模块基本介绍与使用
基本介绍:用于Python与Excel之间的交互,可以轻松地从 Excel 调用 Python,也可以利用Python自动化操作Excel,调用VBA,非常方便。
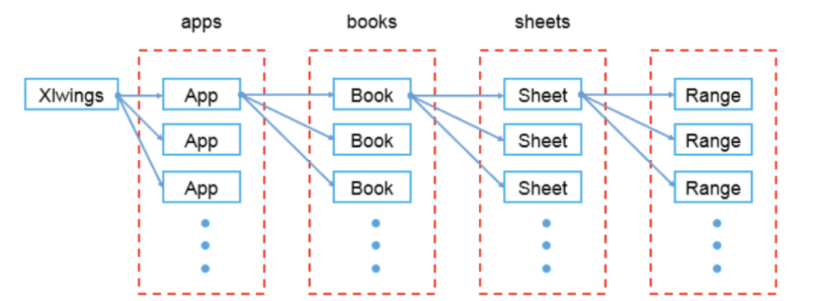
基本使用方法:新建一个excel文件,取名为xlwings_wb.xlsx,并新建一个sheet,取名为first_sht,在其A1单元格内插入字符串Python。
# 导入xlwings,并起一个别名 xw,方便操作 import xlwings as xw # 1、创建一个app应用,打开Excel程序 # visible=True 表示打开操作Excel过程可见 初次接触可以设置为True,了解其过程 # add_book=False 表示启动app后不用新建个工作簿 app = xw.App(visible=True, add_book=False) # 2、新建一个工作簿 wb = app.books.add() # 3、新建一个sheet,并操作 # 3.1 新建sheet 起名为first_sht sht = wb.sheets.add('first_sht') # 3.2 在新建的sheet表中A1位置插入一个值:Python sht.range('A1').value = 'Python' # 3.3 保存新建的工作簿,并起一个名字 wb.save('xlwings_wb.xlsx') # 4、关闭工作簿 wb.close() # 5、程序运行结束,退出Excel程序 app.quit()
基础语法一览
# 基础导入包 import xlwings as xw # 程序第一步 # 打开关闭Excel程序(理解成excel软件打开、关闭) # visible=True 表示打开操作Excel过程可见 初次接触可以设置为True,了解其过程 # add_book=False 表示启动app后不用新建个工作簿 app = xw.App(visible=True, add_book=False) # 程序第二步 # 关闭excel程序 app.close() # 程序最后一步
工作簿相关操作(理解成excel文件)
# 1、新建一个工作簿 wb = app.books.add() # 程序第三步 # 2、保存新建的工作簿,并起一个名字 # 程序倒数第三步,非常关键,保存操作数据结果 wb.save('xlwings_wb.xlsx') # 3、打开一个已经存在的工作簿 wb = app.books.open('xlwings_wb.xlsx') # 程序第三步 # 4、关闭工作簿 wb.close() # 程序倒数第二步
sheet相关操作(理解成工作表)
# 在工作簿中新建一个sheet,起名为 second_sht sht1 = wb.sheets.add('second_sht') # 选中已经存在的sheet sht2 = wb.sheets('first_sht') # 也可以通过索引选择已存在的sheet sht3 = wb.sheets[0] # 选中工作簿中的第一个sheet # 获取工作簿中工作表的个数 sht_nums = wb.sheets.count print('工作簿中的sheet个数为:%d'% sht_nums) # 当前工作表名字 sht1.name # 获取指定sheet中数据的行数 sht1.used_range.last_cell.row # 获取指定sheet中数据的列数 sht1.used_range.last_cell.column # 删除指定的sheet 比如删除:first_sht wb.sheets('first_sht').delete()
单元格相关操作(就是excel单元格子)
写入
''' 写入 ''' # 在工作表中指定位置插入数据 sht1.range('B1').value = '简说Python' # 在工作表指定位置插入多个数据 默认是横向插入 sht1.range('B2').value = [1, 2, 3, 4] # 在工作表指定位置竖向插入多个数据 # 设置options(transpose=True),transpose=True表示转置的意思 sht1.range('B3').options(transpose=True).value = ['老表', '老表Pro', '老表Max', '老表Mini'] # 在工作表指定位置开始插入多行数据 sht1.range('B7').value = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']] # 在工作表指定位置开始插入多列数据 sht1.range('B9').options(transpose=True).value = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']] # 向单元格写入公式 sht1.range('F2').formula = '=sum(B2:E2)'
读出
''' 读取 ''' # 在工作表中读取指定位置数据 print('单元格B1=', sht1.range('B1').value) # 在工作表中读取指定区域数据 一行 print('单元格B2:F2=', sht1.range('B2:F2').value) # 在工作表中读取指定区域数据 一列 print('单元格B3:B6=', sht1.range('B3:B6').value) # 在工作表中读取指定区域数据 一个区域 # 设置options(transpose=True)就可以按列读 不设置就是按行读 print('单元格B7:C10=', sht1.range('B7:C10').options(transpose=True).value)
删除
''' 删除 ''' # 删除指定单元格中的数据 sht1.range('B10').clear() # 删除指定范围内单元格数据 sht1.range('B7:B9').clear()
格式修改
''' 格式修改 ''' # 选中已经存在的sheet sht1 = wb.sheets('second_sht') # 返回单元格绝对路径 sht1.range('B3').get_address() # sht1.range('B3').address # 合并单元格B3 C3 sht1.range('B3:C3').api.merge() # 解除合并单元格B3 C3 sht1.range('B3:C3').api.unmerge() # 向指定单元格添加带超链接文本 # address- 超连接地址 # text_to_display- 超链接文本内容 # screen_tip- 鼠标放到超链接上后显示提示内容 sht1.range('C2').add_hyperlink(address='https://pythonbrief.blog.csdn.net/', text_to_display='简说Python CSDN博客', screen_tip='点击查看简说Python CSDN博客') # 获取指定单元格的超链接地址 sht1.range('C2').hyperlink # 自动调试指定单元格高度和宽度 sht1.range('B1').autofit() # 设置指定单元格背景颜色 sht1.range('B1').color = (93,199,221) # 返回指定范围内的中第一列的编号 数字,如:A-1 B-2 sht1.range('A2:B2').column # 获取或者设置行高/列宽 # row_height/column_width会返回行高/列宽 ,范围内行高/列宽不一致会返回None # 也可以设置一个新的行高/列宽 sht1.range('A2').row_height = 25 sht1.range('B2').column_width = 20
在windows上可以使用以下方法设置单元格文字颜色等格式,如下:
# windows系统下字体设置在 sheet.range().api.Font下 # 颜色 sht1.range('A1').api.Font.Color = (255,0,124) # 字体名字 sht1.range('A1').api.Font.Name = '宋体' # 字体大小 sht1.range('A1').api.Font.Size = 28 # 是否加粗 sht1.range('A1').api.Font.Bold = True # 数字格式 sht1.range('A1').api.NumberFormat = '0.0' # -4108 水平居中 # -4131 靠左 # -4152 靠右 sht1.range('A1').api.HorizontalAlignment = -4108 # -4108 垂直居中(默认) # -4160 靠上 # -4107 靠下 # -4130 自动换行对齐。 sht1.range('A1').api.VerticalAlignment = -4130 # 设置边框线风格和粗细 # Borders(9) 底部边框,LineStyle = 1 直线。 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(9).LineStyle = 1 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(9).Weight = 3 # 设置边框粗细。 # Borders(7) 左边框,LineStyle = 2 虚线。 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(7).LineStyle = 1 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(7).Weight = 3 # Borders(8) 顶部框,LineStyle = 5 双点划线。 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(8).LineStyle = 1 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(8).Weight = 3 # Borders(10) 右边框,LineStyle = 4 点划线。 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(10).LineStyle = 1 sht.range(1,1).api.Borders(10).Weight = 3 ...
在mac下可以通过以下方法设置字体格式:
# 设置单元格的字体颜色 rgb_tuple = (0, 10, 200) sht1.range('B1').api.font_object.color.set(rgb_tuple) # 获取指定单元格字体颜色 sht1.range('B1').api.font_object.color.get() # 获取指定单元格字体名字 可以使用set方法修改字体 set('宋体') sht1.range('B1').api.font_object.name.get() # 设置指定单元格字体格式 可以用get方法查看单元格字体格式 sht1.range('B3').api.font_object.font_style.set('加粗') # 设置指定单元格字体大小 sht1.range('B3').api.font_object.font_size.set(20) # 设置边框线粗细 sht1.range('B2').api.get_border(which_border=9).weight.set(4) # 设置边框线风格 sht1.range('B2').api.get_border(which_border=9).line_style.set(8) ...
进行完所有操作后一定要记得执行以下三句:
# 保存新建的工作簿,并起一个名字(如果已存在有名字的excel文件,就直接save即可) wb.save() # 关闭工作簿(关闭Excel文件) wb.close() # 程序运行结束,退出Excel程序 app.quit()
自动生成统计图
import xlwings as xw # 新建一个sheet app = xw.App(visible=True, add_book=False) wb = app.books.open('xlwings_wb.xlsx') sht3 = wb.sheets.add('third_sht') import pandas as pd import numpy as np # 生成模拟数据 df = pd.DataFrame({ 'money':np.random.randint(45, 50, size = [1, 20])[0], }, index=pd.date_range('2021-02-01', '2021-02-20'), # 行索引和时间相关 ) df.index.name = '消费日期' # 设置索引名字 sht3.range('A1').value = df # 生成图表 chart1 = sht3.charts.add() # 创建一个图表对象 chart1.set_source_data(sht3.range('A1').expand()) # 加载数据 chart1.chart_type = 'line' # 设置图标类型 chart1.top = sht3.range('D2').top chart1.left = sht3.range('D2').left # 设置图标开始位置
除了绘制折线图,我们还可以绘制其他类型的图,修改chart_type值即可。
# 查看其他chart_types值 xw.constants.chart_types
返回结果
('3d_area', '3d_area_stacked', '3d_area_stacked_100', '3d_bar_clustered', '3d_bar_stacked', '3d_bar_stacked_100', '3d_column', '3d_column_clustered', '3d_column_stacked', '3d_column_stacked_100', '3d_line', # 3D折线图 '3d_pie', # 3D饼图 '3d_pie_exploded', 'area', # 面积图 'area_stacked', 'area_stacked_100', 'bar_clustered', # 柱状图相关 'bar_of_pie', 'bar_stacked', 'bar_stacked_100', 'bubble', # 气泡图 'bubble_3d_effect', 'column_clustered', # 条形图相关 'column_stacked', 'column_stacked_100', 'combination', 'cone_bar_clustered', 'cone_bar_stacked', 'cone_bar_stacked_100', 'cone_col', 'cone_col_clustered', 'cone_col_stacked', 'cone_col_stacked_100', 'cylinder_bar_clustered', 'cylinder_bar_stacked', 'cylinder_bar_stacked_100', 'cylinder_col', 'cylinder_col_clustered', 'cylinder_col_stacked', 'cylinder_col_stacked_100', 'doughnut', 'doughnut_exploded', 'line', # 折线图 'line_markers', 'line_markers_stacked', 'line_markers_stacked_100', 'line_stacked', 'line_stacked_100', 'pie', 'pie_exploded', 'pie_of_pie', 'pyramid_bar_clustered', 'pyramid_bar_stacked', 'pyramid_bar_stacked_100', 'pyramid_col', 'pyramid_col_clustered', 'pyramid_col_stacked', 'pyramid_col_stacked_100', 'radar', 'radar_filled', 'radar_markers', 'stock_hlc', # 有意思 股票K线图 'stock_ohlc', 'stock_vhlc', 'stock_vohlc', 'surface', 'surface_top_view', 'surface_top_view_wireframe', 'surface_wireframe', 'xy_scatter', 'xy_scatter_lines', 'xy_scatter_lines_no_markers', 'xy_scatter_smooth', 'xy_scatter_smooth_no_markers')
将本地图片或者matplotlib图片保存到excel
''' matplotlib 生成的图片存入excel ''' import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 随便绘制一个饼图 fig1 = plt.figure() # 先创建一个图像对象 plt.pie([0.5, 0.3, 0.2], # 值 labels=['a', 'b', 'c'], # 标签 explode=(0, 0.2, 0), # (爆裂)距离 autopct='%1.1f%%', # 显示百分数格式 shadow=True) # 是否显示阴影 plt.show() # 将饼图添加到excel指定位置 J17为图片开始位置 sht3.pictures.add(fig1, name='matplotlib', left=sht3.range('J17').left, top=sht3.range('J17').top, update=True)
''' 本地图片存入excel ''' # 将本地图片添加到excel指定位置 J1为图片开始位置 pic_path = './0923.jpeg' sht3.pictures.add(pic_path, name='local', left=sht3.range('J1').left, top=sht3.range('J1').top, update=True)