" + price[1] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x1);
printBill += x1 + "
";
total += money;
break;
case 2:
String x2 = "网球鞋¥" + price[2] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x2);
printBill += x2 + "
";
total += money;
break;
case 3:
String x3 = "网球拍¥" + price[3] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x3);
printBill += x3 + "
";
total += money;
break;
}
System.out.println("**************************************");
// 提示用户输入是否继续购物
System.out.println("是否继续(y/n):");
String answer = input.next();
while (answer.equalsIgnoreCase("y")) {
System.out.println("MyShopping管理系统 > 购物结算");
System.out.println("*********************************");
System.out.println("请选择购买的商品编号:");
System.out.println("1、T恤 2、网球鞋 3、网球拍");
System.out.println("*********************************");
// 提示用户输入商品编号
System.out.println("请输入商品编号:");
index = input.nextInt();
// 提示用户输入购买数量
System.out.println("请输入购买数量:");
num = input.nextInt();
// 计算每次购物的金额=购买商品单价*数量
money = price[index] * num;
switch (index) {
case 1:
String x1 = "T恤¥" + price[1] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x1);
printBill += x1 + "
";
total += money;
break;
case 2:
String x2 = "网球鞋¥" + price[2] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x2);
printBill += x2 + "
";
total += money;
break;
case 3:
String x3 = "网球拍¥" + price[3] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x3);
printBill += x3 + "
";
total += money;
break;
}
// 提示用户输入是否继续购物
System.out.println("是否继续(y/n):");
answer = input.next();
}
System.out.println("折扣:" + discount);
System.out.println("商品总金额:" + total);
System.out.println("应付金额:" + (total * discount));
// // 提示用户输入实付金额,判断后计算找零
System.out.println("请输入实付金额:");
double pay = input.nextDouble();
while (pay < (total * discount)) {// 判断实付金额是否足够支付
System.out.println("您支付的金额不够,请重新支付!");
pay = input.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println("实付金额:" + pay);
System.out.println("找零:" + (pay - (total * discount)));
// 根据顾客决定是否打印购物清单
System.out.println("是否需要打印购物清单(y/n)?");
if (input.next().equalsIgnoreCase("y")) {
System.out.println(printBill);
} else {
System.out.println("谢谢惠顾!欢迎您再次光临本店!");
}
}
}
七、DowhileDemo01(MyShopping管理系统->购物结算)
需求图:

附加说明:提供打印购物清单服务
1、 老师代码:
public class DoWhileDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double money = 0;
String answer = "";
do { // 先执行 再判断
System.out.println("欢迎进入MyShopping管理系统");
System.out.println("***************************");
System.out.println("1.帽子 2.网球鞋 3.球拍");
System.out.println("请您输入购买物品的编号");
int choose = scanner.nextInt(); // 获取用户的选择
System.out.println("请您输入购买的数量");
int count = scanner.nextInt();// 获取用户购买的数量
switch (choose) {
case 1:
System.out.println("您购买的是 1.帽子 ¥50 总金额:" + (count * 50));
money += (count * 50);
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("您购买的是 2.网球鞋 ¥30 总金额:" + (count * 30));
money += (count * 30);
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("您购买的是 3.球拍 ¥5 总金额:" + (count * 5));
money += (count * 5);
break;
}
System.out.println("是否继续购物?(y/n)");
answer = scanner.next();
} while (answer.equalsIgnoreCase("y"));
System.out.println("您本次消费是:" + money);
System.out.println("请您输入支付金额:");
double pay = scanner.nextDouble();
while (pay < money) { // 说明金额不正确
System.out.println("金额不正确!请重新支付!");
pay = scanner.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println("找零:" + (pay - money));
}
}
2、自己代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>DoWhile01购物系统
*<P>Description<P>
*用dowhile实现:
*循环输入商品编号和购买数量
*当输入n时结账
*结账时计算应付金额并找零
*如果顾客需要,打印购物小票
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3下午4:06:53
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DoWhile01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
// 数组输入每个商品的价格
double price[] = { 0.0, 245.0, 1088.0, 2088.0 };
// 购买商品编号
int index = 0;
// 购买商品数量
int num = 0;
// 单次购物金额
double money = 0.0;
// 是否继续购物
String answer = "";
// 定义商品总金额
double total = 0.0;
// 定义折扣(暂时固定)
double discount = 0.8;
// 定义输出小票信息:
String printBill = "";
do {
System.out.println("MyShopping管理系统 > 购物结算");
System.out.println("*********************************");
System.out.println("请选择购买的商品编号:");
System.out.println("1、T恤 2、网球鞋 3、网球拍");
System.out.println("*********************************");
// 提示用户输入商品编号
System.out.println("请输入商品编号:");
index = input.nextInt();
// 提示用户输入购买数量
System.out.println("请输入购买数量:");
num = input.nextInt();
// 计算单次购物的金额=购买商品单价*数量
money = price[index] * num;
switch (index) {
case 1:
String a1 = "T恤¥" + price[1] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(a1);
printBill += a1 + "
";
total += money;
break;
case 2:
String a2 = "网球鞋¥" + price[2] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(a2);
printBill += a2 + "
";
total += money;
break;
case 3:
String a3 = "网球拍¥" + price[3] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(a3);
printBill += a3 + "
";
total += money;
break;
}
// 提示用户输入是否继续购物
System.out.println("是否继续(y/n):");
answer = input.next();
} while ((answer.equalsIgnoreCase("y")));
// 控制台输出折扣、商品总金额、应付金额
System.out.println("折扣:" + discount);
System.out.println("商品总金额:" + total);
System.out.println("应付金额:" + (total * discount));
// 提示用户输入实付金额,判断后计算找零
System.out.println("请输入实付金额:");
double pay = input.nextDouble();
while (pay < (total * discount)) {// 判断实付金额是否足够支付
System.out.println("您支付的金额不够,请重新支付!");
pay = input.nextDouble();
}
System.out.println("实付金额:" + pay);
System.out.println("找零:" + (pay - (total * discount)));
// 根据顾客决定是否打印购物清单
System.out.println("是否需要打印购物清单(y/n)?");
if (input.next().equalsIgnoreCase("y")) {
System.out.println(printBill);
} else {
System.out.println("谢谢惠顾!欢迎您再次光临本店!");
}
}
}
八、dowhileDemo02(摄氏温度华氏温度对照表)
1、老师代码:(下周一)
2、自己代码:
package cn.bdqn.test;
/**
*
*<P>Title<P>DoWhile02
*<P>Description<P>
*使用do-while实现:
*输出摄氏温度与华氏温度的对照表;
*要求它从摄氏温度0度到250度,每隔20度为一项;
*对照表中的条目不超过10条;
*转换关系:华氏温度=摄氏温度*9/5.0+32;
*提示:循环操作:计算摄氏温度,并输出对照条目
*循环条件:
*条目<=10&&摄氏温度<=250
*
* @author alex
* @date 2017-3-3下午4:35:59
* You can either travel or read,but either your body or soul must be on the way
*/
public class DoWhile02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 声明摄氏温度
double celsiusTemperature = 0.0;
// 声明华氏温度
double fahrenheit = 0.0;
// 声明摄氏温度的条目
int i = 1;
// 根据摄氏温度计算华氏温度并输出
System.out.println("******摄氏温度与华氏温度对照表******");
do {
fahrenheit = celsiusTemperature * 9 / 5.0 + 32;
System.out.println("-------------------------------------");
System.out.println("摄氏温度:" + celsiusTemperature + " " + "华氏温度:"
+ fahrenheit);
i++;
celsiusTemperature += 20;
} while (i <= 10 && celsiusTemperature <= 250);
}
}
九、作业:
1、复习消化上午老师讲课内容
2、DVD项目做好周末交到网上T13文件夹
3、视频看到类和对象
十、考试:
具体情况如下:
2017.03.03
15:17开始15:48结束;答题时间:26分钟 ;检查时间:5分钟;
因为网速问题有同学系统崩溃无法提交做题结果,害怕系统崩溃无法提交所以检查到29题就交卷了!ORZ
侥幸得到100分(第49题感觉超出目前个人能力范围,是蒙对的),但个人拙见会敲代码才是王道,继续努力!追赶看完U1的大神们!
十 一、疑问:
1、老师讲课的最后一个DEMO:
case 1:
String x1 = "T恤¥" + price[1] + " " + "数量" + num + " 合计¥"
+ money;
System.out.println(x1);
printBill += x1 + "
";
total += money;
break;
其中的输出部分是如何通过选中后快捷键CTRL+1,操作成现在的样子的?
十二、
老师辛苦了!
