2016年9月 中秋前一天 岗位调整阔别了大爱已久的前端开发部,逐步进入后端开发阶段,不过还是偏前端方面的.
2016.9.19 web前端与后端交互安全问题总结
百度了很久感觉很不错的方式还是没有,也许可能是很多公司的秘密吧?噗~瞎猜的,大多数的意见还是先定IP,总感觉还是差点什么,这里用到的是服务器抓取提交参数IP并且根据客户端抓取到的提交设备信息(设备唯一编码,系统版本号,网络服务商等信息),组成一个设备唯一编码并和系统首次接受到对应用户提交IP地址作为默认绑定,每次提交的时候都会针对用户进行判断,当然这种方式并不是最好的方式,如果有web与后台交互安全性方面的大神希望多多指点!
2016.9.22 IndexOf Contains 字符查询 排序源码理解
原作者:JunBird
C#中字符串的比较操作
字符串比较是比较常用的操作,一般出于以下两个原因比较字符串:
- 判断相等
- 字符串排序
查询API判断字符串相等或排序时,由以下方法:
public override bool Equals(object obj);
public bool Equals(string value);
public static bool Equals(string a, string b);
public bool Equals(string value, StringComparison comparisonType);
public static bool Equals(string a, string b, StringComparison comparisonType);
public static int Compare(string strA, string strB);
public static int Compare(string strA, string strB, bool ignoreCase);
public static int Compare(string strA, string strB, StringComparison comparisonType);
public static int Compare(string strA, string strB, bool ignoreCase, CultureInfo culture);
public static int Compare(string strA, string strB, CultureInfo culture, CompareOptions options);
public static int Compare(string strA, int indexA, string strB, int indexB, int length);
public static int Compare(string strA, int indexA, string strB, int indexB, int length, bool ignoreCase);
public static int Compare(string strA, int indexA, string strB, int indexB, int length, StringComparison comparisonType);
public static int Compare(string strA, int indexA, string strB, int indexB, int length, bool ignoreCase, CultureInfo culture);
public static int Compare(string strA, int indexA, string strB, int indexB, int length, CultureInfo culture, CompareOptions options);
public static int CompareOrdinal(string strA, string strB);
public static int CompareOrdinal(string strA, int indexA, string strB, int indexB, int length);
public int CompareTo(object value);
public int CompareTo(string strB);
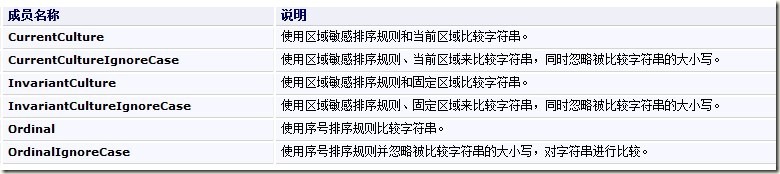
发现上述的方法中大多都有StringComparison类型的枚举,查询msdn后得到:
现简单写一段代码,测试Compare(string strA, string strB, StringComparison comparisonType)方法。分别用到StringComparison.CurrentCulture 和StringComparison.Ordinal。代码如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string strA = "asdfadsfasdfew我ò啊?地?方?的?asd";
string strB = "adsfeaqfaead啊?多à发¢安2德?森-efadsfa";
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
string.Compare(strA, strB, StringComparison.CurrentCulture);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
sw.Reset();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
string.Compare(strA, strB,StringComparison.Ordinal);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
sw.Reset();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
string.CompareOrdinal(strA, strB);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine(sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
}
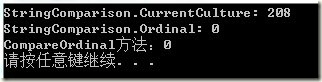
执行结果如下:
测试结果非常明显,StringComparison.Currentculture显式传递了当前语言文化,而传递了String.Ordinal则会忽略指定的语言文化,这是执行字符串最快的一种方式。
使用.NET Reflector查看源代码:
public static int Compare(string strA, string strB, StringComparison comparisonType)
{
if ((comparisonType < StringComparison.CurrentCulture) || (comparisonType > StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
{
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_StringComparison"), "comparisonType");
}
if (strA == strB)
{
return 0;
}
if (strA == null)
{
return -1;
}
if (strB == null)
{
return 1;
}
switch (comparisonType)
{
case StringComparison.CurrentCulture:
return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.Compare(strA, strB, CompareOptions.None);
case StringComparison.CurrentCultureIgnoreCase:
return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.Compare(strA, strB, CompareOptions.IgnoreCase);
case StringComparison.InvariantCulture:
return CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.CompareInfo.Compare(strA, strB, CompareOptions.None);
case StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase:
return CultureInfo.InvariantCulture.CompareInfo.Compare(strA, strB, CompareOptions.IgnoreCase);
case StringComparison.Ordinal:
return CompareOrdinalHelper(strA, strB);
case StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase:
if (!strA.IsAscii() || !strB.IsAscii())
{
return TextInfo.CompareOrdinalIgnoreCase(strA, strB);
}
return CompareOrdinalIgnoreCaseHelper(strA, strB);
}
throw new NotSupportedException(Environment.GetResourceString("NotSupported_StringComparison"));
}
在上例中,同时测试了String的CompareOrdinal方法,效率同样惊人。查看其源代码后发现与Compare方法String.Ordinal源代码一样,此方法只是Compare方法的一个特例:
public static int CompareOrdinal(string strA, string strB)
{
if (strA == strB)
{
return 0;
}
if (strA == null)
{
return -1;
}
if (strB == null)
{
return 1;
}
return CompareOrdinalHelper(strA, strB);
}
接下来看看String.CompareTo()方法的源代码:
[TargetedPatchingOptOut("Performance critical to inline across NGen image boundaries")]
public int CompareTo(string strB)
{
if (strB == null)
{
return 1;
}
return CultureInfo.CurrentCulture.CompareInfo.Compare(this, strB, CompareOptions.None);
}
与类型参数为StringComparison.CurrentCulture的Compare方法相同。
另外StringComparer也实现了字符串比较方法Compare()方法。直接看源代码:
public int Compare(object x, object y)
{
if (x == y)
{
return 0;
}
if (x == null)
{
return -1;
}
if (y == null)
{
return 1;
}
string str = x as string;
if (str != null)
{
string str2 = y as string;
if (str2 != null)
{
return this.Compare(str, str2);
}
}
IComparable comparable = x as IComparable;
if (comparable == null)
{
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_ImplementIComparable"));
}
return comparable.CompareTo(y);
}
如果程序只将字符串用于内部编码目的,如路径名、文件名、URL、环境变量、反射、XML标记等,这些字符串通常只在程序内部使用,不会像用户展示,应该使用String.Ordinal或者使用String.CompareOrdinal()方法
总结及建议:
- 使用显示地指定了字符串比较规则的重载函数。一般来说,需要带有StringComparison类型参数的重载函数
- 在对未知文化的字符串做比较时,使用StringComparison.Ordinal和StringComparison.OrdinallgnoreCase作为默认值,提高性能
- 在像用户输出结果时,使用基于StringComparison.CurrentCulture的字符串
- 使用String.Equals的重载版本来测试两个字符串是否相等。
- 不要使用String.Compare或CompareTo的重载版本来检测返回值是否为0来判断字符串是否相等。这两个函数是用于字符串比较,而非检查相等性。
- 在字符串比较时,应以String.ToUpperInvariant函数使字符串规范化,而不用ToLowerInvariant方法,因为Microsoft对执行大写比较的代码进行了优化。之所以不用ToUpper和ToLower方法,是因为其对语言文化敏感。
转载 dudu 博客关于重定向解决方案深度透析:
Response.Redirect引起的“无法在发送HTTP标头之后进行重定向”
博客后台切换至i.cnblogs.com之后,在日志中发现大量的“无法在发送HTTP标头之后进行重定向”(Cannot redirect after HTTP headers have been sent)的错误信息。
检查代码发现问题是由下面的代码触发的:
IHttpHandler IHttpHandlerFactory.GetHandler(HttpContext context, string requestType, string url, string pathTranslated)
{
context.Response.Redirect("http://i.cnblogs.com/" +
context.Request.RawUrl.Substring(context.Request.RawUrl.LastIndexOf("/") + 1));
//后续也有context.Response.Redirect代码
//...
return PageParser.GetCompiledPageInstance(newurl, path, context);
}
“无法在发送HTTP标头之后进行重定向”问题来源于Response.Redirect之后,又进行了Response.Redirect。
解决方法很简单:在Response.Redirect之后立即返回。
IHttpHandler IHttpHandlerFactory.GetHandler(HttpContext context, string requestType, string url, string pathTranslated)
{
context.Response.Redirect("http://i.cnblogs.com/" +
context.Request.RawUrl.Substring(context.Request.RawUrl.LastIndexOf("/") + 1));
return null;
//...
}
为什么之前没有加return null呢?因为以前一直以为Response.Redirect会结束当前请求,不会执行Response.Redirect之后的代码。
现在残酷的现实说明了不完全是这样的,那问题背后的真相是什么?让我们来一探究竟。
由于微软公开了.NET Framework的源代码,现在无需再看Reflactor出来的代码,可以直接下载源代码用Visual Studio进行查看。
.NET Framework源代码下载链接:http://referencesource.microsoft.com/download.html (相关新闻:微软开放了.NET 4.5.1的源代码)
用Visual Studio打开DotNetReferenceSourceSource dp.sln,搜索HttpResponse.cs,找到Response.Redirect的实现代码:
public void Redirect(String url)
{
Redirect(url, true, false);
}
实际调用的是internal void Redirect(String url, bool endResponse, bool permanent) ,传给endResponse的值的确是true啊,为什么后面的代码还会执行?
进一步查看internal void Redirect()的实现代码(省略了无关代码):
internal void Redirect(String url, bool endResponse, bool permanent)
{
//...
Page page = _context.Handler as Page;
if ((page != null) && page.IsCallback) {
//抛异常
}
// ... url处理
Clear(); //Clears all headers and content output from the buffer stream.
//...
this.StatusCode = permanent ? 301 : 302; //进行重定向操作
//...
_isRequestBeingRedirected = true;
var redirectingHandler = Redirecting;
if (redirectingHandler != null) {
redirectingHandler(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
if (endResponse)
End(); //结束当前请求
}
从上面的代码可以看出,我们要找的真相在End()方法中,继续看HttpResponse.End()的实现代码:
public void End() {
if (_context.IsInCancellablePeriod) {
AbortCurrentThread();
}
else {
// when cannot abort execution, flush and supress further output
_endRequiresObservation = true;
if (!_flushing) { // ignore Reponse.End while flushing (in OnPreSendHeaders)
Flush();
_ended = true;
if (_context.ApplicationInstance != null) {
_context.ApplicationInstance.CompleteRequest();
}
}
}
}
注意啦!真相浮现了!
以前一直以为的Response.Redirect会结束当前请求,就是上面的AbortCurrentThread()情况,如果将Response.Redirect放在try...catch中就会捕捉到ThreadAbortException异常。
通常情况下,我们在WebForms的Page或MVC的Controller中进行Redirect,_context.IsInCancellablePeriod的值为true,执行的是AbortCurrentThread(),所以不会遇到这个问题。
而我们现在的场景恰恰是因为_context.IsInCancellablePeriod的值为false,为什么会是false呢?
进一步看一下_context.IsInCancellablePeriod的实现:
private int _timeoutState; // 0=non-cancelable, 1=cancelable, -1=canceled
internal bool IsInCancellablePeriod {
get { return (Volatile.Read(ref _timeoutState) == 1); }
}
根据上面的代码,触发这个问题的条件是_timeoutState的值要么是0,要么是-1,根据我们的实际情况,应该是0=non-cancelable。
再来看看我们的实际应用场景,我们是在实现IHttpHandlerFactory接口的GetHandler方法中进行Response.Redirect操作的,也就是说在这个阶段_timeoutState的值还没被设置(默认值就是0)。为了验证这个想法,继续看一下_timeoutState在哪个阶段设值的。
Shift+F12找到所有引用_timeoutState的地方,在HttpConext中发现了设置_timeoutState的方法BeginCancellablePeriod,实现代码如下:
internal void BeginCancellablePeriod() {
// It could be caused by an exception in OnThreadStart
if (Volatile.Read(ref _timeoutStartTimeUtcTicks) == -1) {
SetStartTime();
}
Volatile.Write(ref _timeoutState, 1);
}
然后再Shift+F12找到了在HttpApplication.ExecuteStep()中调用了BeginCancellablePeriod():
internal Exception ExecuteStep(IExecutionStep step, ref bool completedSynchronously)
{
//..
if (step.IsCancellable) {
_context.BeginCancellablePeriod(); // request can be cancelled from this point
}
//..
}
从上面的代码可以看出,当step.IsCancellable为true时,会调用BeginCancellablePeriod(),就不会出现这个问题。
而我们用到的IHttpHandlerFactory.GetHandler()所在的IExecutionStep的实现可能将IsCancellable设置为了false。
那IHttpHandlerFactory.GetHandler()是在哪个IExecutionStep的实现中调用的呢?
在园子里木宛城主的一篇写得非常棒的博文(ASP.NET那点不为人知的事)中找到了答案——MapHandlerExecutionStep:
当执行到MapHandlerExecutionStep时会执行如下代码获取最终执行请求:context.Handler = this._application.MapHttpHandler()。HttpApplication对象的MapHttpHandler方法将根据配置文件结合请求类型和URL以调用相应的IHttpHandlerFactory来获取HttpHandler对象。
我们再回到.NET Framework的源代码中看一看MapHandlerExecutionStep的实现:
// execution step -- map HTTP handler (used to be a separate module)
internal class MapHandlerExecutionStep : IExecutionStep {
private HttpApplication _application;
internal MapHandlerExecutionStep(HttpApplication app) {
_application = app;
}
void IExecutionStep.Execute() {
//...
}
bool IExecutionStep.CompletedSynchronously {
get { return true;}
}
bool IExecutionStep.IsCancellable {
get { return false; }
}
}
看到有没有?IExecutionStep.IsCancellable返回的值是false。
到此,水落石出,真相大白!
请看大屏幕——
由于MapHandlerExecutionStep(调用IHttpHandlerFactory.GetHandler()的地方)返回的IsCancellable的值是false,于是在HttpApplication.ExecuteStep()执行时没有调用_context.BeginCancellablePeriod()——也就是没有把_timeoutState设置为1,_context.IsInCancellablePeriod的值就是false。从而造成在Response.Redirect中进行Response.End()时没有执行AbortCurrentThread()(通常情况下都会执行这个)。于是代码继续执行,后面又来一次Response.Redirect,最终引发了——“无法在发送HTTP标头之后进行重定向”(Cannot redirect after HTTP headers have been sent)。
2016-11-10 CMD命令大全
-
cmd命令大全(第一部分)
winver---------检查Windows版本
wmimgmt.msc----打开windows管理体系结构(WMI)
wupdmgr--------windows更新程序
wscript--------windows脚本宿主设置
write----------写字板
winmsd---------系统信息
wiaacmgr-------扫描仪和照相机向导
winchat--------XP自带局域网聊天 -
cmd命令大全(第二部分)
mem.exe--------显示内存使用情况
Msconfig.exe---系统配置实用程序
mplayer2-------简易widnows media player
mspaint--------画图板
mstsc----------远程桌面连接
mplayer2-------媒体播放机
magnify--------放大镜实用程序
mmc------------打开控制台
mobsync--------同步命令 -
cmd命令大全(第三部分)
dxdiag---------检查DirectX信息
drwtsn32------ 系统医生
devmgmt.msc--- 设备管理器
dfrg.msc-------磁盘碎片整理程序
diskmgmt.msc---磁盘管理实用程序
dcomcnfg-------打开系统组件服务
ddeshare-------打开DDE共享设置
dvdplay--------DVD播放器 -
cmd命令大全(第四部分)
net stop messenger-----停止信使服务
net start messenger----开始信使服务
notepad--------打开记事本
nslookup-------网络管理的工具向导
ntbackup-------系统备份和还原
narrator-------屏幕“讲述人”
ntmsmgr.msc----移动存储管理器
ntmsoprq.msc---移动存储管理员操作请求
netstat -an----(TC)命令检查接口 -
cmd命令大全(第五部分)
syncapp--------创建一个公文包
sysedit--------系统配置编辑器
sigverif-------文件签名验证程序
sndrec32-------录音机
shrpubw--------创建共享文件夹
secpol.m转载自电脑十万个为什么http://www.qq880.com,请保留此标记sc-----本地安全策略
syskey---------系统加密,一旦加密就不能解开,保护windows xp系统的双重密码
services.msc---本地服务设置
Sndvol32-------音量控制程序
sfc.exe--------系统文件检查器
sfc /scannow---windows文件保护 -
cmd命令大全(第六部分)
tsshutdn-------60秒倒计时关机命令
tourstart------xp简介(安装完成后出现的漫游xp程序)
taskmgr--------任务管理器
eventvwr-------事件查看器
eudcedit-------造字程序
explorer-------打开资源管理器
packager-------对象包装程序
perfmon.msc----计算机性能监测程序
progman--------程序管理器
regedit.exe----注册表
rsop.msc-------组策略结果集
regedt32-------注册表编辑器
rononce -p ----15秒关机
regsvr32 /u *.dll----停止dll文件运行
regsvr32 /u zipfldr.dll------取消ZIP支持 -
cmd命令大全(第七部分)
cmd.exe--------CMD命令提示符
chkdsk.exe-----Chkdsk磁盘检查
certmgr.msc----证书管理实用程序
calc-----------启动计算器
charmap--------启动字符映射表
cliconfg-------SQL SERVER 客户端网络实用程序
Clipbrd--------剪贴板查看器
conf-----------启动netmeeting
compmgmt.msc---计算机管理
cleanmgr-------垃圾整理
ciadv.msc------索引服务程序
osk------------打开屏幕键盘
odbcad32-------ODBC数据源管理器
oobe/msoobe /a----检查XP是否激活
lusrmgr.msc----本机用户和组
logoff---------注销命令
iexpress-------木马捆绑工具,系统自带
Nslookup-------IP地址侦测器
fsmgmt.msc-----共享文件夹管理器
utilman--------辅助工具管理器
gpedit.msc-----组策略