-------------------- String -----------------------
1、求字符串长度
public int length()//返回该字符串的长度
String str = new String("asdfzxc");
int strlength = str.length();//strlength = 7
2、求字符串某一位置字符
public char charAt(int index)//返回字符串中指定位置的字符;注意字符串中第一个字符索引是0,最后一个是length()-1。
String str = new String("asdfzxc");
char ch = str.charAt(4);//ch = z
3、提取子串
用String类的substring方法可以提取字符串中的子串,该方法有两种常用参数:
1)public String substring(int beginIndex)//该方法从beginIndex位置起,从当前字符串中取出剩余的字符作为一个新的字符串返回。
2)public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)//该方法从beginIndex位置起,从当前字符串中取出到endIndex-1位置的字符作为一个新的字符串返回。
String str1 = new String("asdfzxc");
String str2 = str1.substring(2);//str2 = "dfzxc"
String str3 = str1.substring(2,5);//str3 = "dfz"
4、字符串比较
1)public int compareTo(String anotherString)//该方法是对字符串内容按字典顺序进行大小比较,通过返回的整数值指明当前字符串与参数字符串的大小关系。若当前对象比参数大则返回正整数,反之返回负整数,相等返回0。
2)public int compareToIgnore(String anotherString)//与compareTo方法相似,但忽略大小写。
3)public boolean equals(Object anotherObject)//比较当前字符串和参数字符串,在两个字符串相等的时候返回true,否则返回false。
4)public boolean equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString)//与equals方法相似,但忽略大小写。
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("ABC");
int a = str1.compareTo(str2);//a>0
int b = str1.compareTo(str2);//b=0
boolean c = str1.equals(str2);//c=false
boolean d = str1.equalsIgnoreCase(str2);//d=true
5、字符串连接
public String concat(String str)//将参数中的字符串str连接到当前字符串的后面,效果等价于"+"。
String str = "aa".concat("bb").concat("cc");
相当于String str = "aa"+"bb"+"cc";
6、字符串中单个字符查找
1)public int indexOf(int ch/String str)//用于查找当前字符串中字符或子串,返回字符或子串在当前字符串中从左边起首次出现的位置,若没有出现则返回-1。
2)public int indexOf(int ch/String str, int fromIndex)//改方法与第一种类似,区别在于该方法从fromIndex位置向后查找。
3)public int lastIndexOf(int ch/String str)//该方法与第一种类似,区别在于该方法从字符串的末尾位置向前查找。
4)public int lastIndexOf(int ch/String str, int fromIndex)//该方法与第二种方法类似,区别于该方法从fromIndex位置向前查找。
String str = "I am a good student";
int a = str.indexOf('a');//a = 2
int b = str.indexOf("good");//b = 7
int c = str.indexOf("w",2);//c = -1
int d = str.lastIndexOf("a");//d = 5
int e = str.lastIndexOf("a",3);//e = 2
7、字符串中字符的大小写转换
1)public String toLowerCase()//返回将当前字符串中所有字符转换成小写后的新串
2)public String toUpperCase()//返回将当前字符串中所有字符转换成大写后的新串
String str = new String("asDF");
String str1 = str.toLowerCase();//str1 = "asdf"
String str2 = str.toUpperCase();//str2 = "ASDF"
8、字符串中字符的替换
1)public String replace(char oldChar, char newChar)//用字符newChar替换当前字符串中所有的oldChar字符,并返回一个新的字符串。
2)public String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement)//该方法用字符replacement的内容替换当前字符串中遇到的第一个和字符串regex相匹配的子串,应将新的字符串返回。
3)public String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement)//该方法用字符replacement的内容替换当前字符串中遇到的所有和字符串regex相匹配的子串,应将新的字符串返回。
String str = "asdzxcasd";
String str1 = str.replace('a','g');//str1 = "gsdzxcgsd"
String str2 = str.replace("asd","fgh");//str2 = "fghzxcfgh"
String str3 = str.replaceFirst("asd","fgh");//str3 = "fghzxcasd"
String str4 = str.replaceAll("asd","fgh");//str4 = "fghzxcfgh"
9、其他类方法
1)String trim()//截去字符串两端的空格,但对于中间的空格不处理。
String str = " a sd ";
String str1 = str.trim();
int a = str.length();//a = 6
int b = str1.length();//b = 4
2)boolean statWith(String prefix)或boolean endWith(String suffix)//用来比较当前字符串的起始字符或子字符串prefix和终止字符或子字符串suffix是否和当前字符串相同,重载方法中同时还可以指定比较的开始位置offset。
String str = "asdfgh";
boolean a = str.statWith("as");//a = true
boolean b = str.endWith("gh");//b = true
3)regionMatches(boolean b, int firstStart, String other, int otherStart, int length)//从当前字符串的firstStart位置开始比较,取长度为length的一个子字符串,other字符串从otherStart位置开始,指定另外一个长度为length的字符串,两字符串比较,当b为true时字符
串不区分大小写。
4)contains(String str)//判断参数s是否被包含在字符串中,并返回一个布尔类型的值。
String str = "student";
str.contains("stu");//true
str.contains("ok");//false
5)String[] split(String str)//将str作为分隔符进行字符串分解,分解后的字字符串在字符串数组中返回。
String str = "asd!qwe|zxc#";
tring[] str1 = str.split("[!|#]");//str1[0] = "asd";str1[1] = "qwe";str1[2] = "zxc";
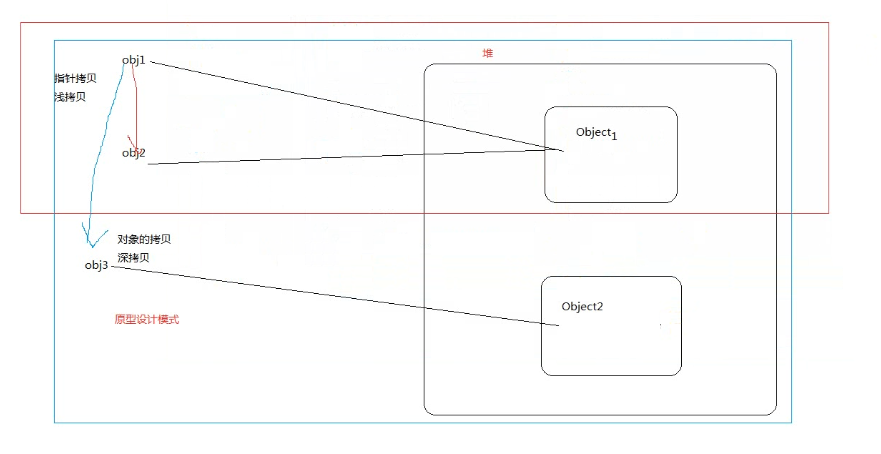
深拷贝、浅拷贝
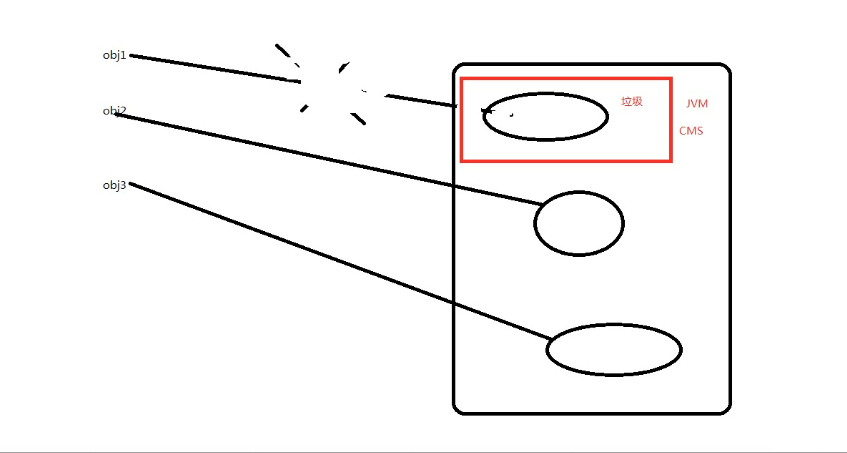
垃圾回收
package com.demo.obj; /** * 学习Object类 * native 本地栈方法, 方法使用使用c语言中实现的方法 * hashcode 就是一个对象在内存中地址 * toString * clone * equals * finalize * @author Administrator * * // 再次强调静态方法中不能使用this关键字 * */ public class ObjectTest extends Object implements Cloneable { public static void main(String[] args) { // 创建一个对象 ObjectTest obj = new ObjectTest(); // 使用System.out.println打印一个对象的时候会自动调用该对象的toString()方法 System.out.println(obj); // @15db9742 // 使用hashcode方法 System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(obj.hashCode())); // 使用toString方法 // System.out.println(obj.toString()); Object obj1 = obj.cloneObject(); System.out.println(obj1); // @6d06d69c Object obj3 = obj; // equals方法 (==) 比较2个对象的引用(内存地址)是否相同 System.out.println(obj == obj1); // false 内存地址不同 System.out.println(obj3 == obj); // true 内存地址相同 System.out.println(obj.equals(obj1)); System.out.println(obj3.equals(obj)); // obj1=null; System.gc(); // 手动调用系统中的垃圾回收器 // 需要使用垃圾回收触发finalize调用 } @Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println("== 对象的销毁 =="); super.finalize(); // 调用父类中gc回收对象的时候就会调用 } //@Override // 重写了父类中toString()方法 /*public String toString() { return "ObjectTest []"; }*/ public Object cloneObject() { Object obj = null; try { // java.lang.CloneNotSupportedException: com.demo.obj.ObjectTest // 必须实现Cloneable接口 obj = this.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return obj; } }
字符串操作
package com.demo.str; import java.util.Arrays; /** * 运算符: instanceof * System.out.println(name2 instanceof String); * 计算某个对事是否为某个对象的实例。 * @author Administrator * */ public class StringTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 定义一个字符串(使用双引号引起来的字面量) String name = "张三A"; String name1 = new String(); // 创建字符串对象 String name2 = new String("张三A"); // equals 比较2个对象值是否相同 System.out.println(name.equals(name2)); // == 比较2个对象的内存地址是相同 System.out.println(name1 == name2); System.out.println(new Object() instanceof String); // 把所有字符串中字母转换为小写toLowerCase System.out.println("SKJDdkfkDJDKJ".toLowerCase()); // 把所有字符串中字母转换为大写toUpperCase System.out.println("SKJDdkfkDJDKJ".toUpperCase()); // equalsIgnoreCase 忽略字母大小写比较2个字符串的值是否相同 System.out.println(name.equalsIgnoreCase(name2)); // contentEuals (比较少) System.out.println(name.contentEquals(name2)); // 获取字符串长度 System.out.println(name.length()); // chatAt 根据下标获取某个字符 String str = "abc好124你好"; System.out.println(str.charAt(3)); // 让其str倒序输出 for (int i = str.length()-1; i >= 0 ; i--) { System.out.print(str.charAt(i)); } System.out.println("==============="); // subString(startIndex, endIndex)截取一个范围内字符串 从0开始[startIndex,endIndex) String url = "http://192.34.23.1/index.html"; String url1 = "ftp://192.34.23.1/ff/ff/f/index.html"; String ip = url1.substring(7, 18); System.out.println(ip); //indexOf,lastIndexOf 查找某个字符串位置 // 如果找到返回对应索引,如果为找到返回-1 int startIndex = url1.indexOf("//") + 2; // 从startIndex开始查找"/"首次出现的位置 int endIndex = url1.indexOf("/", startIndex); System.out.println(url1.substring(startIndex, endIndex)); // 正则表达式(验证); // replace方法替换方法 System.out.println("fuck fuck fuck".replace("f", "l")); // 不能使用正则表达式 System.out.println("fuck fuck fuck".replaceAll("f", "l")); // 可以使用正则表达式 // split把一个特殊字符串切割为一个数组 String personString = "张三_10_男"; String[] person = personString.split("_"); // 使用对象循环 for (String info : person) { System.out.println(info); } System.out.println(Arrays.toString(person)); String str1 = "张三_10_男,李四_20_女"; String[] strings = str1.split("[_,]"); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings)); //concat 连接字符串 String concat = name.concat("ASDDKDKF"); System.out.println(concat); } }