For a binary tree T, we can define a flip operation as follows: choose any node, and swap the left and right child subtrees.
A binary tree X is flip equivalent to a binary tree Y if and only if we can make X equal to Y after some number of flip operations.
Given the roots of two binary trees root1 and root2, return true if the two trees are flip equivelent or false otherwise.
Example 1:
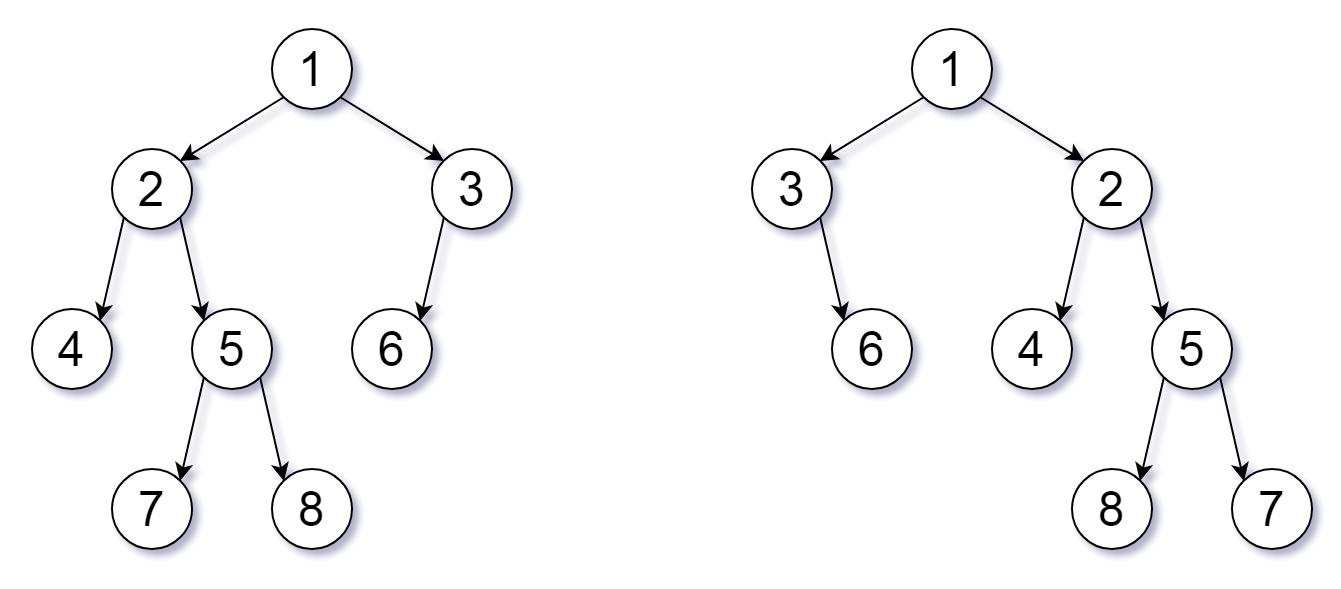
Input: root1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,null,null,null,7,8], root2 = [1,3,2,null,6,4,5,null,null,null,null,8,7] Output: true Explanation: We flipped at nodes with values 1, 3, and 5.
Example 2:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [] Output: true
Example 3:
Input: root1 = [], root2 = [1] Output: false
Example 4:
Input: root1 = [0,null,1], root2 = [] Output: false
Example 5:
Input: root1 = [0,null,1], root2 = [0,1] Output: true
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in each tree is in the range
[0, 100]. - Each tree will have unique node values in the range
[0, 99].
class Solution { public boolean flipEquiv(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) { if(root1 == null || root2 == null) return root1 == root2; if(root1.val != root2.val) return false; return (flipEquiv(root1.left, root2.left) && flipEquiv(root1.right, root2.right)) || (flipEquiv(root1.left, root2.right) && flipEquiv(root1.right, root2.left)); } }
牛逼的。。首先跟小编来理解一下flip后相等是怎么回事,好的就是这么回事,你懂了吗?
题目要flip或者不flip后相等,就可以分成两种情况。
首先是终止条件:说起来是flip,实际上还是比较root是不是相等。如果root1或者root2是null了,直接看他俩是否相等。然后因为要相等,所以要判断root1和root2的val。如果不相等直接返回false
然后进入递归,前面我们说了有两种情况。1. 不flip,就返回比较他俩left和right child的情况 2. flip,返回比较root1.left, root2.right,和root1.right, root2.left的情况。
https://leetcode.com/problems/flip-equivalent-binary-trees/discuss/200514/JavaPython-3-DFS-3-liners-and-BFS-with-explanation-time-and-space%3A-O(n).